We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Access Management Guide – What is It and How to Manage/Monitor

UPDATED: January 10, 2024
Access management is an IT security operation that prevents invalid users from accessing the network and stealing data. Management of access rights is probably one of the most important aspects when securing your data. The process can create, provision, and effectively manage different users, groups, roles, and policies.
An Identity Access Management (IAM) application does exactly that.
It keeps user information, their roles, which group they belong to, and the policies that need to be enforced. The application handles user access requests by checking the user’s profiles and roles.
Below are the best access management tools that are worth checking out; go on reading till the end!
- SolarWinds Access Rights Manager – FREE TRIAL This tool is a must-have for every IT industry to understand risk and prevent threats. It allows users to manage and check for access rights across the organization. It has plenty of great features, such as role-based access control, one-drive permissions, cyber security management, and many more. Download a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine AD360 – FREE TRIAL This tool allows you to store your confidential identity digitally with secure access. It includes advanced features such as automated identity life cycle management, secure SSO, approval-based processes, threat protection, and historical audit reports to fulfill your IAM requirements. Access a 60-day free trial.
- ManageEngine ADAudit Plus FREE TRIAL This tool is the first priority of leading industries for securing directories and servers. It helps to monitor user behavior and check for insider threats. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Apache Directory A Java-based directory server that is flexible and embeddable. These include an Open Group-certified LDAP v3 compatible directory server (ApacheDS) and Eclipse-based directory tools (Apache Directory Studio).
- FreeIPA Free IPA is basically an integrated identity and authentication tool for linux users to store data on various hosts or groups securely.
- LDAP Account Manager It is basically a webfront tool to manage user entries, DHCP settings and all other technical details. This tool can be easily used by a person with a non-technical background to manage and access LDAP entries.
The two systems that control user permissions management and make it easier, are Active Directory (AD) and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). Although they both have a similar purpose, they are different in functionality.
Active Directory (AD) is a service. It is a hierarchical directory database that contains all information about users in a network and it is only compatible with Windows OS.
LDAP on the other hand, is a protocol. It provides indexing and directory services and it is used to communicate with the AD.
In the complete guide to Access Management, we will discuss the following:
- What is Active Directory?
- Checking Credentials with Active Directory
- What is Lightweight Directory Access Process?
- LDAP Structure and Functionality
- Other Ways to Control Access
- The Identity and Access Management System
- Recommended Access Management Tools
- Summary
What is Active Directory?
As mentioned above, Active Directory (AD) is a hierarchical directory service developed by Microsoft especially for Windows domain networks. It contains all the information about users and profiles in the network.
AD started as a centralized domain management service for Windows Server 2008. The service became so popular that it became the key to most of directory-based services. Everything that was related to “Identity” was instantly delegated to AD.
The service stores any information about network objects and makes it available and easy to find. Objects are usually those shared resources, such as folders, printers, servers, accounts, etc.
AD uses a structured data storage as the foundation for its hierarchical organization of the entire directory information. This data storage is known as the directory, which contains all information about directory objects.
Security provided by AD
Admins can control all the directory data and its organization from the entire network through single network logon. AD secures a domain through logon authentication and access control to objects located in the directory.
An Active Directory Domain Services or (AD DS) is the one in charge of providing the method for storing directory information and making it available to anyone (users or admins). In other words, an AD DS keeps all information about user accounts and allows authorized users to access this information.
An AD DS server is often referred as a domain controller (DC), which authenticates and authorizes all users in a network. A domain controller has the responsibility of assigning and enforcing policies. It is also responsible of installing and updating software for the entire Windows domain network.
The Structure of AD
Any object that is made under an AD can be grouped into domains. To keep up with security, all the objects that belong to a domain are stored in a single and separate database. One or more of these domains can be represented by a tree.
The following picture represents an AD Domain tree with sub domains. For example, acme.com.tw is the main domain, followed by its branches, or sub domains.
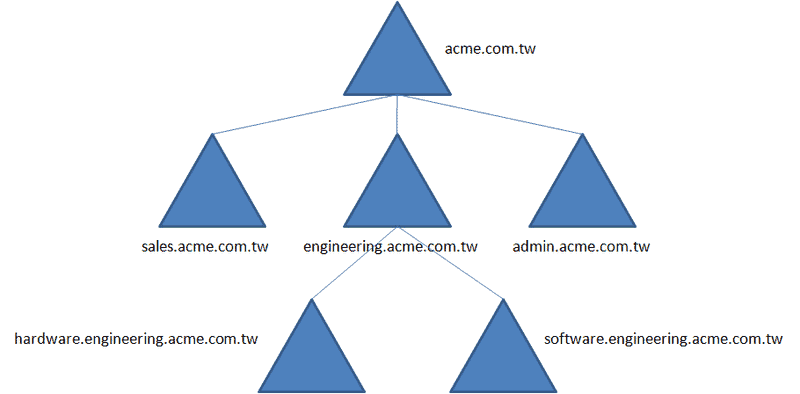
A collection of these trees is a forest. All trees in a forest share commonalities, such as catalog, directory schema, structure, and directory configuration. An advantage of the forest, is that the global catalog of the DC can be easily replicated and maintained.
Similarity to DNS
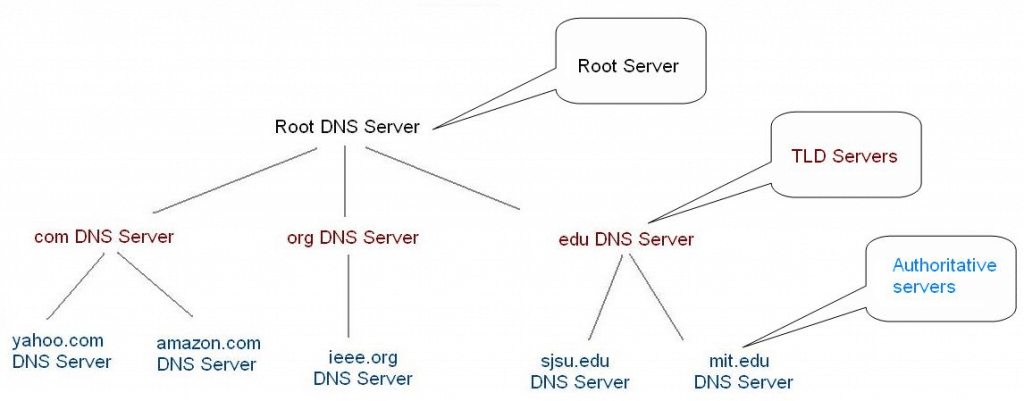
The above hierarchical structure is very similar to a DNS. Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical naming system used for networks, services, and other resources to translate domain names into IP address, and vice versa. In fact, DNS is an essential component of AD.
A DNS query can not only initiate a hostname to IP address conversion, but it also can find the specific records that identify the roles and functions of AD. For example, when a user wants to log into a machine within a domain, the client finds the domain controller first, by using the SRV records.
Checking Credentials with Active Directory
When a Windows client receives the user or service credentials for the first time, it protects that information to be delivered to the authenticating target, or in most cases the domain controller.
The user credentials connect the user’s identity to some sort of authenticity proof. The credentials can be a password, a certificate or even PIN number. They are collected through a logon user interface input or through an API and sent to the authenticating server.
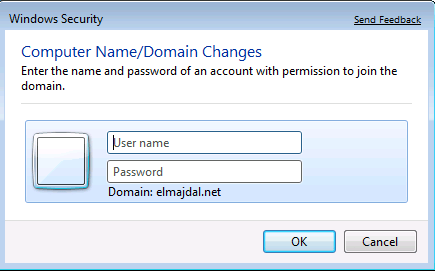
During the Windows logon, the credentials are first validated against the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database in the local computer. The SAM is present in all Windows operating systems and stores local user information and groups.
But when the computer is joined to a domain, the credentials are sent to the AD and checked against the global catalog located in the local Domain Controller. The user credential authentication process sends username and password to the authenticating target and also includes the details of the computer in which the user requested access to.
Even though a user introduced the correct username and password, the access might still be denied because the device in which the user is trying to gain access does not have the necessary permissions to access the network.
When a user tried and had too many incorrect password attempts, all Domain Controllers in a forest can be quickly notified and locked against that specific user.
Related Post: Best Active Directory Monitoring Tools
What is Lightweight Directory Access Process?
The Lightweight Directory Access Process (LDAP) is an open and industry-standard protocol, it can be used with many distributed directory systems, such as Apache DS, OpenDS, Red Hat DS, etc. This protocol has been around much longer than AD.
LDAP, as the name implies is a lightweight method used for accessing and maintaining directory services over TCP/IP. With this protocol you can share information about, users, groups, and networks between servers through the Internet. It provides a central place to store credentials and help with authorization. Many services and applications use this protocol to help validating the user.
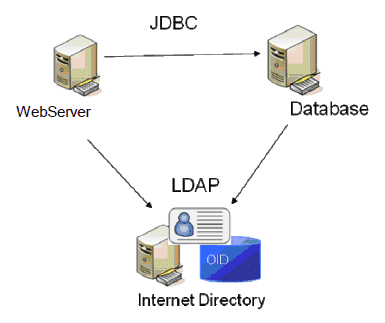
A LDAP server does name lookup and credentials validations. It also stores the Access Control List (ACLs) file and directory objects.
LDAP was based on X.500
This protocol was based on the early authentication system the X.500. When it comes to directory service mechanisms, X.500 specifies many standards about how directory mechanisms work.
Although LDAPv2 had many features covering the X.500 series of standards, the newer LDAPv3 is simpler, lighter, and covers a larger subset of the X.500 features. Specially when it comes to the improved security protection for LDAP communications. LDAPv3 comes with a Simple Authentication and Security Layer authentication framework.
LDAPv3’s Improved Security
The intended purpose of LDAP was to provide authentication information, but the newest versions of the protocol have a lot more applications. The most important upgrade of LDAPv3 was its improved security.
When the user tries to authenticate, the client initiates an LDAP session by first connecting to the LDAP server. The client might request operations such as, a secure connection through the LDAPv3 TLS (Transport Layer Security), an authentication through a specific LDAP protocol version, or a search to look and retrieve specific directory entries. This gives much more flexibility and added security.
On top of that, LDAP communication can also be secured using an SSL Tunnel (Secure Sockets Layer). The use of this method was used in the previous version LDAPv2, but it was never standardized in any formal specification, until LDAPv3.
LDAP Structure & Functionality
The LDAP directory has a hierarchical tree structure. All the entries or objects in this directory have a defined position. An object can be a user or a resource, such a shared computer or printer. The hierarchy where the objects are defined is called the Directory Information Tree (DIT), which consists of Distinguished Names (DNs) of the directory service entries.
All kinds of lists of information can be organized into DITs, which are stored in the LDAP database. By itself, the LDAP permissions database is also stored and organized in a DIT. If a user wants to access information located in an LDAP database, the user would need to authenticate first.
Similar to AD, the functionality of LDAP can be illustrated by how DNS works.
DNS uses LDAP Procedure.
In fact, access to the DNS system is managed through an LDAP procedure.
What makes DNS fast is that it doesn’t hold every copy of the entire database. It checks its local database first, and if it doesn't find the record, it will query a parent server until it finds the answer.
Similar to DNS, when there is a query, LDAP is able to forward it to the location of the requested data. When a user needs to access an LDAP remote resource, the local server will send an access permission request to the local database first.
For example, in a DNS query scenario, if a user wants to find yahoo.com, it would first consult its local DNS server, but if it doesn’t have the answer, it would need to consult the Root DNS Server, which has the answer and knows how to get there.
Other Ways to Control Access
Access Control Lists are probably the most common and simple ways to control access in systems and networks.
An ACL is basically a list of permissions on a file or a directory, given to specific users or groups. Although ACLs are not considered directory services, they can be used as access management systems for directories and files.
For example, ACLS are really powerful for managing permissions within a file system, such as NFS. They can manage access, because they can provide the normal read, write, and execute permissions for an individual or group of users, and you may have as many lists to give or deny the permission.
Although ACLs are not exactly authentication mechanisms, they can provide excellent protection to the company assets.
The Identity and Access Management System
The automation and maintenance of directory services and protocols like AD and LDAP are usually undertaken by other applications. For the set up and initial configuration of this services you need to use an Identity and Access Management system (IAM).
The main purpose of a system like this, is to oversee the entire information available in the access directory services in one place. An IAM is basically a framework that simplifies the management and access of different identities. It contains all the policies and technologies that are needed to manage identities easily.
A complete IAM system may come with a role-based access control, which allows you to manage and regulate access networks and systems based on the roles of the users. A role can be defined based on authority, responsibility and job competency of a user. For example, if a user has an auditor role, he may be granted access to read all the files. In other case, an engineer might be granted access to read, write, and view only certain types of files.
Other features that an IAM system may include?
- Mechanisms to capture and document user login information.
- Ability to manage user identity database.
- Manage the allocation and removal of access privileges.
- Ability to simplify user provisioning process and setup accounts.
- Capable of monitoring and modifying access rights.
- Help comply with regulations that require periodical data access reports.
Recommended Access Management Software
As mentioned before, an IAM is a framework for managing digital identities and access. With this framework you can monitor and control all risks from a central place.
Some of our recommended IAM tools belong to complex and complete network management systems; they integrate access control within their product suite. This type of tools can be pricey but are suitable for enterprise networks.
Others are free and open source simple directory interpreters that can help you manage system permission on a basic level. They are perfect for individual and small networks, but can be challenging to set up.
Our methodology for selecting an Access Management Tool
Below, we have deeply researched and mentioned some of the proven methodologies for selecting the best access management tools.
- Know Your business requirements first
- Check for Compatibility and Integration with your existing systems
- Consider Scalability and performance
- Consider security features according to your business priority
- Check its audit and reporting capabilities
- Consider compliance standards suitable to your industry
- Consider cost, customer support, and other trainings
- Consider future developments and other technological advancements
The following list is our choice of the Best Access Management Tools for any type of network and budget:
Here's a list of the Access Management Tools
Below you'll find a Quick description of each tool, some screenshots and where to download a free trial to get started!
1. SolarWinds Access Rights Manager – FREE TRIAL
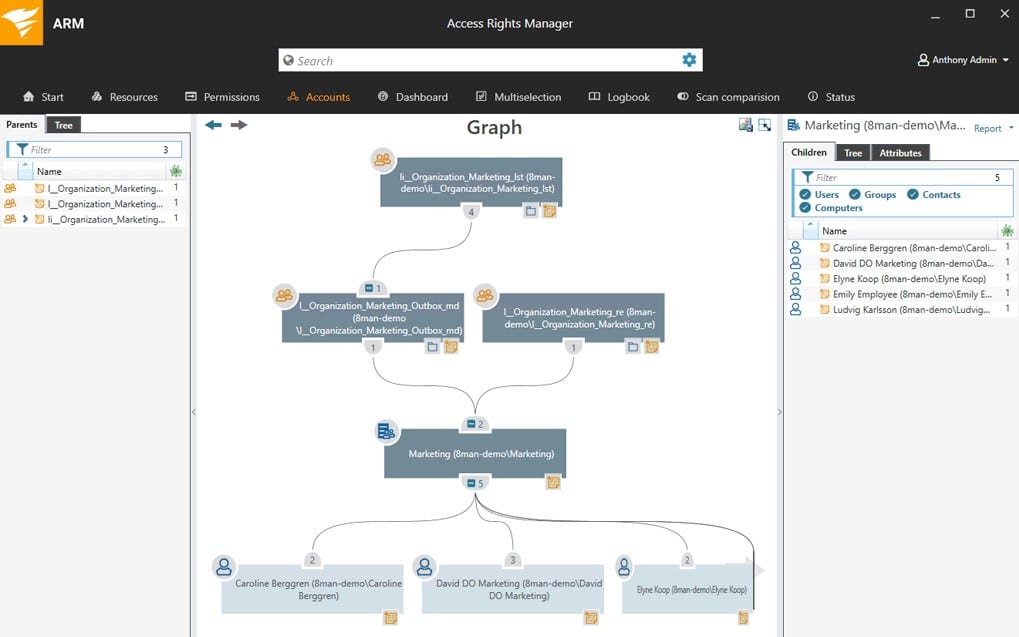
SolarWinds develops software that helps you manage networks, systems and IT infrastructure. They acquired access rights management provider 8MAN, to add auditing functionality to its enterprise customers and changed the name to Access Rights Manager (ARM). Although ARM is not the only SolarWinds tool able to monitor Access Directory, it is without a doubt, the most complete.
Key Features:
- Active Directory monitoring and tracking.
- Windows File Share auditing.
- SharePoint access management and monitoring.
- User provisioning and deprovisioning with templates.
- Microsoft Exchange Monitoring.
Why do we recommend it?
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager is known for its exceptional ability to enhance compliance through rapid change detection, swift identification of access privileges, and efficient account provisioning. It has fast and accurate features to ensure safe access management, making it a top choice for seamless and secure operations.
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager (ARM) helps managers configure user authorization and access permissions, and protect networks from unauthorized use and data destruction. The software only supports Active-Directory-based networks, so it can only run in Windows Server.
This product’s main goal is to allow easy user provisioning, user removal, and tracking. By controlling and limiting access to key components such as file servers, Active Directory, and the Microsoft Exchange Server, ARM can help protect systems and data from unauthorized use or destruction.
ARM can generate customized reports that show who has access to what and when this data was accessed. You can also provision and deprovision users easily and quickly with the help of role-specific templates.
Who is it recommended for?
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager is the best choice for large businesses and organizations who are looking to streamline access management. It's ideal for IT administrators and other high-level managers, healthcare, finance, or government sectors who want secure and compliant access control tailored to diverse organizational needs.
Pros:
- Provides a clear look into permission and file structures through automatic mapping and visualizations
- Preconfigured reports make it easy to demonstrate compliance
- Any compliance issues are outlined after the scan and paired with remediation actions
- Sysadmins can customize access rights and control in Windows and other applications
Cons:
- SolarWinds Access Rights Manager is an in-depth platform designed for sysadmin which may take time to fully learn
Price: The license starts at $2,995.00.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
SolarWinds Access Rights Manager is our first priority when it comes to choosing the best access management tool due to its unparalleled combination of robust security features, seamless integration capabilities, and user-friendly interface. It is trusted by leading industries for its efficiency in user provisioning, compliance adherence, and real-time threat detection; it offers a comprehensive solution that aligns perfectly with industry needs.
Download: Start a 30-day free trial
Official Site: https://www.solarwinds.com/resources/video/solarwinds-access-rights-manager-overview
OS: Windows Server 2008 R2 or later
2. ManageEngine AD360 – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine develop enterprise IT management software for security, service management, operations management, and Active Directory.
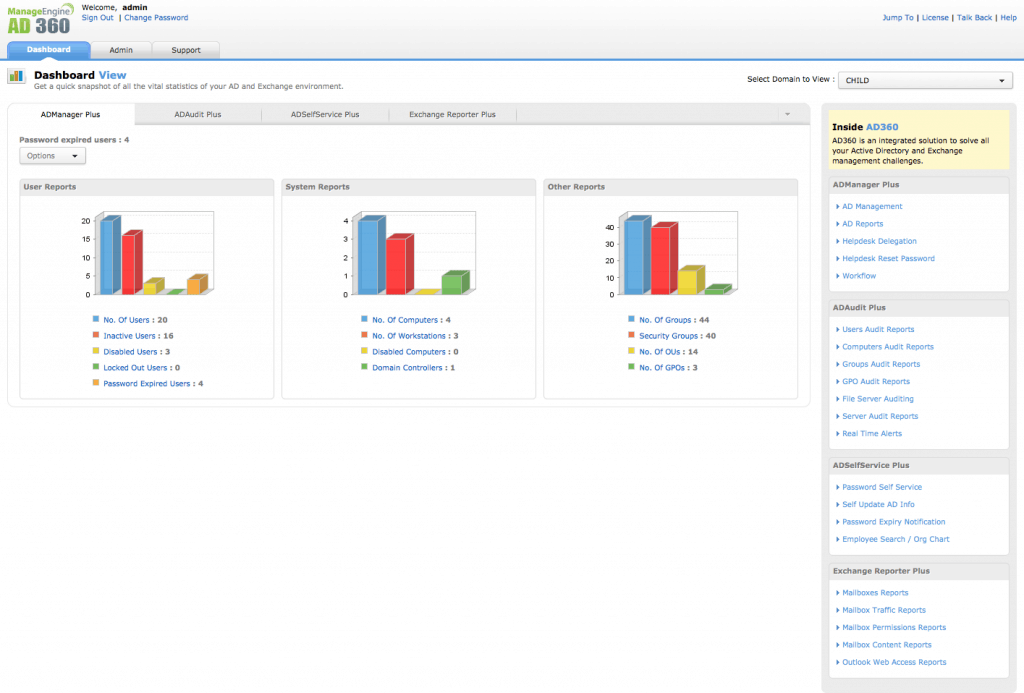
AD360 from ManageEngine, is an integrated solution for easy management of AD and Exchange. This software is a comprehensive IAM solution designed for user identity management, resource access control, security enforcement, compliance fulfilment. AD360 is designed for Windows environments.
The software can perform advanced access management features with the help of its easy-to-use interface.
Key Features:
- Automate provisioning and de-provisioning of user accounts.
- Manage self-service passwords.
- Monitor changes on the Active Directory.
- Securely audit AD, Office 360, or file servers.
- Ensure regulatory compliance such as HIPAA, SOX, etc.
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine AD360 is a versatile tool with a suite of features encompassing identity life cycle management, self-service password management, and identity automation. It stands out as a comprehensive solution to manage identity and access management for organizations.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine AD360 is designed for businesses and organizations across various industries seeking robust identity and access management solutions. It is widely useful to healthcare and finance industries, providing comprehensive features like identity lifecycle management, self-service password management, MFA, AI-driven analytics, and role-based access control.
Pros:
- Dramatically improves the usability of Active Directory, making routine tasks easier to perform and automate
- Can monitor changes across both local and cloud-based AD environments
- Supports SSO and MFA, great for securing your access management with multiple layers of authentication
- Extensive 60-day trial period
Cons:
- Can take time to fully explore the entire platform
Price: The price starts at $595. Choose the components that you need and get a quote from ManageEngine to get a better estimate.
Download:Get a 60-day free trial.
3. ManageEngine ADAudit Plus – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus protects AD instances against unauthorized changes. You should have a very limited number of personnel who are allowed to access your Active Directory domain controllers and create, change, or delete objects, so unexpected changes are a problem.
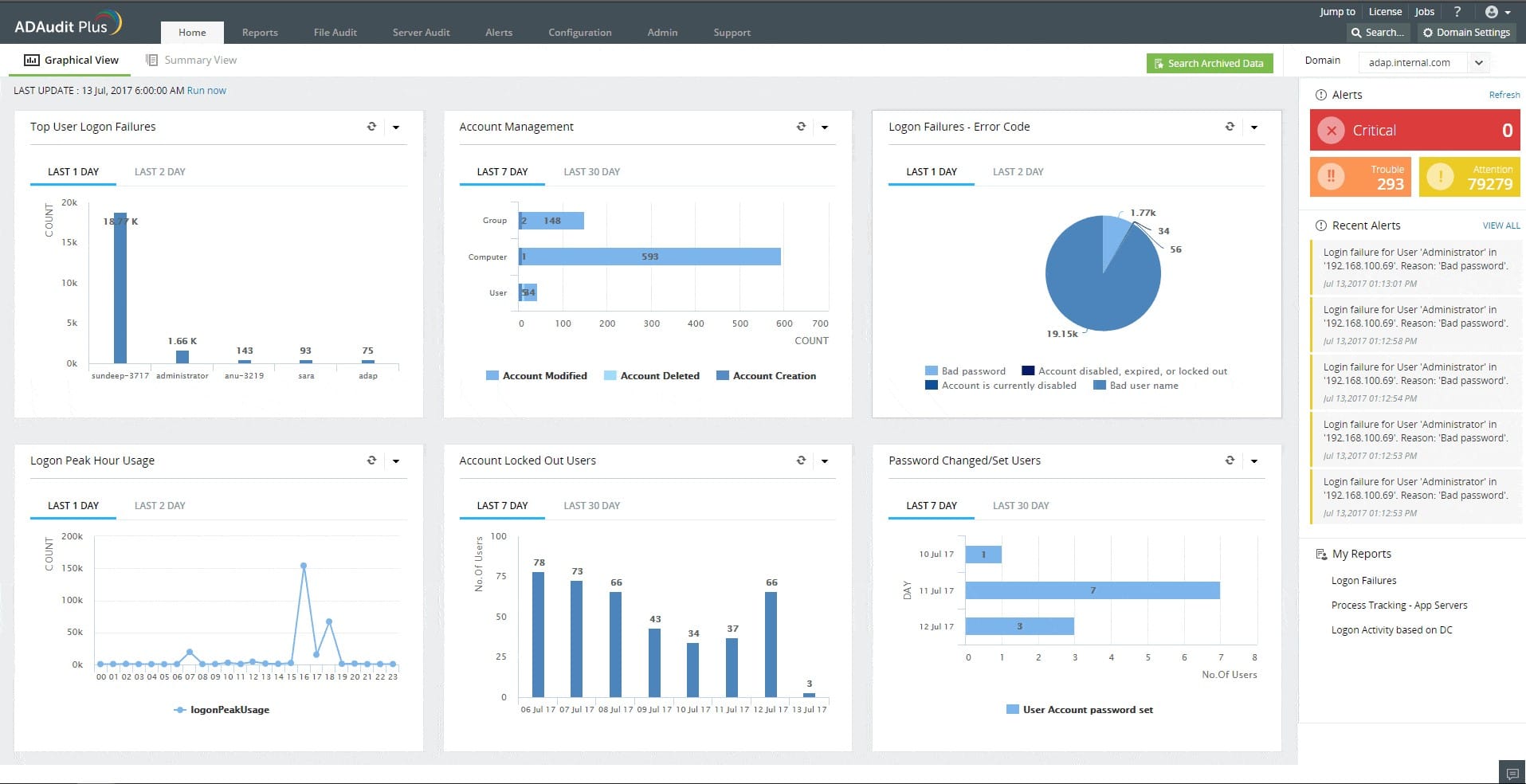
The ADAudit Plus system sends you an alert every time that a change is made within Active Directory. After checking with the limited group of administrators whether these changes were genuine, you have the ability to undo those alterations. This event would also be a trigger to get you and your colleagues to change system passwords because it is likely that hackers have got hold of someone’s credentials.
ADAudit Plus tracks user activities by collecting log files from operating systems and applications. The tool searches through these records, looking for file access events. This service enables an administrator to spot when a user account’s activities suddenly change, which could represent an insider threat or account takeover by hackers. The ADAudit Plus system runs on Windows Server and it is also available as a service on AWS and Azure.
Key Features:
- Tracks changes in Active Directory with alerts
- Performs user behavior analytics (UBA)
- Records file access events and logs content changes
- Compliance auditing and reporting for SOX, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, FISMA, GDPR, and GLBA
Why do we recommend it?
ADAudit Plus excels in tracking and analyzing changes in Active Directory environments. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive reporting make it a perfect choice for effective security and compliance management.
Who is it recommended for?
ManageEngine ADAudit Plus has powerful auditing capabilities, which are widely used and trusted by cybersecurity experts. It helps security-conscious organizations and IT professionals seeking proactive threat detection. With advanced statistical analysis and machine learning, it helps to analyze user behavior, providing a robust solution for those prioritizing real-time security monitoring and rapid response to potential threats.
Pros:
- Focused heavily on compliance requirements, making it a good option for maintaining industry compliance
- Preconfigured compliance reports allow you to see where you stand in just a few clicks
- Features insider threat detection – can detect snooping staff members or blatant malicious actors who have infiltrated the LAN
- Supports automation and scripting
- Great user interface
Cons:
- Better suited for larger environments
ManageEngine offers a 30-day free trial of ADManager Plus. There is also a Free edition that is limited to collecting logs from up to 25 workstations and if you decide not to buy at the end of the trial period, your installation switches over to the Free edition.
Price:
- Free
- Standard: From $595 per year
- Professional: From $945 per year
Download: Get the 30-day free trial.
4. Apache Directory
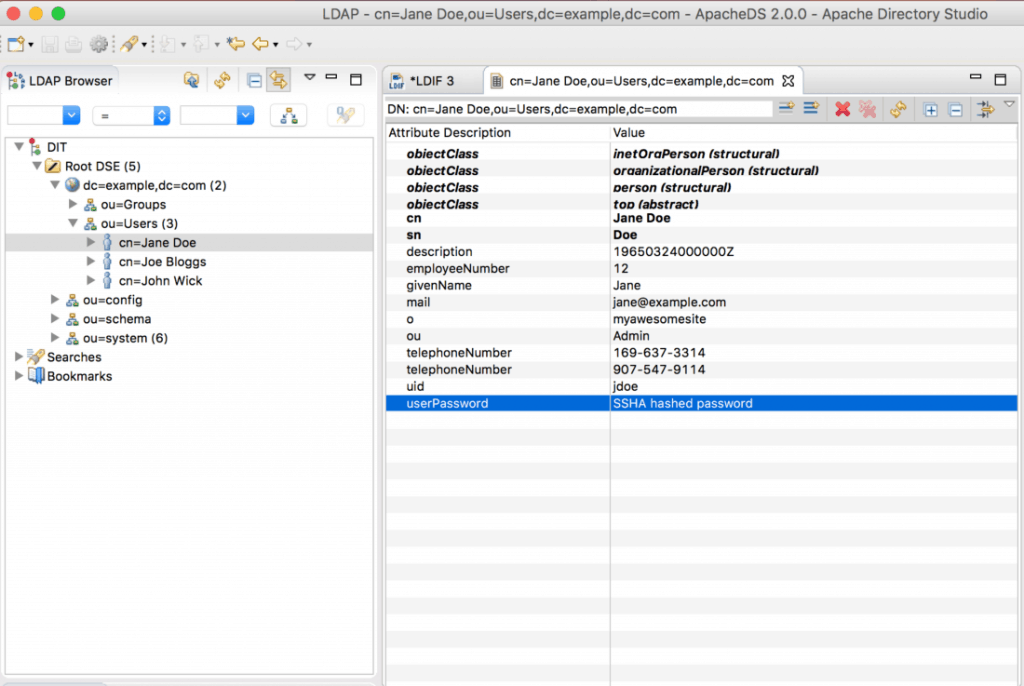
The Apache Directory is an open source project developed by the Apache Software Foundation. It is Apache’s own application of the LDAP Directory server. The software was written in Java and it is available under the Apache Software License.
The Apache Directory (ApacheDS 2.0) is an extendable and embeddable LDAP directory server which is fully compatible with LDAPv3. The software may also support other network protocols, such as Kerberos and NTP (Network Time Protocol).
More directory sub-projects have been developed under the main Apache Directory project that make the software highly compatible with other services. Some sub-projects are, Apache Directory Studio, eSCIMo, Fortress, Kerby, LDAP API, and Mavibot.
Apache DS is multi-platform. It can be installed on MacOS, Linux, and Windows. It has many features that makes it one of the best among LDAP Servers.
Key Features:
- Supports pluggable components and subsystems.
- It is able to implement virtual directories, proxy servers, and gateways to X.500 directories.
- It supports BTree-based partitions.
Why do we recommend it?
Apache directory helps to create virtual directories, proxy servers, and gateways to X.500 directories which is the biggest reason for organizations seeking adaptable and scalable directory management tools.
To make access management easier, Apache developed the Apache Directory Studio, which is a free directory platform, built especially for ApacheDS. The following screenshot, shows the software in action.
Who is it recommended for?
System administrators and developers, telecommunications, and various other industries find the Apache directory a useful option because of its reliable directory management. Also, it has a great community support making it an ideal choice for diverse enterprise needs.
Pros:
- Broad support for Windows, Linux, Unix, and Mac OS
- Robust access-right management, allowing users to modify records directly from the main interface
- Offers numerous extensions at no cost
Cons:
- The interface needs work, large networks are more difficult to work with
Price: Free. The license is open source.
Download: Get ApacheDS from its official site.
5. FreeIPA
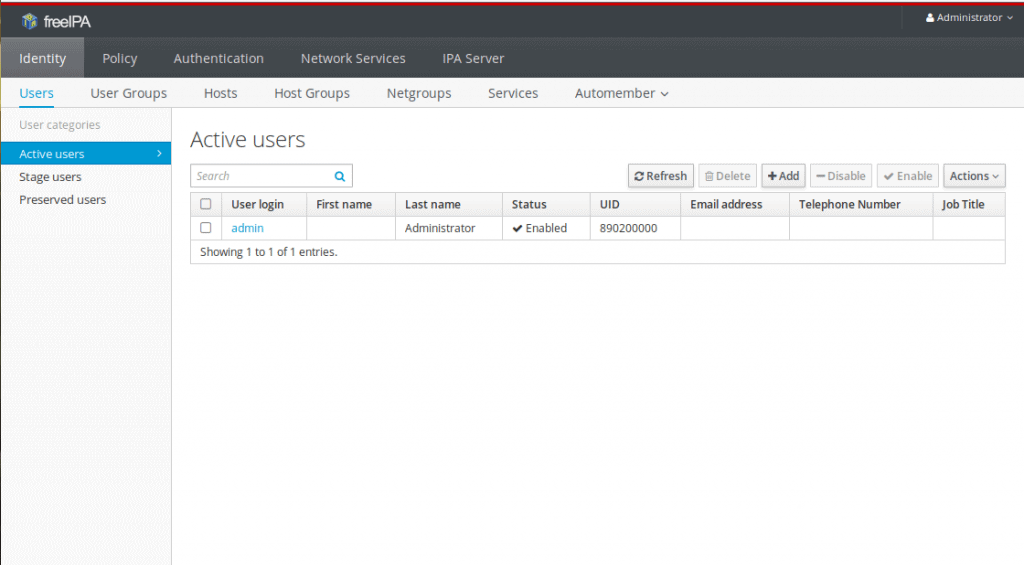
FreeIPA is an open source identity management solution for Linux systems. The software aims to help manage, Identity, Policy, and Audits (IPA) for free. FreeIPA was designed with a strong focus to provide easy management and automation of deployment and configuration tasks.
FreeIPA is an IAM platform made easy for Linux admins. Although the software is intended for Linux, it can also be installed on RHEL, MacOS, and Unix. The software allows you to manage users, groups, hosts, services, and much more, all from a central place. It can do this with the help of its extensible interfaces, WebUI, RPC, CLI, and JSONRPC API.
You can protect identities with the help of FreeIPA by defining Kerberos authentication and authorization policies for all your systems and devices. A big advantage of this software is that you work alongside other IAM systems such as Microsoft AD.
Key Features:
- Enable Single-Sign-On authentication for your systems.
- Set Kerberos authentication and authorization policies.
- Manage services such as SUDO, SELinux, DNS, NTP, and autofs.
Why do we recommend it?
With a strong emphasis on easy management and automation of deployment and configuration tasks, FreeIPA offers a robust solution for organizations seeking efficient and cost-effective identity management in their IT infrastructure.
And the best part is that…
FreeIPA imitates the feel of Active Directory, something that is not available in Linux systems.
Who is it recommended for?
Free IPA tool is suitable for System administrators and security experts to ensure comprehensive Identity, Policy, and Audits (IPA) management. It is useful for the company that needs to manage a large scale of users and different groups of people.
Pros:
- Simple and intuitive interface
- Easy to manage both users and groups from the GUI
- Supports permissions management audit reports
- Can manage both on-premise and cloud environments
Cons:
- Relies on 389 Directory Server – not the best option for those looking for an alternative to that product
Price: As the name implies, FreeIPA is free.
Download: Get the software in FreeIPA’s official site, for Fedora, RedHat, CentOS, or Debian.
6. LDAP Account Manager
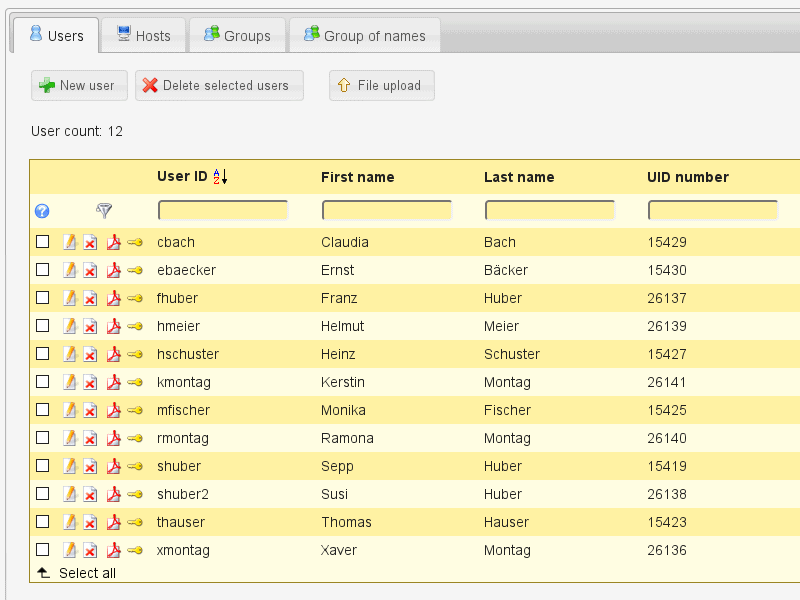
The main idea of LDAP Account Manager (LAM) is to simplify the technical complexities of LDAP. LAM allows entries like users and groups, that are kept in the LDAP directory to be managed easily through its web application.
Key Features:
- Self-service registration and password reset option.
- Multi-factor authentication option.
- Samba password synchronization.
- Multiple login methods support, such as uid and email.
- Integration of external CSS files.
Why do we recommend it?
It simplifies user account management, access control, and LDAP server configuration. The tool has a user-friendly interface for simplified management and also allows editing LDAP entries directly through the integrated LDAP browser.
LAM is basically an account-based IAM which gives the administrator an abstract view of the entire directory. The software offers LDAP database viewer and editor. LAM can be installed on Debian, Fedora, and SUSE Linux.
The original application of LDAP Account Manager is free and open source, but there is a premium and extended version under the commercial license. The paid version is called LDAP Account Manager Pro and includes extra features. Although the paid version is not as complete as the other products on the list, the price is much cheaper and could be a great choice for an enterprise network.
Who is it recommended for?
LDAP Account Manager is ideal for IT administrators and organizations who are looking to manage and edit the LDAP directory without any technical knowledge.
Pros:
- A good option for those looking for a lightweight GUI access management tool for Linux
- Can easily control access via basic LDAP integrations
- Is a good option for those looking for a barebones account manager
Cons:
- Lacks audit functionality
- Competing tools offer more options in an easier-to-use interface
Price: This software is available for free, but there is also a premium version. LDAP Account Manager pro license price for single use, starts at 149(EUR), and for a company, starts at 549(EUR) for 1 year subscription.
Download: Get the LDAP Account Manager for free from their official site.
Summary
Access control and management is one of the most important components to keep an organization’s network secured. The main problem that IAM software is trying to solve is, to control those users with excessive access privileges in order to protect the network from insider attacks.
The solution is to use a platform that can help control access to Active Directory (or LDAP), file servers, and Exchange. This ensures that all data and systems are protected from unauthorized use, misuse, modification, and destruction.
But choosing the right IAM is not an easy task.
There are three dominant factors that could influence the decision when choosing a product, one is the operative system running in your network, the other network size, and finally the budget.
Operating System
Not that LDAP is incompatible with Windows, but if you are running Windows Server in your network, you are much better off running Active Directory. With AD you can leverage Windows network and access control,and also interact directly with Exchange servers and Office 365. On the other hand if you are using Linux systems, you will need to use LDAP-based IAM software.
Size of the network
If your network is large, features such as single-sign-on authentication and self-service password reset can be crucial for admins to perform faster. But those features may not be suitable for a small network.
Budget
Not everyone has the budget to afford the best products in the market. But all products listed here come with a free trial or either are 100% free. So you can test the waters, before diving into the ocean.
The first thing you can do is to define your Operating System needs, the size of network and your budget, and give some of those products a try.
Which product suits your requirements best?
We hope this article gave you a better understanding of Access Management the importance it plays in your network infrastructure and role as an IT Admin or Engineer!
Access Management Guide FAQs
What are the main components of an access management system?
The main components of an access management system typically include identity and access management (IAM) software, authentication methods, authorization policies, and auditing and reporting capabilities.
What is access deprovisioning?
Access deprovisioning is the process of revoking access privileges when a user no longer needs access to a system or resource.
What is an access management policy?
An access management policy is a set of rules and guidelines that govern how access to resources is managed and controlled within an organization.
How can organizations implement effective access management?
Organizations can implement effective access management by implementing a comprehensive access management system that includes IAM software, authentication methods, authorization policies, and auditing and reporting capabilities. Additionally, organizations should regularly review and update their access management policies and procedures to ensure that they are effective and meet changing security needs.