We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Beginner’s Guide to ManageEngine Endpoint Central

UPDATED: April 26, 2023
ManageEngine Endpoint Central (formerly Desktop Central) is Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) that performs end-to-end remote management, security, and monitoring for endpoints. Endpoint Central lets you perform various management tasks to multiple endpoints (servers, laptops, mobiles, etc.) in a LAN, WAN, or cloud from a single central location.
In this beginner’s guide to Manage Engine Endpoint Central, we will go through the basics of Endpoint Central’s solution. You’ll learn how it works, its strengths and limitations, its integration with other tools, and, most importantly, how to start using it.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to ManageEngine Endpoint Central
- How does ManageEngine Endpoint Central work?
- Endpoint Central’s Strengths and Limitations
- Getting started with Endpoint Central
- How to install an agent on ManageEngine Endpoint Central?
- How to manage endpoints with Endpoint Central?
- Endpoint Central Integration with other tools
- Final Words
1. Introduction to ManageEngine Endpoint Central
a. What is Endpoint Central?
ManageEngine Endpoint Central is a web-based and mobile RMM software that lets you manage, monitor, and secure endpoints from a central console. It gives admins different controls to manage (internal or external) endpoints, including servers, workstations, desktops, laptops, mobiles, or tablets.
ManageEngine Endpoint Central provides practical management controls for system admins, including automated patch management, software deployment, service pack installation, inventory management, remote system control, real-time asset management, OS imaging and deployment, mobile device management, system tools, Active Directory reports, and much more.
b. Background
Endpoint Central was Desktop Central— a traditional remote desktop software with added management and control. Now, ManageEngine has rebranded and improved the technology behind it. Endpoint Central is now considered a next-generation desktop management system or UEM (Unified Endpoint Management) and is built with automation, scalability, alerting, reporting, and more.
c. Endpoint Central: Product details
- Who uses Endpoint Central This product is an excellent fit for systems and network admins managing hundreds to thousands of endpoints in large networks such as enterprises or Managed Service Providers (MSPs).
- Where can you use Endpoint Central You can use Endpoint Central on your premises or through its cloud-based version (via SaaS). If you prefer to deploy on-premises, you can install Endpoint Central through its .exe format on a Windows server. The agents can be installed in various clients, including Windows, Linux, macOS, mobiles (iOS, Windows, Android), and other devices.
- Editions and pricing ManageEngine offers four different editions of Endpoint Central at different prices; these include Free ($0.00), Professional ($795.00), Enterprise ($945.00), and UEM ($1095). The free edition allows up to 25 endpoints. The prices listed for the commercial editions are for an annual subscription, including support, additional features, and +50 endpoints.
- Free trial If you want to manage more than 25 endpoints for free, you can try ManageEngine’s Endpoint Central’s free trial for 30 days.
2. How does Endpoint Central work?
Endpoint Central is based on the client-server architecture, where many distributed clients (endpoints) can either request or receive a specific service from the centralized server (Endpoint Central). System admins can use the Endpoint Central solution in either a LAN (Local Area Network) or a WAN (Wide Area Network).
a. The Endpoint Central Server
The server is responsible for most of the endpoint management processes. It can start scans, connect to agents, check for inventory and patches in real-time, deploy configuration and software, generate reports, and more. Admins can access the Endpoint Central server through its web-based application and manage all those endpoints from a single location. The Endpoint Central server can be deployed on-premise or via the cloud.
- On-premises To run the Endpoint Central server on-premises, you’ll need to self-host (and self-manage) the application. You usually need high-end infrastructure to run the server and support many endpoints.
- The Cloud The Endpoint Central Cloud is the cloud-based UEM solution that uses the SaaS approach. ManageEngine provides the hosting infrastructure (along with its management) through Zoho’s Corp data centers, so you don’t need to worry about installing and maintaining backend infrastructure.
b. The Endpoint Central Agent
The Endpoint Central solution uses agents installed on the clients. This agent is a lightweight software running on the background of the endpoint. It receives instructions and tasks from the Endpoint Central server and executes them on the endpoint. It also reports the updates of the configurations and software deployments back to the server. There are various ways to install agents on endpoints: manually, automatically, through GPO, network shares, and more.
c. Database
A third vital component of the ManageEngine Endpoint Central is the patch database. This database hosts the latest patches to protect endpoints against vulnerabilities. The Endpoint Central server uses this database to synchronize and update patch information within its local repository. The server downloads these patches, updates its data, and scans the registered endpoints to determine the ones missing the patches. Any endpoint missing this patch will immediately download it from the local repository and install it.
d. Other Components
- Notification Services These services are used for mobile management. ManageEngine Cloud uses notification services such as APNs for iOS mobiles or FCM for Android devices to route communication from the Cloud server to the mobile devices.
- Distribution Servers These servers are used for managing branch offices in WAN deployments. Distribution servers communicate with the Endpoint Central Cloud server to get and forward tasks for the branch’s office agents.
3. Endpoint Central’s Strengths and Limitations
a. Strengths
As mentioned at the beginning of this guide, Endpoint Central is a UEM solution. It allows admins to centrally manage and secure a wide range of endpoints, whether internal, on LAN or WAN, or external, on the cloud. The strengths of Endpoint Central are:
- Endpoint management automation Endpoint Central is a fantastic automation solution for endpoint management. It allows admins to automate the entire patching process for multiple OSs, deploy software, automate OS imaging and its installation, and much more.
- Remote control and support Endpoint Central is an excellent product for endpoint remote management and control. Admins can use tools like file transferring, video calls, chatting, sending commands, geo-fencing, and much more. In addition, Endpoint Central can also integrate service management and ticketing software to transform into an all-in-one endpoint management and monitoring solution.
- Improve endpoint security Not only can Endpoint Central strengthen endpoint security when dealing with vulnerabilities by patching systematically and automatically, but it can also introduce other vital security tools to the table. It provides threat mitigation, browser security, BitLocker management, DLP, and an anti-Ransomware solution.
b. Limitations
Although Endpoint Central is a must-have solution for enterprises and MSPs dealing with hundreds to thousands of endpoints, it has a few limitations you should be aware of.
- Technical and customer support needs improvement Although ManageEngine provides various free documentation, videos, white papers, etc., included with their free support, paying customers often need more technical and account support than what's available. According to many admins with Classic and Premium support, ManageEngine should improve customer support in different areas, including technical, account, and crisis management.
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) could be improved Many admins often complain that Endpoint Central's GUI needs improvement. First, the UI can be challenging to use— the items in the menus are not so self-intuitive (if you are a beginner). And second, the UI does not offer many customization options to personalize it further.
- Employees' privacy is at risk due to micromanagement and control The level of management and control over endpoints is not a limitation but more of a risk to the privacy of endpoint users. A Central endpoint admin could easily monitor screens, record transactions, track software usage, control USBs (and other inputs), and even track devices geographically. Organizations leveraging Endpoint Central need to have solid privacy policies in place to avoid privacy issues.
4. Getting started with Endpoint Central
The easiest way to start with Endpoint Central is to register for the Endpoint Central Cloud’s 30-day free trial. You’ll only need a valid email and no credit card.
As mentioned in the beginning, Endpoint Central uses a web console client as the user interface for accessing the Endpoint Central server. So, if you are using Endpoint Central Cloud, you’ll be able to immediately access endpoint management and security tasks from your web browser. You’ll only need to configure and add the agents.
- If you are running the Endpoint Central Cloud, you’ll be able to access this web console from anywhere. Just enter the following URL in your web browser: https://endpointcentral.manageengine.com/webclient
- If you are already running the Endpoint Central Server, you’ll need to start by installing the agents, configuring desktop management, and creating reports.
a. How to install an agent on ManageEngine Endpoint Central?
First, you’ll need to install the agents for all the computers, servers, or mobiles— or any endpoint that will be managed and secured. You can install agents manually via workgroup, Active Directory (AD), or through remote office computer software.
- From your Endpoint Central console, you can go to “Agent,” located on the main menu, and then “Computers”. You’ll notice an alert saying that there are no agents installed.
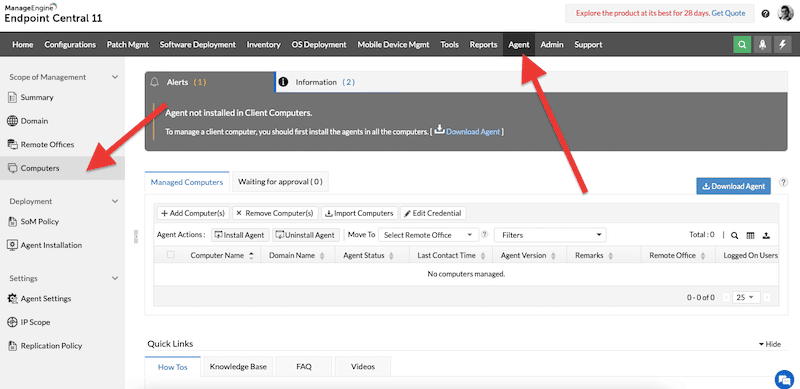
- Click on the “Download Agent” in the “Agent” window.
- You’ll see a new “Download Agent” window with a few options, including “Remote Office,” “Install,” and “Platform”. Leave the remote office by default, select an agent, and choose your client’s right operating system. In our case, we will download the agent for a Mac machine.
- Click on “Download Agent”
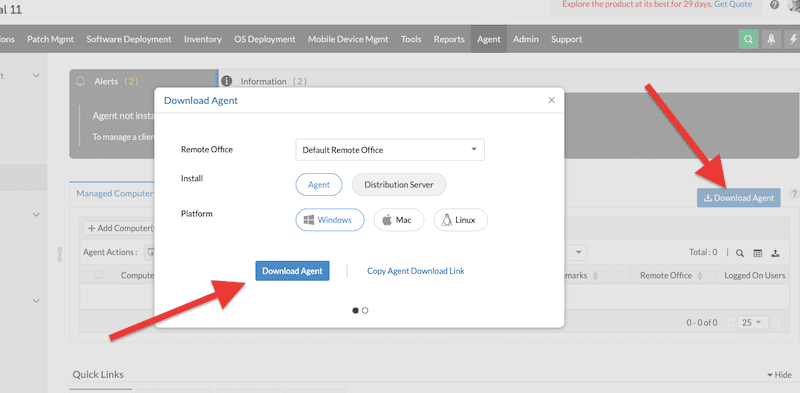
- Bear in mind that the package you download from the Endpoint Central web console will be ready to connect to this specific cloud-based server.
- When you download the agent, navigate to where you downloaded it and open it. The package contains the following files, as shown in the screenshot below.
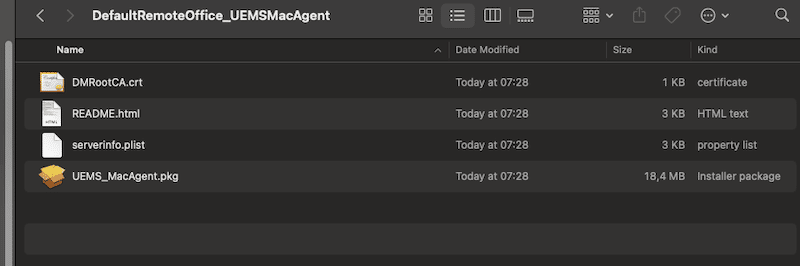
- Extract the .zip file and locate the UEMS_MacAgent.pkg (for Windows should be .exe). Double-click on the .pkg file to install the agent.
- Go ahead and install the agent on your client endpoint. Follow the installation workflow steps.
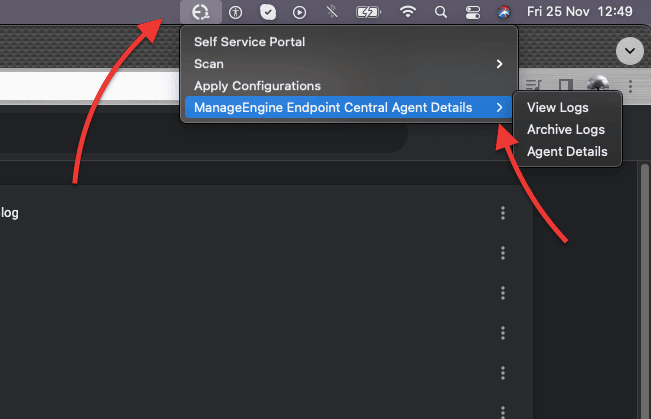
- On the client side, the Endpoint Central agent can be seen on the top bar (screenshot shown below). The end-user (if allowed to) can scan, apply configurations, or view logs.
- You could also install agents remotely within a LAN or WAN. To install agents on clients in the same LAN, simply scan the network, choose the computers, and start agent installation from the web console.
Approving the agent installation
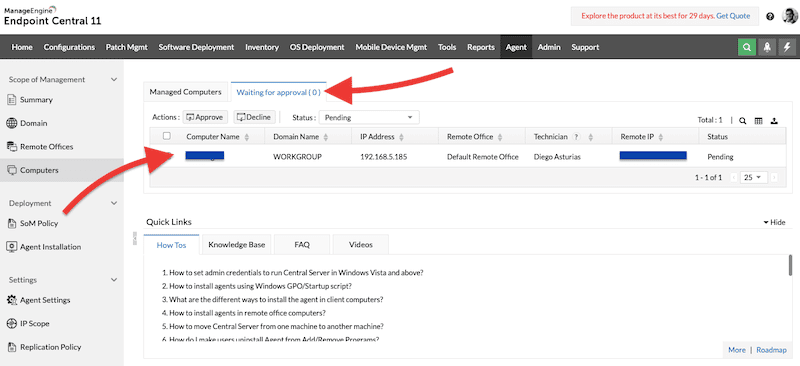
- Once your agent is installed successfully on the client, the computer (macOS, in our case) should be listed on the SoM (Scope of Management) page of the Endpoint Central server web console. It should now be visible on the Agent > Scope of Management > Computers menu. Although the agent communicates with the server, you’ll be unable to manage it from the server until you approve the installation.
- To approve this agent installed on our Mac (or for any other client), go to “Scope of Management” (or SoM) > “Computers” and look under the “Waiting for Approval” menu tab. Select whether to “approve” or “decline”.
- If you approve the new installation, the “managed endpoint item” should move to the “Manage Computers” tab. In addition, this endpoint will also start communicating with the agent (remote client), so the remote end-user will likely begin to see the agent is registered.
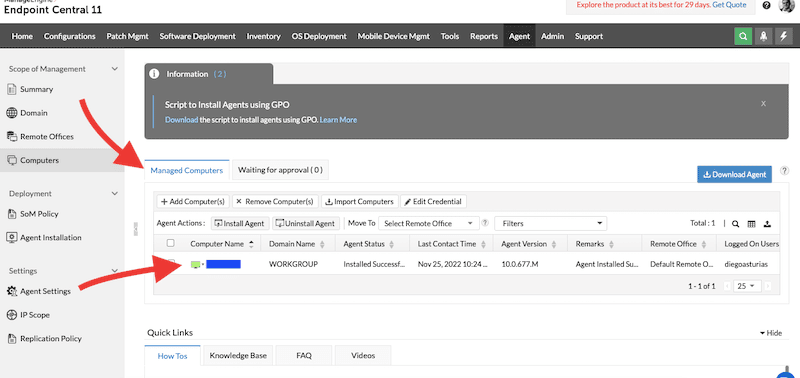
- Within this Computer list, you will see all the details for your new endpoint, including public IP, computer name, domain name, agent status, logged-on users, and more.
b. How to manage endpoints with Endpoint Central?
Now, we have one agent successfully installed, we have already approved the installation, and Endpoint Central has already registered it. You can do the same for other (Linux, Windows, or macOS) machines running in workgroups, AD, or remote offices.
Now, it is time to start managing the endpoints. As mentioned earlier, you can deploy software, install patches, push configurations (services, security policies, firewall, etc.), scan for vulnerabilities, or run tools such as remote control, defragmentation, and more.
As an example, we will deploy a simple configuration on our newly installed agent.
Deploying a configuration on an endpoint
- Selecting and defining the configuration. Go to “Configurations” > “All Configurations” “+ Create Configuration”. Go ahead and choose the right platform where you will deploy this new configuration.
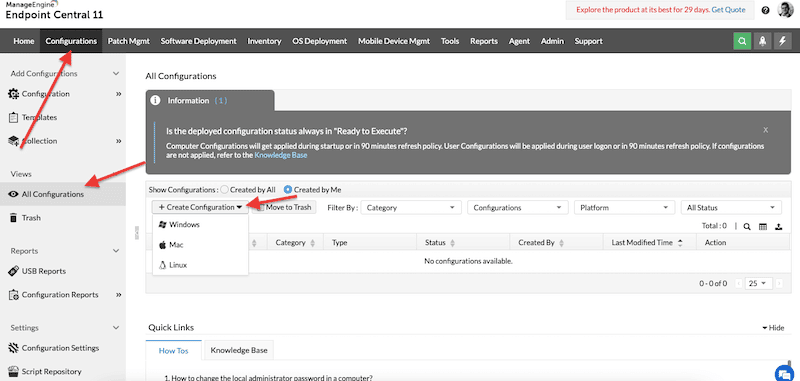
- As an example, we will create a new “message box”. Fill in your configuration as necessary.
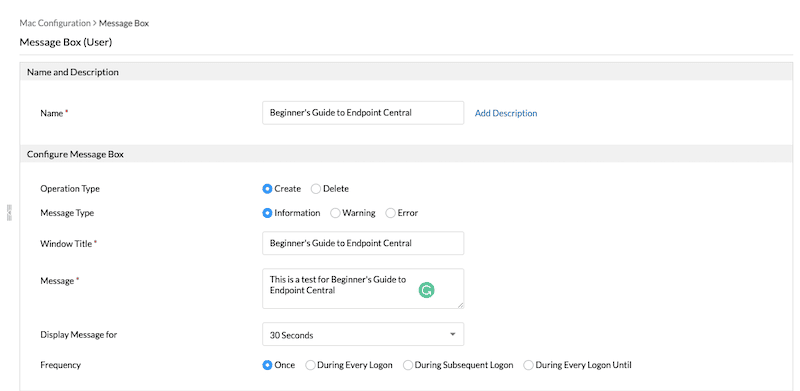
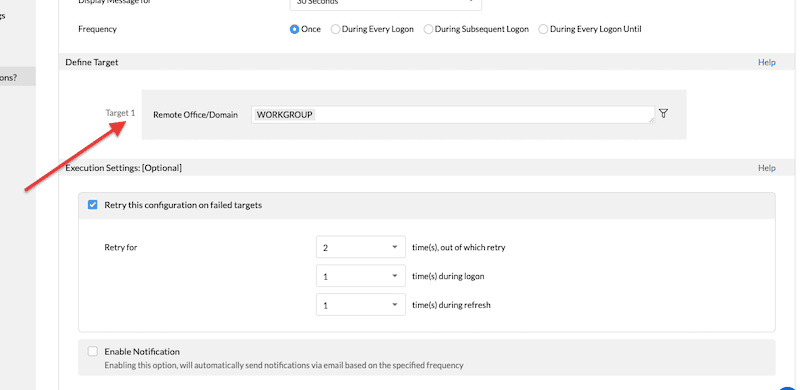
- Configuration deployment frequency: You have a couple of options here: to apply this configuration only once, during user logon, during subsequent logins, or during every login (with a condition). You can also deploy configuration during computer startup for other types of setups.
- Select the target computer (or user). If you scroll down, you’ll see a section that lets you define a target. Our recently added agent was deployed (by default) under the domain: WORKGROUP, but you may have also deployed on a Remote Office. Keep in mind that this specific configuration will target the entire domain.
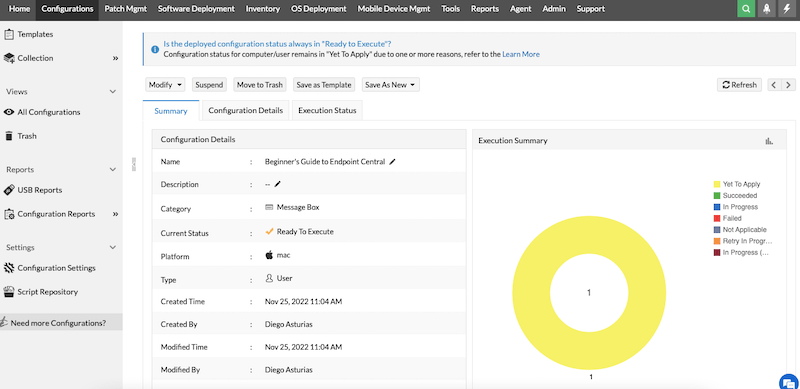
- Once your configuration is ready, you’ll be able to see a summary of this configuration.
- After some time (or as conditions are met), the configured message box will come across the managed endpoint. This is how it looks:
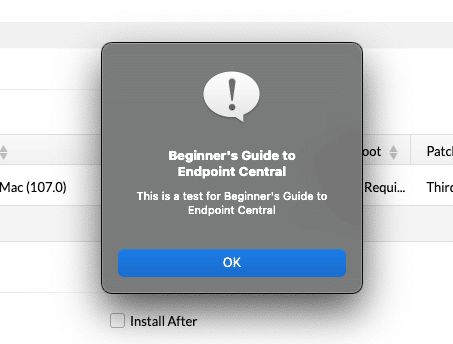
Let’s scan and deploy a patch on our newly configured endpoint
The process of managing patches with ManageEngine Endpoint Central is relatively straightforward. The Patch Management console on Endpoint Central allows you to do all patch management and also see a report of all installed and missing patches on your network, along with the recommendations.
The steps are simple: Start by installing the agent > scanning computers > viewing missing patches > > and installing patches manually or automating patch installation.
- To start this: go to “Patch Mgmt” on the main menu tab > “Systems” > and then “By Patches”.
- You should see all your endpoints (already scanned) along with their computer name, logged-on users, OS, domain, and most importantly: all missing patches.
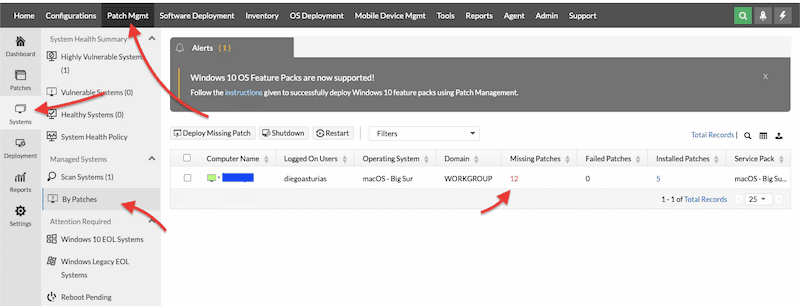
- You can click on the “missing patches” label to get a detailed view of all missing patches on this specific system.
- To get an overview of all patches (missing, installed, or stalled) in your network, including news about vulnerabilities, you can check the patches’ “Dashboard”.
- This dashboard will show graphs to get an idea of how to take action.
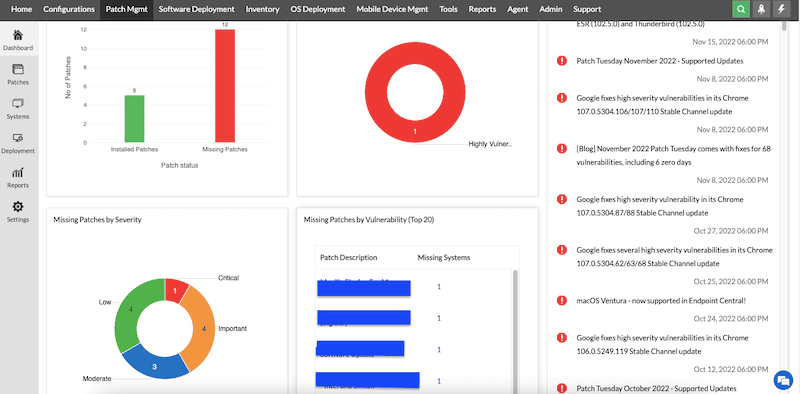
Let’s install a patch
Hey, we don’t want to be vulnerable to unpatched systems, so we will patch whatever is necessary. Fortunately, Endpoint Central found a few missing patches on our recently added client. We will remotely install this missing patch on our managed macOS computer.
- To install a patch, go to “Patch Mgmt” > “Patches” > “Missing Patches” > select the patch (or list of patches) that you want to install and > click on “Install Patch”.
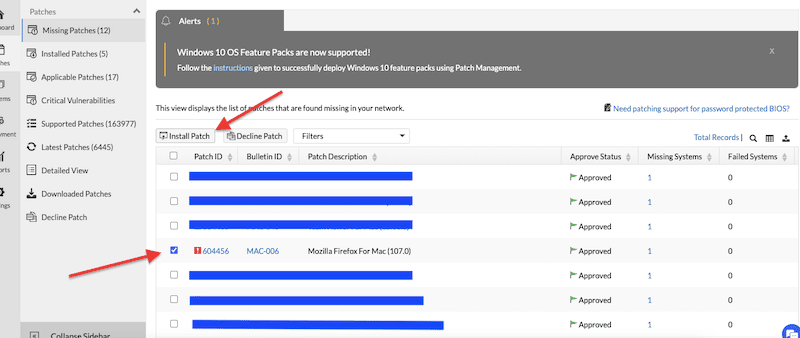
- Notice that you have various options when installing the missing patch. You can, for instance, manually install the patch, automate it, create a deployment policy, and other options.
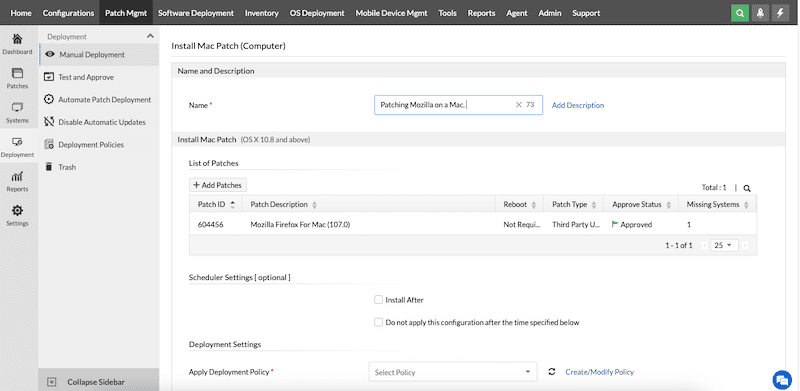
- Once you set up all patch deployment configurations, including schedule, deployment policy, target, and execution settings, you can go ahead and deploy.
- Once ready, you will be able to see a Deployment summary. As you might have noticed, we are deploying the patch immediately because we consider it critical to fix this vulnerability.
- You’ll also see some notifications in this summary that are pretty handy.
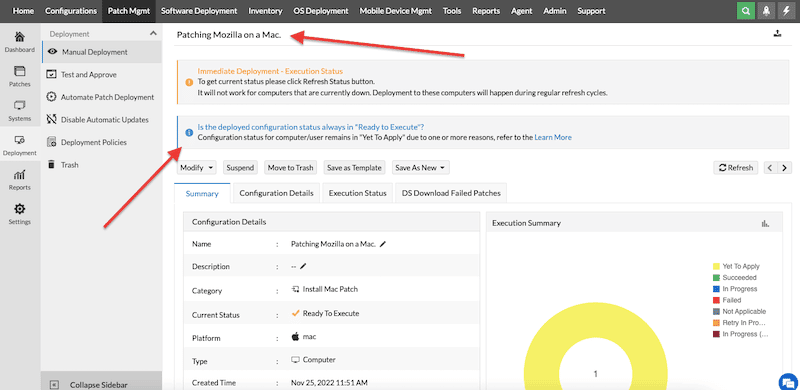
- If you see your patch is in a “Yet To Apply” state, that could be due to several reasons. To learn about this, check the configuration details or execution status. Find this option, next to the Summary tab.
- In our case, this specific patch won’t be installed because its deployment policy (Download immediately and deploy during the deployment window) states that its deployment window is from 00:00 to 23:59.
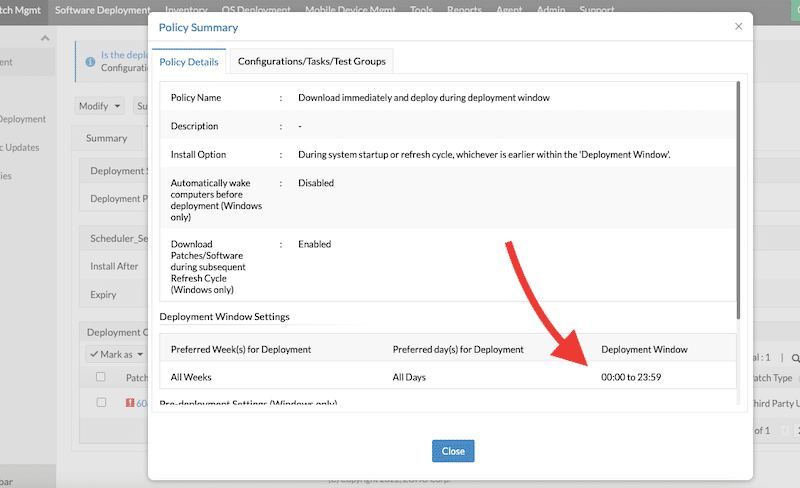
- If you want to deploy a patch immediately, you can change the deployment policy or create a new one and assign it to the task.
5. Endpoint Central Integration with other tools
You can integrate Endpoint Central with third-party or ManageEngine tools to improve its IT management, monitoring, and security capabilities. Endpoint Central allows you to integrate with popular IT service management, helpdesk, IT asset management, Business Intelligence (BI) tools, Enterprise Protection Platforms, and other tools.
Popular IT service management tools that can integrate into Endpoint Central include:
- Jira Service Management A tool to receive, track, manage, and resolve end-user requests. Integrate Endpoint Central to help and solve issues via Jira’s service management.
- ServiceNow A cloud-based (SaaS) IT services management tool used for technical management support. Integration with Endpoint Central can help you centralize ITIL processes. Empower ServiceNow technicians to perform endpoint management and resolve issues faster.
- Spiceworks A 100% free and comprehensive helpdesk solution that provides ticketing, monitoring, capacity planning, and more. Integrating Spiceworks with Endpoint Central allows you to manage all incidents from a single place.
- Freshservice ITIL-aligned ITSM service desk software with robust automation capabilities for managing incidents, assets, and more. Integrating Freshdesk with Endpoint Central will strengthen your help desk platform.
- Tenable A cloud-based vulnerability management solution that provides end-to-end visibility into the assets and vulnerabilities of a network. Integrating Tenable with Endpoint Central allows Tenable to detect vulnerabilities and Endpoint Central to push the patches to where they are needed.
- Zendesk A cloud-based help desk solution that offers various tools such as a customer service portal, knowledge base, live chat, and more. The integration between Zendesk and Endpoint Central gives Zendesk technical support a solid endpoint management and security solution from a central location.

Aside from integrating with the popular third-party IT service management tools, Endpoint Central seamlessly integrates with other ManageEngine tools; these include ManageEngine’s Service Desk solution (Plus Cloud to resolve tickets from the cloud) and Analytics Plus (for Business Intelligence and advanced insights).
6. Final Words
Endpoint Central benefits the system admin managing endpoints in large enterprises or MSP networks. They can automate the entire endpoint management life cycle, achieve operational efficiency, enhance productivity, and improve security by protecting from vulnerabilities.
Starting with Endpoint Central is easy. Although you can choose between on-premises and cloud, starting with the cloud-based SaaS version is much easier. You’ll get a fully hosted Endpoint Central server so that you can focus on more critical tasks. And fortunately, you can also start right now with their 30-day free trial.