We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud

UPDATED: July 19, 2024
Among the leading cloud providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud stand at the forefront, offering a myriad of services to meet the evolving demands of network administrators. This article delves into a comprehensive comparison of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud with a specific focus on their cloud storage offerings, which form the backbone of network administration. As businesses embrace digital transformation and the ever-growing influx of data, the choice of a cloud storage provider becomes pivotal in maintaining a secure, efficient, and scalable network infrastructure.
In this exploration, we will dissect the cloud storage services offered by each of these industry giants, analyzing their strengths and unique attributes. From object storage to block storage, file storage, and archival solutions, we will uncover how AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud address the diverse storage requirements of network administrators.
Performance is a paramount consideration for network administrators, and we will scrutinize the performance characteristics of each provider's storage offerings. Moreover, data security and compliance are critical concerns, and we will delve into the security features and compliance certifications that ensure the protection and legality of data stored in the cloud.
Network integration is another vital aspect of network administration, and we will examine how each provider facilitates the seamless integration of cloud storage with existing network infrastructures. Furthermore, we will explore the tools and services provided by AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud for data transfer and migration, crucial for network administrators tasked with moving data to and from the cloud.
In an era where data fuels decision-making and network efficiency is paramount, the choice of a cloud storage provider holds immense significance. By the end of this comprehensive comparison, network administrators will be armed with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions that align with their organization's unique network administration requirements.
AWS Cloud Storage Services
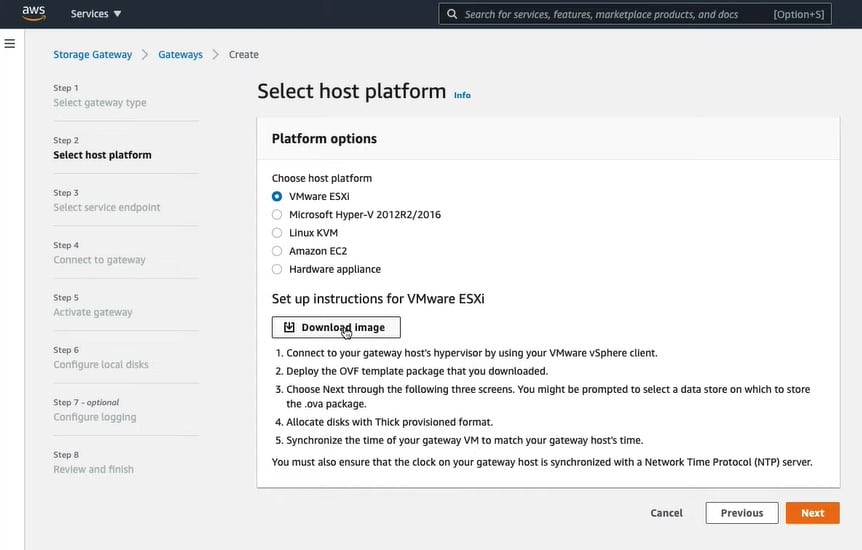
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud service provider, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud storage services designed to meet a wide range of storage needs. These services are a vital component of AWS's extensive cloud infrastructure, supporting businesses and network administrators in storing and managing data efficiently and securely.
- Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) Amazon S3 is perhaps the most well-known AWS storage service. It offers scalable object storage designed for durability, availability, and performance. S3 is ideal for a wide range of use cases, from hosting static website content to storing backup archives. One of its notable features is versioning, which allows you to maintain multiple versions of objects, ensuring data integrity and recoverability. Additionally, S3 offers various storage classes, such as Standard, Intelligent-Tiering, and Glacier, each tailored to different access and cost requirements.
- Amazon EBS (Elastic Block Store) EBS provides block-level storage volumes that can be attached to EC2 instances, making it suitable for use as primary storage for applications and databases. It offers a variety of volume types, including General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPS SSD, and Magnetic (HDD-based) volumes. These options allow you to select the right storage performance characteristics for your specific workloads. EBS also supports features like snapshots, which enable data backup and recovery, and EBS encryption for data security.
- Amazon Glacier Glacier is AWS's solution for long-term archival storage. It offers extremely low-cost storage with durability and retrieval options optimized for infrequently accessed data. With Glacier, you can store large volumes of data, such as historical records or regulatory compliance data, without incurring high storage costs. It's a great choice for organizations that need to retain data for compliance purposes or for those who want to maintain extensive historical archives.
- Amazon EFS (Elastic File System) EFS is a managed file storage service that provides scalable and shared file storage for EC2 instances. It's a fully managed service, making it easy to set up and operate. EFS is suitable for a variety of use cases, such as content repositories, data analytics, and application data sharing. It offers strong consistency, making it ideal for applications requiring shared access to files across multiple instances. Moreover, EFS is designed for high availability and durability, ensuring your data is always accessible.
AWS storage services are renowned for their durability, availability, and scalability. They provide high levels of redundancy, data replication, and geographic distribution, making them suitable for critical and mission-critical workloads. AWS's global network of data centers and edge locations ensures low-latency access to data regardless of your location.
Azure Cloud Storage Services
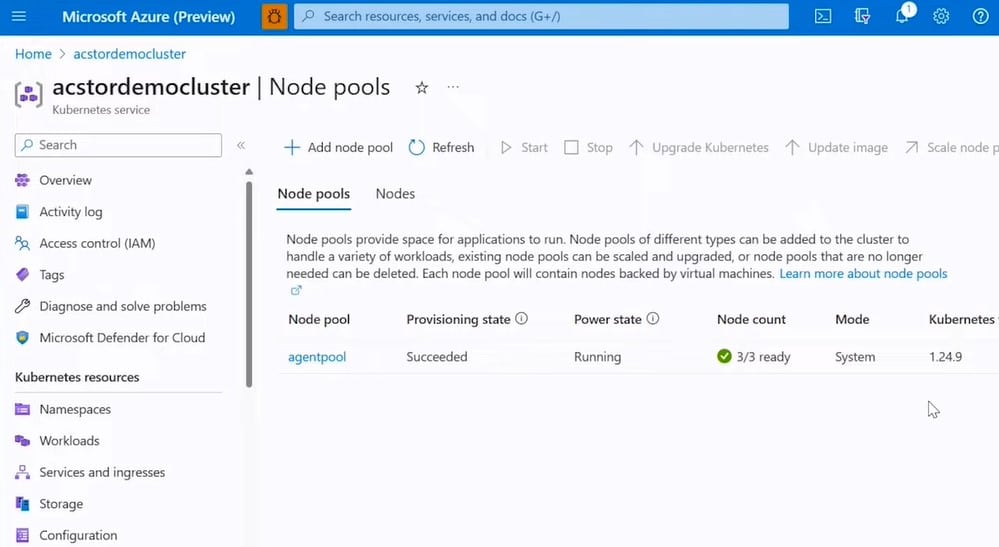
Microsoft Azure, a formidable competitor in the cloud computing arena, offers a robust suite of cloud storage services designed to cater to the diverse needs of network administrators and businesses alike. These services, integrated seamlessly into the Azure ecosystem, provide scalable and secure storage solutions, ensuring data accessibility, durability, and performance.
- Azure Blob Storage A highly scalable object storage service, ideal for storing and managing vast amounts of unstructured data such as documents, images, videos, and backups. It offers various access tiers, including Hot, Cool, and Archive, allowing you to optimize storage costs based on data access frequency. With support for Azure Data Lake Storage, Blob Storage seamlessly integrates with big data analytics and data processing services, making it a versatile choice for both structured and unstructured data.
- Azure Files Provides fully managed, network-attached file shares that can be accessed from anywhere using the Server Message Block (SMB) protocol. This service is particularly valuable for businesses and administrators looking to share files across multiple virtual machines and applications. It supports features like Azure AD authentication, Azure File Sync for hybrid scenarios, and disaster recovery with Azure Backup.
- Azure Disk Storage Offers block-level storage designed to be attached to Azure virtual machines (VMs). It comes in two primary types: Azure Managed Disks and Azure Ultra Disks. Managed Disks simplify disk management by handling disk availability, reliability, and scalability. Ultra Disks, on the other hand, are optimized for high IOPS and low latency, making them suitable for I/O-intensive workloads like databases and SAP HANA.
- Azure Data Lake Storage A scalable and secure data lake solution built for big data analytics and data warehousing. It offers a hierarchical file system, which enables data organization and access control at various levels. With support for industry-standard protocols like HDFS and Apache Spark, Data Lake Storage seamlessly integrates with analytics services, making it a powerful choice for data-driven organizations.
Azure storage services are characterized by their strong focus on data security and compliance. They offer encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control (RBAC), and Azure AD integration for identity management. Additionally, Azure complies with a wide range of industry standards and certifications, including GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, making it suitable for organizations with strict regulatory requirements.
Azure's pricing model is flexible, with various options for optimizing costs based on data access patterns and redundancy requirements. Azure Storage offers features like Geo-redundant Storage (GRS) and Read-Access Geo-redundant Storage (RA-GRS) to enhance data availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Azure's deep integration with other Microsoft products and services, such as Azure Active Directory, Azure Virtual Network, and Azure DevOps, simplifies storage management and enhances network administration capabilities. Azure also provides a wide range of development tools, including Azure Storage Explorer and Azure PowerShell, to streamline storage configuration and maintenance tasks.
Google Cloud Storage Services
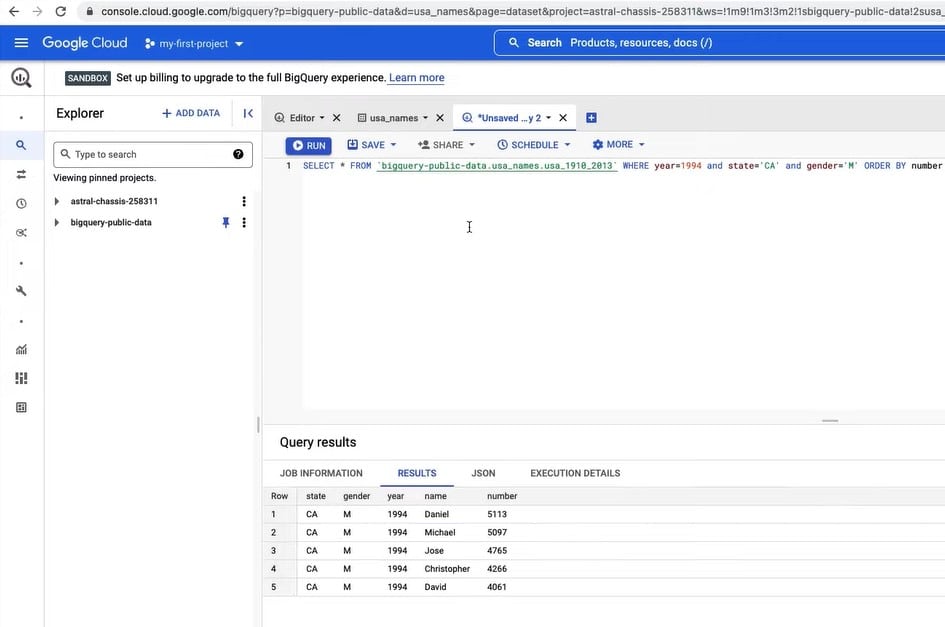
Google Cloud offers a comprehensive range of cloud storage services designed to meet the diverse needs of network administrators and businesses. These services are a vital part of Google Cloud's ecosystem, providing scalable and secure storage solutions that ensure data accessibility, durability, and performance.
- Google Cloud Storage A versatile and scalable object storage service designed to store and manage unstructured data, such as multimedia files, backups, and archives. It offers multi-regional, regional, and nearline storage classes, allowing users to optimize costs based on data access frequency. With features like lifecycle management policies and versioning, it's easy to automate data management tasks and ensure data integrity.
- Google Persistent Disk A block storage service that can be attached to Google Compute Engine virtual machines (VMs). It offers Standard, SSD, and local SSD options, enabling users to select the right storage type based on their workload requirements. Persistent Disk also supports features like snapshots for data backup and disaster recovery and encryption for data security.
- Google Cloud Filestore Provides fully managed Network Attached Storage (NAS) for Google Cloud virtual machines. It offers two types of file systems: Standard and High Scale, catering to different performance needs. Filestore is well-suited for applications that require shared file access, such as content management systems and development environments. It integrates seamlessly with Google Kubernetes Engine and Compute Engine instances.
- Google Cloud Storage Nearline and Coldline Google Cloud Storage also offers Nearline and Coldline storage classes for archival and backup purposes. Nearline provides low-cost storage with rapid data access, making it suitable for data that needs to be retrieved infrequently but quickly. Coldline, on the other hand, offers the lowest storage costs but with a longer retrieval time, making it ideal for data that rarely needs to be accessed.
Security and compliance are paramount in Google Cloud's storage offerings. Google Cloud Storage provides server-side encryption by default, and customers can also use customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) for added control over data security. Google Cloud is compliant with various industry standards and certifications, including ISO 27001, HIPAA, and SOC 2, making it a trusted choice for organizations with strict compliance requirements.
Google Cloud's pricing model is designed to be cost-effective and transparent. Users can choose from various storage classes and redundancy options to optimize costs based on their specific needs. Additionally, Google Cloud offers a free tier with a certain amount of storage and data transfer, allowing users to explore the platform without incurring charges.
Google Cloud Storage seamlessly integrates with other Google Cloud services, including Google Kubernetes Engine, BigQuery, and Cloud Identity and Access Management (IAM). This integration simplifies storage management and enhances network administration capabilities. Google also provides a range of developer tools, such as the Google Cloud Console and gsutil command-line tool, to facilitate storage configuration and maintenance tasks.
Performance Comparison
When evaluating cloud storage services from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, performance is a critical factor that network administrators must consider. Each of these cloud providers offers robust storage solutions, but their performance characteristics can vary significantly based on the specific service and storage class chosen.
In terms of raw performance, AWS offers Amazon EBS with various volume types, including General Purpose SSD, Provisioned IOPS SSD, and Magnetic (HDD-based) volumes. This flexibility allows users to select the storage type that best matches their workload requirements. For I/O-intensive applications, AWS also provides Amazon EBS-optimized instances, ensuring that storage throughput and latency are optimized for demanding workloads. Additionally, Amazon S3, AWS's object storage service, is designed for high performance, making it suitable for a wide range of use cases, from hosting websites to supporting data analytics.
Azure offers Azure Disk Storage, which provides both Standard and SSD options, as well as Azure Ultra Disks for high IOPS and low latency. Azure Ultra Disks are particularly well-suited for applications that demand extreme performance, such as high-performance databases and real-time analytics. Azure Blob Storage is also designed for performance, with a variety of storage tiers to balance performance and cost efficiency. Azure's global network ensures low-latency access to data from around the world.
Google Cloud, like its competitors, offers a range of performance-optimized storage options. Google Persistent Disk provides both Standard and SSD options, catering to different performance requirements. Google Cloud Storage offers multi-regional and regional storage classes, allowing users to select the level of performance and redundancy that suits their needs. Google Cloud Filestore offers two performance options, Standard and High Scale, giving users flexibility in choosing the right performance tier for their file storage workloads.
In terms of performance comparison, it's important to note that the specific performance characteristics can vary depending on factors such as the chosen storage class, the workload's I/O patterns, and the selected cloud provider's region. Network administrators should thoroughly test and benchmark their applications with the intended storage service and class to ensure optimal performance for their specific use case.
Data Transfer and Migration
Efficient data transfer and migration capabilities are essential for network administrators when considering cloud storage solutions. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer a range of tools and services to facilitate the movement of data into and out of their respective cloud environments.
AWS provides several options for data transfer and migration. AWS DataSync simplifies data transfer between on-premises systems and AWS storage services like Amazon S3 and Amazon EFS. AWS Snowball devices allow for large-scale data transfer by shipping physical appliances to the customer's location for data ingestion and then shipping them back to AWS for data import. AWS offers the AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) for database migration and the AWS Server Migration Service (SMS) for server migration. These services simplify the process of migrating databases and applications to the AWS cloud.
Azure offers various data transfer and migration tools as well. Azure Data Factory allows users to create data-driven workflows for data integration and migration tasks. Azure Site Recovery enables disaster recovery and migration of on-premises virtual machines to Azure. Azure Database Migration Service simplifies database migration to Azure SQL Database and Azure Cosmos DB. Azure also offers Azure Data Box, similar to AWS Snowball, for transferring large volumes of data to Azure via physical appliances.
Google Cloud offers its data transfer and migration solutions. Google Transfer Appliance provides a physical device for secure data transfer to Google Cloud. Google Cloud Storage Transfer Service automates the movement of data between on-premises systems and Google Cloud Storage. Google's BigQuery Data Transfer Service allows scheduled data transfers from various sources into Google BigQuery for analytics. For database migration, Google offers services like Cloud SQL for MySQL and PostgreSQL and Google Cloud Database Migration Service for migrating databases to Google Cloud.
All three cloud providers offer robust online data transfer methods, which are particularly useful for ongoing data synchronization and migration between on-premises systems and the cloud. They also provide documentation, best practices, and tooling to assist network administrators in planning and executing data migration projects efficiently.
When choosing a cloud provider for data transfer and migration, consider factors such as the volume of data, data transfer speed, and the specific services or databases you need to migrate. Additionally, assess the cost implications of data transfer and migration, as some providers may offer free or discounted transfer options within their cloud ecosystems. Proper planning and execution of data transfer and migration are crucial to ensure a seamless transition to cloud storage solutions while minimizing downtime and disruptions to your network infrastructure.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are paramount considerations when selecting a cloud storage provider for network administration tasks. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud recognize the importance of safeguarding data and offer robust security features and compliance certifications.
AWS provides a comprehensive suite of security tools and services, including Identity and Access Management (IAM) for fine-grained access control, encryption at rest and in transit, and the AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for managing encryption keys. AWS is compliant with numerous industry standards and certifications, such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and FedRAMP, making it suitable for organizations with stringent compliance requirements.
Azure offers strong security features, including Azure Active Directory (AD) for identity management, role-based access control (RBAC) for access permissions, and Azure Disk Encryption for data protection. Azure also complies with various industry standards, including GDPR, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and SOC 2, ensuring that data stored in Azure meets rigorous compliance criteria.
Google Cloud emphasizes data security with features like Identity and Access Management (IAM) for access control, encryption at rest with Google Cloud Storage encryption and customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK), and robust network security with Google Cloud VPC Service Controls. Google Cloud complies with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, HIPAA, and GDPR, providing a strong foundation for regulatory compliance.
All three providers offer security best practices and compliance documentation, aiding network administrators in configuring their storage solutions securely. However, the specific implementation and configuration may vary, and administrators should carefully configure security settings to align with their organization's requirements.
Network Integration
Efficient network integration is crucial for seamless data access and management within a cloud environment. AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud all provide robust network integration options to ensure that their respective cloud storage services seamlessly integrate with existing network infrastructures.
AWS offers several tools and services for network integration. Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) allows users to create isolated network environments and connect them to AWS resources securely. Direct Connect offers dedicated network connections between on-premises data centers and AWS, ensuring low latency and reliable connectivity. AWS Transit Gateway simplifies the management of network connectivity across multiple VPCs and accounts. Moreover, AWS offers a range of CDN (Content Delivery Network) solutions, such as Amazon CloudFront, for optimizing content delivery and enhancing user experiences.
Azure provides similar network integration capabilities. Azure Virtual Network allows users to create isolated network environments, and Azure ExpressRoute offers private, dedicated connections to Azure data centers, ensuring consistent and secure network performance. Azure also provides Azure Virtual WAN to simplify branch-to-branch and branch-to-Azure connectivity. Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) services, such as Azure CDN, enhance content delivery and reduce latency for end-users.
Google Cloud emphasizes network integration through its Google Cloud VPC (Virtual Private Cloud) offering, allowing users to create isolated network environments and connect them to Google Cloud resources. Google Cloud Interconnect offers dedicated connections between on-premises data centers and Google Cloud, ensuring low latency, reliable, and secure network connectivity. Google Cloud CDN services, including Google Cloud CDN and Google Cloud Load Balancing, optimize content delivery and improve application performance.
All three cloud providers offer various VPN (Virtual Private Network) options for secure connectivity, enabling network administrators to establish encrypted connections between their on-premises infrastructure and cloud resources. Additionally, they provide options for private IP addressing, security groups, and firewall rules to control traffic flow within their respective cloud environments.
When it comes to network integration, the choice between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud may depend on your organization's existing network architecture and specific requirements. Each cloud provider offers a range of services and tools to facilitate seamless network integration, ensuring that cloud storage services can be securely accessed and utilized within your network infrastructure. Network administrators should carefully assess their organization's networking needs and consider factors such as existing technologies, geographic locations, and security requirements when choosing a cloud provider for network integration.