We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
How to Fix Packet Loss in 7 Simple Steps

UPDATED: September 13, 2024
Dropped connections, choppy video, and slow page speed could all be symptoms of packet loss on a network. In this guide, we’ll explore the common causes of packet loss, how to stop packet loss, and what you can do to prevent it in the first place. Let’s dive in.
Here is our list of the best tools to fix and prevent packet loss quickly:
- ManageEngine OpManager – EDITOR'S CHOICE Helps detect packet loss on Windows and Linux operating systems by sending SNMP checks on different devices. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Paessler Packet Loss Monitoring with PRTG – FREE TRIAL Uses customizable sensors to monitor network performance and have QoS settings to manage and shape traffic. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL A comprehensive solution for diagnosing and resolving packet loss, ensuring smooth network performance. Start a 30-day free trial.
How do I fix packet loss?
While packet loss can be frustrating, the source of the problem can usually be identified relatively quickly. Use these seven steps to help find and fix your packet loss problems.
- Restart your router While this seems like a cop-out answer, this solves most packet loss issues in smaller network environments. Consumer class hardware is known for having problems that can sometimes only be ‘cleared’ when power cycling. Unplug your router for 15 seconds and then plug it back in.
- Check your connections If your PC is wired to the router or switch, do a quick check of the cable. Reseat it and make sure it is inserted correctly. While rare, these cables can fail, when stretched too far, or put under something heavy.
- Check your network performance Are people streaming movies, playing video games, or listening to music online? These can all impact performance, especially on home networks. Sysadmins should use tools like SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor for more technical details.
- Update device drivers If only one device is having an issue, consider updating the network card drivers on the device. The same applies to wireless access points and other equipment. You’ll also want to make sure the firmware is also up to date.
- Switch to a wired connection If you’re on wifi and having issues, consider switching to a wired connection if possible. If that makes a difference, your packet loss is likely only over the wifi network.
- Replace older hardware Sometimes older hardware can't take advantage of the latest networking technologies or handle more modern traffic loads. If you haven’t upgraded your hardware in a long time, consider investing in newer equipment.
- Use QoS when possible QoS stands for Quality of Service and is a setting that allows you to prioritize traffic. Utilize this setting in your router to prioritize the services that are most important to you.
What exactly is packet loss?
Packet loss occurs when packets of information are dropped and do not reach their destination. This can happen for numerous reasons, which we will discuss in more detail below. When data is shared across the network, it's broken down into smaller chunks, called packets.
These smaller packets can move across the network and through different devices much more accessible than if the data was sent all at once. Once the packets have reached their destination, they are reassembled to display their content. This could be a streaming video on Netflix, a VoIP conference call, or just an email.
Packet loss is most noticeable over streaming media like video or voice chat because when just a few packets are lost, the impact is easily visible. When those packets of information don’t reach their destination, audio can sound jumbled, and videos can freeze up.
Related Post: Network Jitter – What is it and How to Monitor it
What causes packet loss?
This is a tricky question because there are several different reasons for packet loss. However, troubleshooting in the proper manner can help quickly narrow down the culprit. Let’s take a look at a few of the most common causes of packet loss.
Network Congestion
Packet loss can occur as the connection struggles to hand out enough bandwidth to everyone at the same time. While this results typically in latency, which is experienced as slowness, it can also cause packets to drop altogether. Having too many devices on a network, all sending and receiving, can cause traffic to not only slow down but drop entirely.
If this might be the case, consider testing the network speeds of your machine. Test both from a wired connection and a wireless connection to get a complete understanding of the scope of the issue.
In this case, QoS can help direct and prioritize traffic, so noisy networks don’t drop critical packets. In the router's QoS settings, you can choose to put specific applications and services above others and even restrict how much bandwidth some applications can use.
Faulty Hardware
Misconfigurations in routers, firewalls, or switches can cause packets to drop. In-home networks, a simple power cycle usually fixes the issue, but this may get more complicated in corporate environments. When sysadmins have security filters, NAT policies, and packet inspection services running, a more detailed look must be taken.
The helpdesk should log all changes made to networking equipment to avoid any headaches or downtime caused by undoing a change. Better yet, administrators can use a Network Configuration Manager to help monitor and audit hardware changes. This way, changes to larger, more complex environments can be easily tracked and undone if necessary to rectify the issue.
As mentioned earlier, sometimes hardware needs to be replaced. PoE switches can start to lose power on switches, and old firewalls can struggle to keep up with an increase in traffic. Always audit your network hardware, and check to make sure that both your calling and switches can handle the amount of traffic you’re putting through it.
Drivers & Firmware
Simply put, drivers are what allow your device to communicate with the network hardware. If those are out of date or installed incorrectly, your device can experience a myriad of issues, including packet loss.
Check to see when your network drivers were last updated on your device. Even if they’re only a few years old, consider updating them. Be wary of third-party sites that offer automatic driver updaters and only download drivers from the manufacturer’s website. Many times these third-party tools can either install malware or the incorrect driver resulting in more headaches.
Updating firmware can also fix packet loss issues, especially on enterprise networking equipment. Devices like wireless access points can struggle when one of the access points has older firmware. Most network configuration managers can push out firmware updates en mass and monitor this automatically.
How do I test for packet loss?
You can quickly test for packet loss by running a simple ping command. A ping command sends small ICMP packets to the target device of your choosing. This can be a device inside your network like a switch, or a server somewhere else like Google. For troubleshooting purposes, using a simple Ping command to the outside world allows you to check to see if you’re losing packets quickly.
If you’re not sure you’re losing packets, you can test this quickly from any device running Windows using the following command.
Launch a command prompt by holding Windows Key + R and typing cmd in the Run box. Then press Enter.
To test the connection for packet loss out to the internet, run the following command:
ping google.com -t
To stop the ping check, press Ctrl+C.
If you see anything other than “Reply from…” you’re likely experiencing packet loss. Packet loss may occur sporadically, so let the test run for a while. You might see a no-response message, a request timed out, or a general failure when packet loss occurs.
When you end the test, you should see a summary of the results that displays the number of packets sent, how many were lost, the average response times, and your fastest and slowest times in milliseconds.
What can I do to prevent packet loss?
Preventing packet loss can be challenging on more extensive networks, but it isn’t impossible. There are specialized tools that can help proactively alert when devices begin to lose networking connectivity and even attempt to reroute that traffic over to failover if possible. Let’s take a look at a few tools that can be used to fix packet loss.
The Best Tools for Fixing Packet Loss
Our methodology for selecting packet loss prevention tools and software
We reviewed the network monitoring tools and software market and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- The ability to automatically identify and correct packet loss
- Ease of use
- Integrations into other monitoring applications
- A facility to analyze network performance over time
- Graphical interpretation of data, such as charts and graphs
- A free trial period, a demo, or a money-back guarantee for a no-risk assessment
- A good price that reflects value for money when compared to the functions offered
1. ManageEngine OpManager – FREE TRIAL
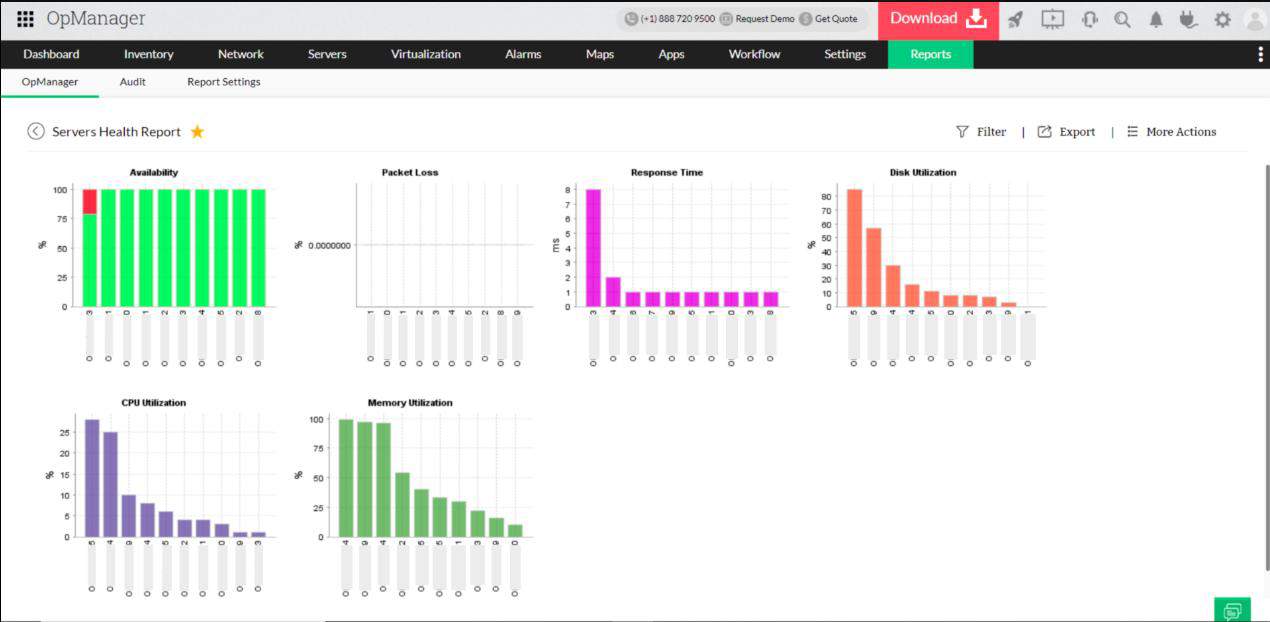
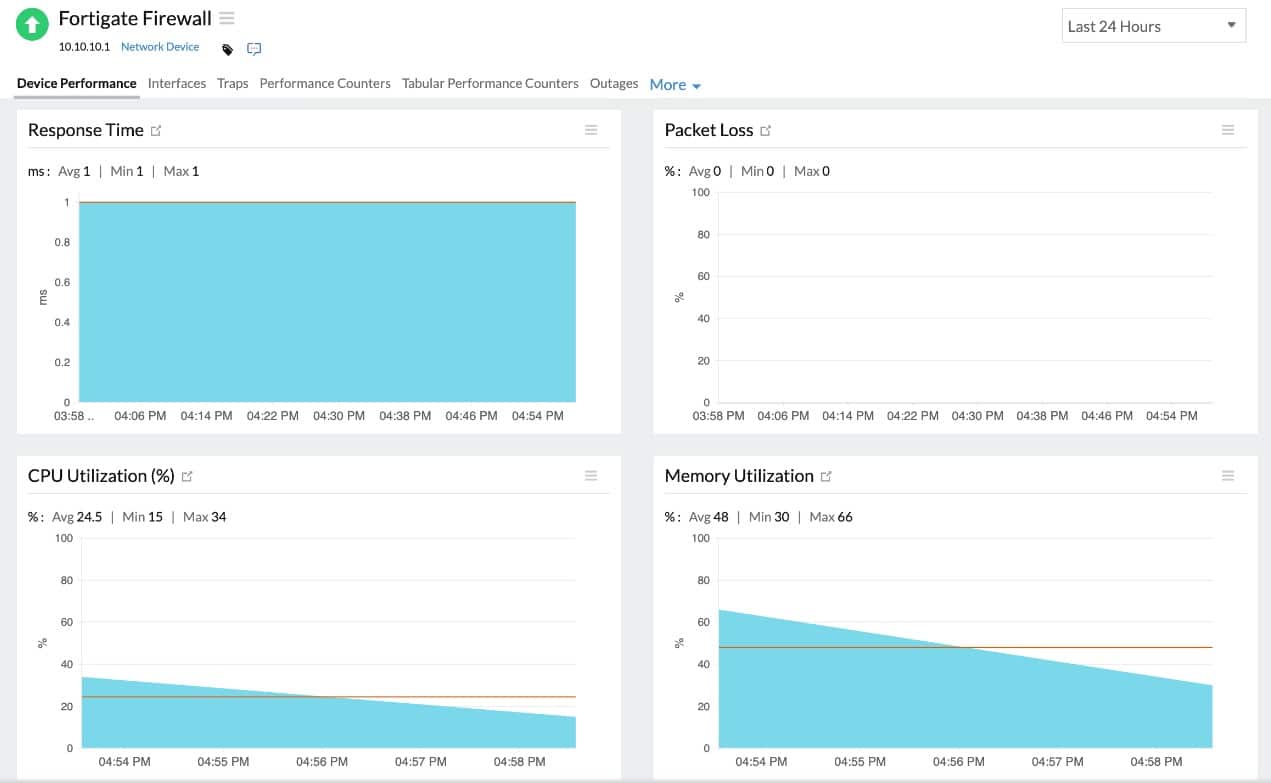
ManageEngine OpManager is a robust enterprise tool that offers monitor capabilities well beyond simple packet loss detection. The centralized dashboard provides a flexible and customizable way for administrators to manage their networks, individual applications, and other server environments.OpManager is an excellent choice for multiple teams or network operations centers, as templated dashboard views can be created.
Key Features:
- Router Monitoring: Gives important details about router performance regarding errors, buffer statistics, voltage, temperature, and more.
- Switch Monitoring: Presents information about the status and availability of ports. This feature helps to automatically discover switches and place them in suitable ports over the network.
- WAN RTT Monitoring: See various links on the graphical maps at the WAN RTTs dashboard. Each link contains information and alerts to ensure the good health of WAN.
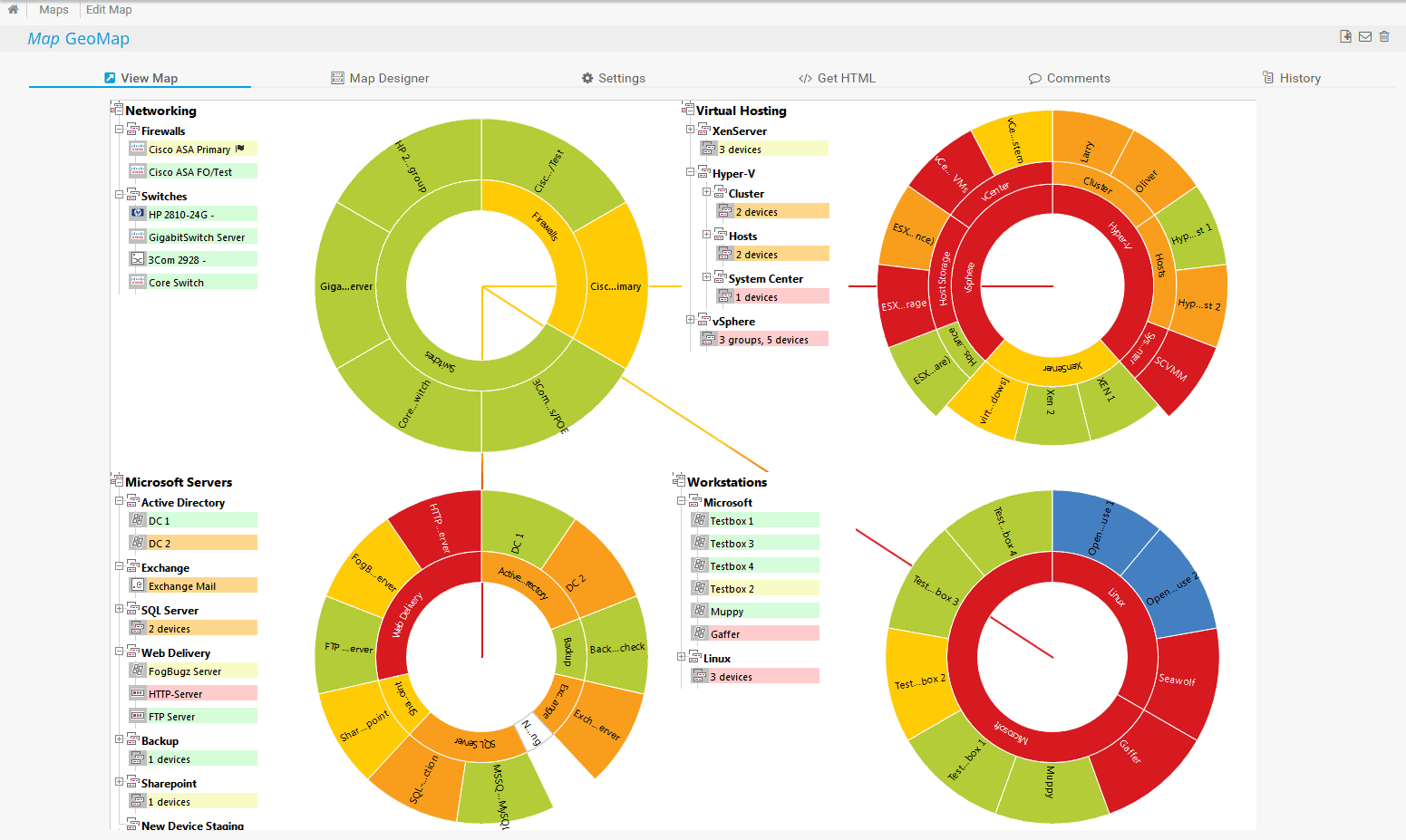
- Network Mapping: Features quickly identify which device has a problem, meaning you can immediately take action on the exact problem.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend ManageEngine OpManager because it is suitable for all types of organizations. It offers customizable dashboards for each user, ensuring flexibility without losing overall coherence. It comes with features like network health monitoring, VoIP monitoring, Cisco NBAR reporting, network mapping, and server monitoring out of the box, making it versatile and comprehensive for diverse needs.
You can think of OpManger as an uptime optimizer. Sensors can monitor and alert you to packet loss and changing network conditions. This automation can either fire off alerts via SMS or email, or you can opt for certain conditions to execute a script. For instance, if a device has known issues where it needs a power cycle, you can create a script to power cycle it if it fails to respond after so many seconds.
Who is it recommended for?
OpManager is recommended for network administrators and IT professionals who need to monitor network health across all devices. It utilizes SNMP to monitor devices continuously and sends out alerts, known as “traps,” directly to the dashboard or via text and email notifications. It also provides specific alerts for packet loss, identifying responsible devices for better troubleshooting.
Pros:
- Designed to work right away, features over 200 customizable widgets to build unique dashboards and reports
- Leverages autodiscover to find, inventory, and map new devices
- Uses intelligent alerting to reduce false positives and eliminate alert fatigue across more extensive networks
- Supports email, SMS, and webhook for numerous alerting channels
- Integrates well in the ManageEngine ecosystem with their other products
Cons:
- It is a feature-rich tool that will require a time investment to learn correctly.
This combination of automation and infrastructure management makes OpManager one of the best tools to detect and prevent packet loss. OpManager is available for both Windows and Linux and is available for a 30-day free trial.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine OpManager is our top pick for a packet loss solution because faulty switches are the main cause of dropped packets and this tool checks on network device statuses. The system scans the network and identifies all connected equipment, generating a hardware inventory. The package also draws up a network map. The system uses the Simple Network Management Protocol to request reports from device agents. If a device develops a component problem, its agent sends out a warning, called a Trap message. Opanager catches these special notifications and displays them as alerts in the dashboard. It can also send alerts to technicians by email or SMS. If a switch stops working properly, it can result in packets being forwarded out of sequence, at irregular intervals, or not being sent on at all. This system is a software package for Windows Server or Linux and you can choose to get it as a service on AWS or Azure.
Download: Get a 30-day free trial
Official Site: manageengine.com/network-monitoring/
OS: Windows Server, Linux, AWS, and Azure
2. Paessler Packet Loss Monitoring with PRTG – FREE TRIAL
Paessler PRTG Network Monitor is an incredibly flexible platform that uses tiny sensors to gather data on anything, including packet loss. While each sensor is customizable, many preconfigured sensors are tailored to specific SLAs, outcomes, or devices. For example, PRTG offers three sensors that are already tuned to monitor data relating to network performance.
Key Features:
- Network Discovery: PRTG's Network Discovery feature will automatically scan your network to detect all connected devices. It can monitor every device and network segment effectively without manual configuration.
- SNMP Processes: Collects data such as bandwidth usage, CPU load, and memory utilization, enabling you to detect issues and optimize network performance proactively.
- Status Alerts: These alerts can be configured based on predefined thresholds or custom conditions, ensuring timely response and mitigation of potential problems.
- SaaS Option: This option eliminates the need for on-premises servers and infrastructure, providing flexibility, scalability, and ease of management for organizations of all sizes.
Why do we recommend it?
Paessler is a great recommendation because the majority of its features mainly focus on packet loss. The tool has a high-quality alert system that instantly finds warnings and unusual activities over the network. You can also create a custom sensor to keep a check on various network paths to track packet loss.
The Ping sensor runs a simple ICMP check where the sensor is located. If a drop is discovered, this endpoint likely experienced traffic loss. The QoS sensor tests and reviews packet loss over each device in the networks. The QoS sensor can help sysadmins prioritize specific devices over the network. Lastly, the Cisco IP SLA sensor integrates directly with Cisco products and can help pull brand-specific data from those devices into your centralized dashboard.
The dashboard in PRTG balances informative and straightforward, without going overboard with too many visuals or overwhelming log feeds. The entire home screen can easily be customized to monitor packet loss and other network performance metrics through a simple widget-based system.
Each device can be tuned to alert based on specific thresholds, allowing you to create very custom alert scenarios and build SLAs that aren’t tied to an entire network or subnet. When problems arise, remediation can be completely automated or done in a few clicks. For example, if a single application stresses the network, you can block it or throttle it right away from the QoS dashboard.
Unlike some enterprise platforms, PRTG charges based on the number of sensors you have deployed. This helps both large and small networks use scalable monitoring that is both budget-friendly and predictable. Speaking of budgets, PRTG has a free version that supports up to 100 sensors, making it an excellent option for those who want to test it out themselves.
Who is it recommended for?
Paessler Packet Loss Monitoring with PRTG is recommended for network administrators and IT professionals seeking comprehensive network monitoring. Experts utilize this tool to monitor application performance, prevent network overloads by identifying traffic spikes, track traffic sources to specific endpoints, and mitigate device overloading efficiently.
Pros:
- A flexible platform that allows businesses to expand their monitoring capabilities easily
- Pricing is based on usage, making it a scalable platform for both small and large networks
- Can alert via several different mediums, ensuring the right teams are in the loop
- Can check to ensure site elements are all loading properly and can track metrics like Time to First Meaningful Paint (FMP)
- The same platform can be used to set up internal monitoring of networks, applications, and user activity
Cons:
- PRTG is a dense feature platform that may require time invested in utilizing all of its features fully
You can try the full version of Paessler PRTG through a 30-day free trial.
3. Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL
Site24x7 emerges as a comprehensive solution in addressing the challenge of packet loss, which is a critical issue in network management. It provides a robust set of tools designed to diagnose and resolve packet loss problems, ensuring smooth network performance. Site24x7's capabilities make it particularly useful for network administrators and IT professionals who are tasked with maintaining optimal network health.
Key Features
- Network Device Monitoring: Keep an eye on all the devices in your network, such as routers, switches, and servers, and make sure these devices are functioning correctly.
- Traffic Analysis: Analyze the traffic on your network to understand how it's being used and identify any potential bottlenecks or security threats.
- Early Warnings: By monitoring key performance indicators and alerting you to abnormalities or trends that could indicate trouble, Site24x7 helps you address issues before they turn into major problems.
Why do we recommend it?
We recommend Site24x7 for its effective monitoring and troubleshooting capabilities specifically tailored to address packet loss issues. Its real-time alerts and detailed network analysis tools make it an essential resource for maintaining a healthy and efficient network.
Who is it recommended for?
Site24x7 is ideal for network administrators, IT professionals, and businesses of all sizes that rely on stable and efficient network performance. It’s especially beneficial for organizations with complex network infrastructures that require in-depth monitoring and rapid resolution of connectivity issues.
Pros:
- Efficient detection and troubleshooting of packet loss issues
- Real-time monitoring and customizable alerts for network performance
- Detailed network analysis tools for comprehensive oversight
Cons:
- The extensive feature set and detailed analysis tools may be more than necessary for smaller networks or basic packet loss issues
Conclusion
No one likes packet loss or the problems it brings. But by using the simple steps listed above, anyone can identify packet loss as a problem and root out the cause in no time at all. For sysadmins, some of the tools listed above can be a lifesaver, especially when proactively preventing packet loss, and ultimately application outages.
What impact does a five-minute outage have on your organization? What about an hour? If you calculate network downtime into a dollar amount, you’ll quickly see that for many enterprise networks, these networking tools pay for themselves rather quickly. All the tools listed above have free trials, so pick one and give it a shot.
Have you struggled with packet loss on your network? If so, what caused it, and how did you fix it? Let us know your experience in the comments below.
How to Fix Packet Loss FAQs
How does packet loss affect network performance?
Packet loss can negatively impact network performance by reducing the speed and reliability of data transfers, leading to slow response times and increased downtime.
How can packet loss be detected?
Packet loss can be detected through network monitoring tools, such as network performance management software and network monitoring probes.
How can packet loss be prevented?
Packet loss can be prevented by implementing measures such as increasing bandwidth, upgrading network devices, improving network routing, and implementing Quality of Service (QoS) policies.
What are the consequences of high packet loss?
High packet loss can result in slow data transfer speeds, poor application performance, and increased downtime, leading to decreased productivity and customer satisfaction.
What is an acceptable level of packet loss?
An acceptable level of packet loss is typically considered to be less than 1%. However, the acceptable level may vary depending on the specific requirements and demands of a network.