We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Cyber Attacks – A Detailed Guide, Different Types & How To Protect Against Them

UPDATED: April 30, 2024
What is a cyber-attack? — A cyber-attack is a strike against an organization’s computer network or an internet application. It is usually a malicious attempt to benefit from breaking into the systems, interrupting service, and stealing data. It is usually performed by an individual or group of black-hat hackers.
They use a variety of tools and practices to perform the attacks, these include exploit kits, Malware, Ransomware, SQL injections, etc.
Is not uncommon to see countless headlines about businesses losing money, compromising customer’s data and getting fined due to cyber-attacks.
It’s a fact, cyber-attacks occur every day. According to The 2017-2018 Global Application & Network Security Report by Radware, cyber-attacks are becoming more frequent and efficient. More than 62% of the surveyed businesses from different industries experienced daily attacks and 15% of those had complete outages.
Here is our list of the best cyber attack security monitoring software:
- SolarWinds Security Event Manager – FREE TRIAL A SIEM package that focuses on log management to create a data pool doe security breach detection. Runs on Windows Server.
- ManageEngine Log360 – FREE TRIAL A log manager and SIEM service that collects, consolidates, and files log messages as well as detecting malicious activity. Available for Windows Server.
- ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL This package scans your entire IT system to ensure that it is hardened against cyber attack. Available for Windows Server.
- Splunk Enterprise A famous packet sniffer that has an add-on service to create a SIEM service. Installs on Linux, Unix, and macOS or can be taken as a SaaS package called Splunk Cloud.
- RSA NetWitness Suite A cloud platform that offers a SIEM, and an extended detection and response system to identify and shut down malicious activity.
Reasons Why Hackers Attack
Hackers have multiple reasons to perform a cyber-attack on target vulnerable networks. One of the most common reasons hackers attack is to either steal or leak information. This can be data from real-life customers, internal employees, or sensitive business data. Hackers use this information to steal identities, credit cards, and bank accounts and finally steal money.
But not all hackers are after making a profit. Some of them attack for the pleasure and glory. The more services they interrupt, the more they prove themselves, the more reputation they gain. Others perform cyber-attacks just to prove their ideals and protest against different political or economical movements.
What is a Botnet?
Some skilled hackers are able to take down complete websites and business services. They stand behind while their army of bots to their job. A bot is a malicious software unintentionally downloaded to a computer. It allows hackers to gain full control of the computer and use it to distribute malware, phishing scams, distribute spam, send out spyware, etc.
When a hacker is able to accumulate a large number of these bots, the collection of these bot-infected computers becomes the botnet. An attacker (also called a bot herder) creates a botnet to increase the magnitude of the attack. A botnet is frequently used to shut down services with deadly DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks.
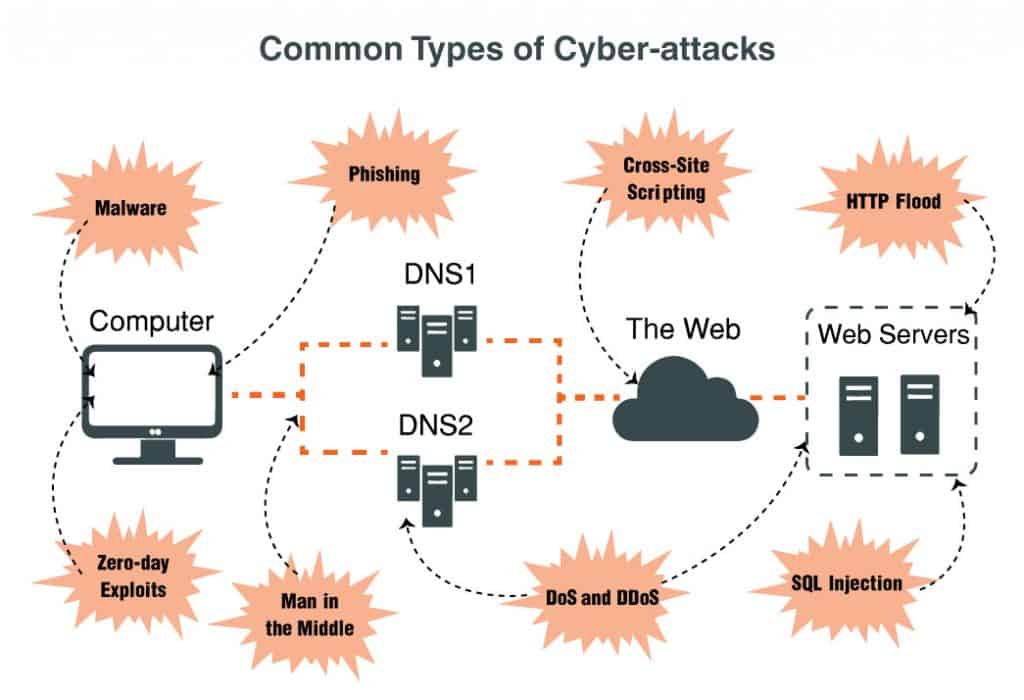
Common Types of Cyber-Attacks
The following section describes what are the most common types of cyber-attacks and how they work.
- Malware
- Phishing
- Man in the Middle
- DoS and DDoS
- Cross Site Scripting
- SQL Injection
- Zero Day Exploits
1. Malware Used in Cyber Attacks
Malware “Malicious Software” is developed by a cyber-attacker with the purpose of invading the target’s computer and taking some or full control. Usually, Malware can infect the system or network with the initial unintentional and unknowing help from a human and continue to self-replicate automatically. Once security is breached and the Malware is in the system, it can do serious damage.
Hackers lure a user to click an email attachment, download an executable software hidden as an ebook, or infect portable devices so that they can spread faster.
Here are the Most common types of Malware:
- Virus Spreads with user action, such as opening an infected file. They depend on a host file.
- Worms They replicate themselves automatically, without the use of a host file.
- Trojan Horse Malware that disguises as legitimate software. Once you install the “legitimate software” the malware takes control of your system.
- RootKit Hidden deeply within the computer files. It provides continued privilege or backdoor access to the computer.
- Logic Bomb A set of instructions inserted into software that sets off a malicious action when a certain condition is triggered.
- Exploit Kit Searches for software vulnerabilities. It is very effective on unpatched systems.
- Adware Stands for Malicious Ads. It presents continuous unwanted ads on a computer. Some adware monitors the user’s behavior so it can serve tailored ads.
- Ransomware It blocks (kidnaps) key files or data on the computer and asks for money so they can be liberated.
2. Phishing
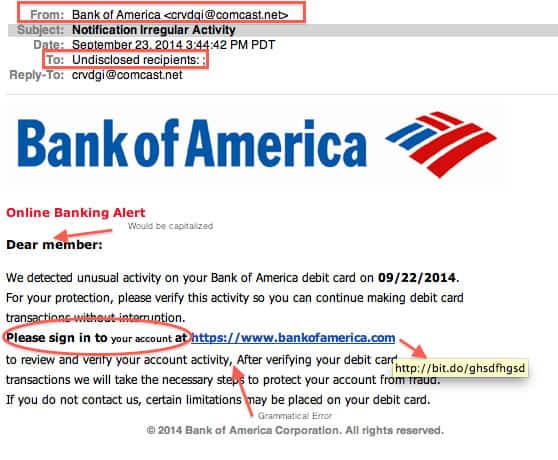
A cyber-attack that aims to obtain sensitive information by cheating targets into believing fake messages. Phishing attackers disguise themselves as a trustworthy source and send lures usually through email, social media, or other electronic media.
Phishing relies on social engineering to be able to deceive its targets. It makes a user enter their personal information, such as username, password, credit card, etc to a fake website that looks like the legitimate site, but it is not. The fake website either keeps sensitive information or installs Malware on the user’s computer.
3. Man in the Middle Attack
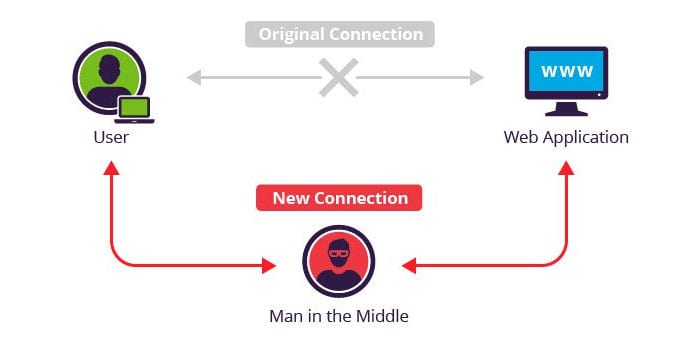
As the name implies, an attacker sits in the middle of the communication between two targets and is able to eavesdrop. The Man-In-The-Middle Attack or MITM attempts to secretly intercept and listen to the legitimate communication between two hosts.
The attacker acts as a relay who listens and sometimes even alters the conversations with the two hosts. It intercepts the entire communication passing through the two victims and even inserts new messages.
A MITM can happen in any sort of online or electronic communication.
Here are the Most Common of MITM attacks:
- Email Hijacking
- Wireless LAN Eavesdrop
- Session Hijacking
4. DoS and DDoS Denial of Service Attack
This cyber-attack floods the systems with too much traffic that it overloads resources and bandwidth, making servers and network unavailable. With too much information a server or system is often unable to respond to valid requests so it overloads. DoS attackers attempt to make network resources unavailable to its legitimate users by flooding the servers with junk and oversized requests.
In a DDoS Distributed Denial of Service attack, the source of DoS traffic comes from multiple different places. An attacker usually crafts a DDoS with an army of bots (or botnet). All bots (also referred to as Zombies) in a botnet are infected systems that can be controlled to send loads of malformed traffic.
A variation of DDoS is the HTTP Flood. This attack controls the HTTP and POST unwanted requests to attack a web server. The HTTP Flood uses a botnet to overwhelm a server with too many HTTP requests.
5. Cross Site Scripting
This attack aims to insert malicious code into a website which targets a visitor’s browser. Cross Site Scripting, also knowns as XSS targets trusted web applications. The attacker uses the web app to inject the code such as a browser or client-side scripts that is viewed by other users of the same application.
This attack is performed by hackers to bypass and gain access to applications. An XSS works because some web applications use inputs from users found in the output generated without validation. The web browser of the victim doesn’t know that the script came from somewhere else. The web browser trusts the legitimate site, so it allows the third-party “malicious” script to access cookies, session tokens, and other sensitive information kept on the web browser.
6. SQL Injection
An SQL injection attack interferes with the queries that a web application makes to the database. An attacker inserts crafted SQL (Structured Query Language) code lines that allow data to be revealed. This data is retrieved from the database which could be information about other users. The attacker gains access because the database is unable to recognize the “incorrect statements” and filter out the illegal input values.
In some cases the SQL injection can also modify or remove data, harming the content of the databases and the application’s normal behavior. To perform an SQL injection is just a matter of submitting the malicious SQL statements into any vulnerable entry field such as a search box.
7. Zero-day Exploits
When new software is developed, it usually contains countless bugs and vulnerabilities. When software developers find their own vulnerability they quickly develop patches and updates. But sometimes this process is slow.
Black-hat hackers take advantage of zero-day exploits and are able to find vulnerabilities in new software much faster. They are able to target this vulnerability before users update their software.
Solutions for Monitoring Against Cyber Attacks
Social Engineering bypasses all technologies, including firewalls…
– Kevin Mitnick, World Famous Hacker & Security Consultant
When it comes to defending your network against cyber-attacks, the best tools are your own judgment, common sense, and a solid basic cyber-security training. It is believed that only about 3% of Malware is able to exploit a technical flaw. The remaining, 97% relies on tricking humans through social engineering to gain easier access into the network, [Source: KnowBe4].
Training personnel to avoid being tricked and scammed is one of the core elements for a strong cyber-security. But threats come from different directions and in different forms, that is hard to remain 100% defensive. Although you might be able to tackle that 97 % of social engineering threats, you still need to protect from the 3%, which is a lot.
Protecting from the whole spectrum of cyber-attacks is really challenging. Although Operating Systems come with their own security, it is usually not enough. Cyber-security tools and SIEMs (Security Information and Event Management) come in pretty handy when your network is medium to large.
The following section shows some of the best network security monitoring tools in the market.
Some of the Best Cyber Attack Security Monitoring Tools:
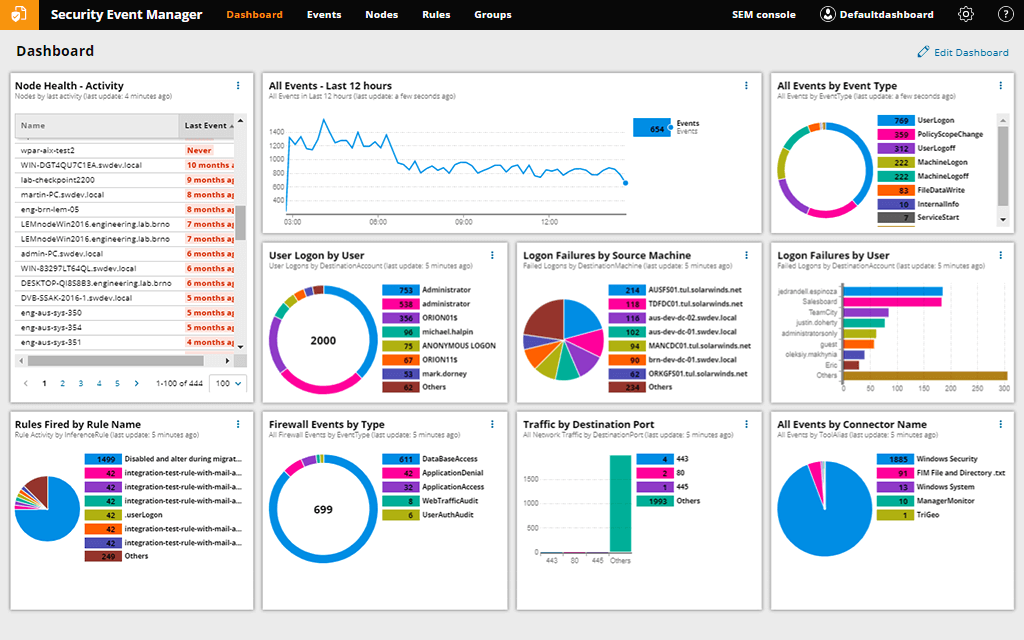
1. SolarWinds Security Event Manager – FREE TRIAL
SolarWinds develops network monitoring software. Their IT security software includes “Patch Manager”, “Access Patch Manager”, and “Security Event Manager”. The later is an amazing SIEM tool, that allows easy management of event logs for security or compliance reasons.
The Security Event Manager tool is able to identify threats with an event-time suspicious activity detection system. You can also use the tool to perform event investigation and data forensics to mitigate present and future risks. The Log and Event Manager allows you to achieve auditable compliance with out-of-the-box reports for PCI DSS, HIPAA, ISO, and much more.
Pros:
- Enterprise-focused SIEM with a wide range of integrations
- Simple log filtering, no need to learn a custom query language
- Dozens of templates allow administrators to start using SEM with little setup or customization
- Historical analysis tool helps find anomalous behavior and outliers on the network
Cons:
- SEM Is an advanced SIEM product built for professionals, requires time to fully learn the platform
Price: Starts around $4,300 for a license.
Download: Get a fully functional 30-day free trial from SolarWinds official site.
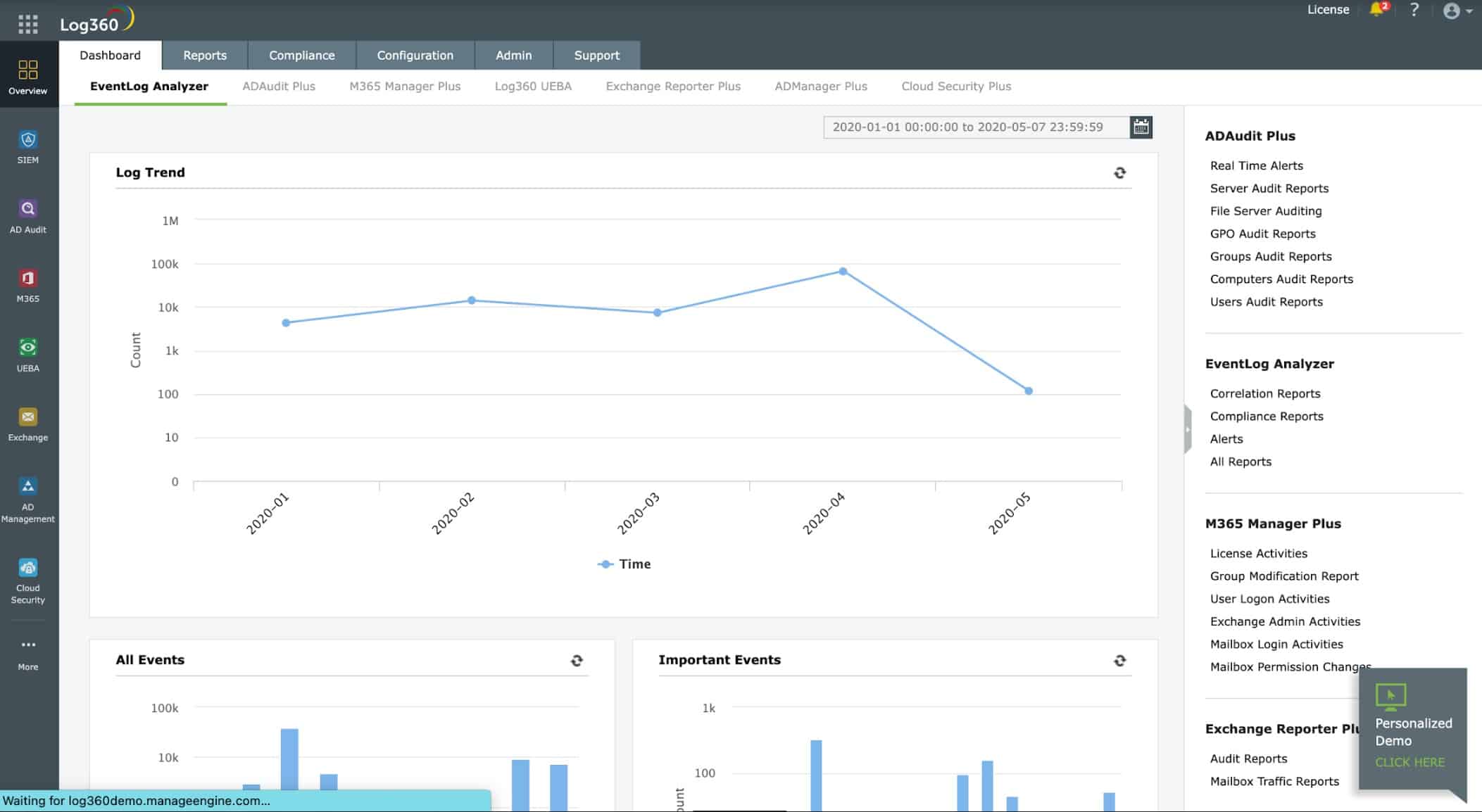
2. ManageEngine Log360 – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine offers a comprehensive IT Security Compliance Suite that helps you manage IT security, audit activity, and ensure regulatory IT compliance. They offer tools that perform Log Management, Firewall Security and Configuration Management, SIEM & Network Threat Mitigation, and much more.
For SIEM and threat mitigation, ManageEngine offers the Log360, which is a complete SIEM solution that combines AD auditing components and log management in a single interface. With it, you’ll be able to audit changes in the Active Directory, collect logs network devices, and deeply examine different servers all from a single console.
Pros:
- Great dashboard visualizations, ideal for NOCs and MSPs
- Can integrate multiple threat data steams into the platform
- Offers robust searching of logs for live and historical event analysis
- Provides monitoring cross-platform for Windows, Linux, and Unix systems
- Can monitor configuration changes, preventing privilege escalation
Cons:
- ManageEngine offers a suite of advanced services and features can time to explore and test out
Price: The price is not published in ManageEngine website, but you can get a quote.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial without restrictions.
3. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus – FREE TRIAL
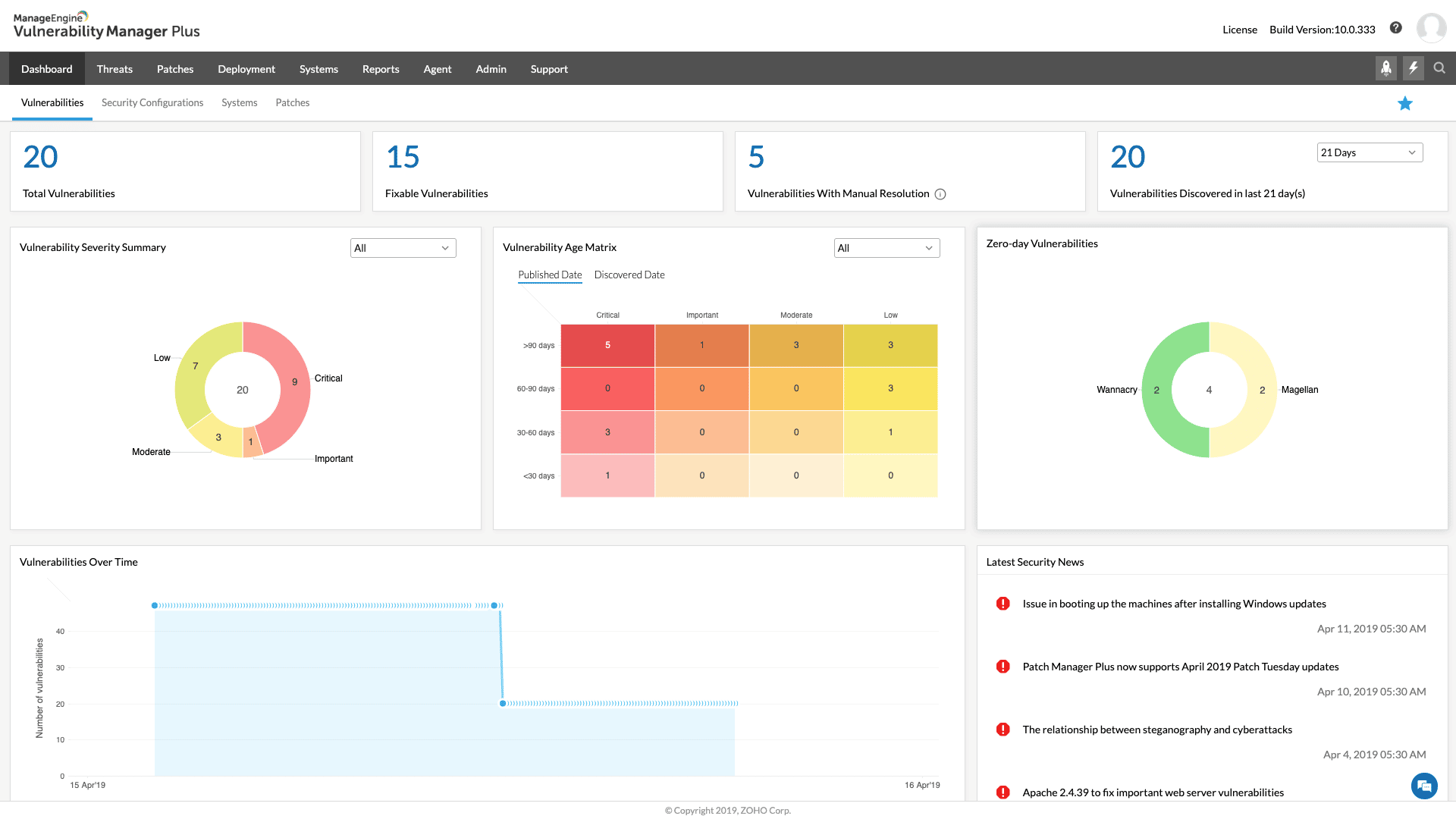
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus is an on-premises software package that ensures your IT assets are as resilient to attack as possible. The package assesses all endpoints, looking for well-known weaknesses that hackers and malware regularly use to get into a system. The dashboard lists the discovered vulnerabilities. Some can be fixed by the Vulnerability Manager Plus system. However, many will need manual intervention. The console produces guidance in these instances.
The ManageEngine package creates a software inventory. It will check regularly with the Zoho Central Patch Repository to see whether updates are available. The system will patch outdated software and also the Windows, macOS, and Linux operating systems. The package also examines Web servers for weaknesses.
Pros:
- System discovery creates hardware and software inventories
- Daily checks for patch availability
- Automated patch installation
- Guidance on fixes for misconfigurations
Cons:
- No cloud-based version
ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus runs on Windows Server.
Price:
- Free – Manages 20 workstations and five servers: $0
- Professional – Protects a LAN: Starting at $$695
- Enterprise – Coverage for a WAN: Starting at $1,195
Get a 30-day free trial.
4. Splunk
Splunk is a lightweight, fast, and flexible network monitoring tool. It is designed for real-time data analysis and historical browsing. It indexes and compares captured data in a searchable archive in order to create reports, alerts, and graphs. With this tool, it is very easy to diagnose problems and provide insights. Splunk is widely used for application management, cyber-security, and compliance.
Although the core product is designed to analyze high volumes of machine data, Splunk also offer an Enterprise Security tool. It is a security information and event management SIEM platform, able to provide insights from machine data generated from network devices such as firewalls, access points, edge routers, anti-virus/malware, etc.
Pros:
- Uses excellent visuals to display collected data and insights
- Supports a multitude of environments for data collection
- Uses machine learning to identify new data sources and monitor behavior
- Caters to enterprises with excellent support and a wide range of integrations
Cons:
- Many features and services cater to large enterprise networks
Price: Splunk Enterprise starts at $173.00 per month.
Download: Get a free trial, from Splunk’s official site.
5. RSA NetWitness Suite
RSA NetWitness Suite is a popular SIEM and threat detection tool for large enterprises in different industries. This solution uses advanced technology to detect threats and respond accordingly. It employs behavioral analysis and threat intelligence to help security admins find and resolve attacks before they happen. It also features machine learning and automation with orchestration.
The complexity of its elements and implementation limits this platform for large enterprises with experienced IT security auditors and teams. But those enterprises able to implement it, can benefit from its advanced threat intelligence that includes multiple threat feeds, from the intelligence of RSA FirstWatch research team.
Pros:
- Highly flexible cloud-based solution
- Simple yet informative interface
- Built with enterprise networks in mind
- Leverages large intelligence networks to identify and prevent new threats
Cons:
- No free trial
- Must contact for pricing
Price: Speak to an RSA representative and get a quote.
Download: No free trial is available, but you can request a demo to see the product in action.
Conclusions
Cyber-risks are real and they are causing extreme damage. While it would be impossible to protect from all sides and all types of attacks, but you can start taking the right precautions right now.
Start with the fundamentals. Educate yourself and your team on social engineering, and how to avoid the most common cyber-attacks. Protect what really matters to you and your business and have a plan on how to react properly in front of a threat. Start protecting your data, services integrity, but most important your reputation.
The Best Cyber Attack Monitoring tools shown above are a good starting point to audit and get to know your own vulnerabilities and act upon them.