We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Beginner’s Guide to ManageEngine OpManager
UPDATED: June 1, 2023
ManageEngine OpManager is a robust network monitoring and management software that provides network admins with an all-in-one interface console to keep track of their networks, including hardware/virtual resources like routers, servers, firewalls, switches, and even printers.
In this Beginner’s Guide to ManageEngine OpManager, we will introduce you to the software, its key features, and the essential details you need to get started. We will download, install, open it, and perform basic configurations on OpManager. Although this beginner’s guide is just the tip of the iceberg of what this tool can do, it does provide you with a comprehensive understanding, helping you decide if it’s the right fit for your organization's needs.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to ManageEngine OpManager
- Features
- What is not OpManager?
- ManageEngine OpManager Software Details
- Getting started with ManageEngine OpManager
- OpManager minimal system requirements
- Download and installation process
- Opening OpManager
- Configuring OpManager
- ManageEngine OpManager Integrations
- ManageEngine OpManager: Strengths and Limitations
- Final Words
1. Introduction to ManageEngine OpManager
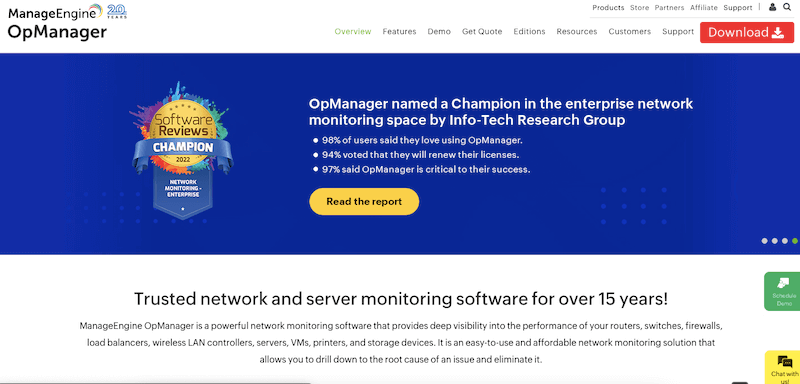
ManageEngine OpManager is a network and server performance monitoring software that's been one of the market leaders for over 15 years. It offers extensive insight into the performance and health of your networks, including services and devices such as routers, switches, firewalls, load balancers, wireless LAN controllers, servers, virtual machines, printers, and storage devices. Furthermore, OpManager can also monitor cloud-based resources deployed in AWS and Azure.
The software provides world-class real-time alerts, dashboards, and reporting capabilities. Its fault management system allows the correlation of raw network events, filtering unwanted events and presenting meaningful alarms to operators classified by severity levels. In addition, OpManager also comes with robust (and highly customizable) reporting and dashboards. One of the highlights is that OpManager provides network visualization through Layer2 Maps, virtual topology maps, Business Views, and 3D floor and rack views.
a. ManageEngine OpManager features
- Network monitoring basics Real-time monitoring of CPU/memory, device health, availability, errors/discards, traffic, and performance of any IP-based device on the network.
- Distributed network monitoring ManageEngine can also monitor distributed networks with centralized monitoring of networks across multiple locations with probe-specific controls.
- Physical and virtual server monitoring Monitoring of physical and virtual servers, including a wide range of multi-vendor servers like Hyper-V, VMware, Citrix, Xen, and Nutanix HCI servers, to ensure they are running at optimal performance levels.
- Wireless monitoring In-depth monitoring of wireless networks, including access points, wireless routers, switches, and Wi-Fi systems, including Wi-Fi strength and traffic.
- WAN monitoring Visualizing and tracking WAN links using Cisco IPSLA technology to troubleshoot outages and performance issues.
- Monitor Cisco ACIs Complete monitoring of Cisco ACI infrastructure, including controllers, fabric, tenants, and endpoint groups.
- Advanced storage monitoring Monitoring of storage devices such as Fiber channel switches, storage arrays, and tape libraries.
ManageEngine OpManager has received several awards and recognitions. Some of its more significant ones include Gartner's Peer Insights Customer's Choice for Network Performance Monitoring and Diagnostics Software (May 2019) and Customer Choice for IT Infrastructure Monitoring Tools, also by Gartner Peer Insights. In addition, OpManager was awarded Champion for the Network Monitoring Enterprise by Software Reviews in 2022.
b. What ManageEngine OpManager is not
ManageEngine OpManager is not intended to monitor applications. It is rather designed to monitor application's supporting infrastructure, i.e., servers and networks. In addition, OpManager does not deal with security monitoring or IT operations management. OpManager can integrate with a robust ManageEngine’s IT Operations Management (ITOM) solution called OpManager Plus (for unified server, network, and application management) via a plug-in. For network cybersecurity and management, refer to other ManageEngine products.
2. ManageEngine OpManager Software Details
This section will go through a few basic details you need to know to start using the software. Who can use it? What are its installation options? And other information like integrations, customer support, editions, and pricing.
- Who can use ManageEngine OpManager? System and network administrators working in organizations of different sizes and industries can use OpManager to ensure their network's availability, health, and performance. It can also be used by IT service providers, MSPs, and Cloud Service Providers to monitor their customers' infrastructure.
- Installation options ManageEngine OpManager is only available as an on-premise solution for Windows, Linux, AWS, and Microsoft Azure. You can install OpManager in your servers (whether deployed on-premises, as virtual, or via the cloud) and access it through a web browser. In addition, OpManager also offers iOS and Android apps to monitor networks on the go.
- Integrations and add-ons You can extend the functionality and capabilities of OpManager by integrating it with other ManageEngine (ME) software and third-party tools. You can, for instance, integrate OpManager with other ME software like ServiceDesk Plus, AlarmsOne, and Analytics Plus. You can also integrate OpManager into apps like ServiceNow, ServiceDesk, Slack, or more via Webhook or their REST API.
- Customer support ManageEngine OpManager provides various options for customer support. Their free online support includes sources like a knowledge base, user guides, an online community, and FAQs. Additional customer help (Classic and Premium) provides phone support, email support, webinars, remote support, and professional services. The level of customer support varies according to the type of license or subscription.
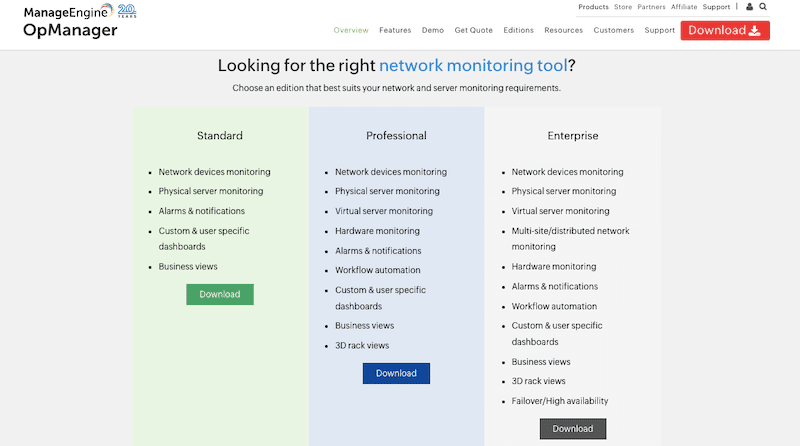
- OpManager pricing and editions ManageEngine OpManager is available in four different editions, each with its own features and pricing options. The editions (along with starting prices) include Free Edition ($0 for three devices and two users), Standard/Professional Edition ($245 for ten devices – suitable for SMBs), Professional Edition ($345 for ten devices – suitable for SMBs), and Enterprise Edition ($11,545 for 250 devices – designed for large organizations).
- Free trial ManageEngine offers a 30-day free trial for Standard/Professional and Enterprise editions. The free trial comes with all features. You must buy a license if you want to extend the evaluation period. You can also get the 100% free ManageEngine OpManager by downloading the free edition.
3. Getting started with ManageEngine OpManager
ManageEngine OpManager’s software needs to be self-deployed and self-managed. It must be installed on your hardware or a cloud-based platform that you control. The software is supported by Windows and Linux and is ready to be downloaded from the official ManageEngine site.
The OpManager software is also available on popular public cloud marketplaces, including AWS Marketplace and Windows Azure Marketplace. You can buy OpManager AMI from the AWS store or install it in your AWS EC2 instance. If you are running OpManager in the Azure cloud, you can get an image from the Azure marketplace or run the software from Azure’s cloud-based VMs.
Note: ManageEngine does not offer a fully-managed service or hosted software (SaaS-based version) of the OpManager solution.
a. OpManager minimal system requirements
Requirements will vary according to the software edition being deployed, evaluation or production, the license type (no. of devices and allowed users), and whether you are running OpManager with add-ons.
- Hardware requirements For the minimum 1-250 (devices), you would need an Intel Xeon 2.0 GHz 4 cores processor, 4GBs memory, and at least a 20 GB hard disk.
- Software requirements For production, you’ll need Windows Server (2022/ 2019/ 2016/ 2012 R2/ 2012/ 2008 R2) or Linux (Red Hat 7 and above / CentOS Stream 8/ CentOS 7 and above, up to 8.5). For the web-based console, use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or IE11.
- Port requirements The OpManager software uses ports 22 (SSH), 8060 (webserver), 7275 (RDP), and 9990-9999 (for PDF reporting exports). In addition, OpManager also uses ports for device discovery, data collection, and monitoring: 7 (ICMP), 23 (Telnet), 161 (SNMP), 135, 5000-6000, 49152-65535 (WMI), 162 (SNMP Trap), and 514 (SYSLOG). Ensure these ports are available to service ManageEngine OpManager.
- Database requirements OpManager is bundled with PostgreSQL, which you may use as a failover or as the primary database. Microsoft SQL is recommended. Supports (SQL 2019 (from build 125379), SQL 2017, SQL 2016, SQL 2014, SQL 2012, or SQL 2008).
Note: OpManager gets resource-intensive (as its monitoring scope grows), so you’ll have to consider the aforementioned system requirements.
b. Download and installation process
For demonstration purposes, we will install OpManager’s free edition on Windows 2022 (an individual EC2 instance running on the AWS cloud).
- Choose your download option from ManageEngine OpManager’s official download site.
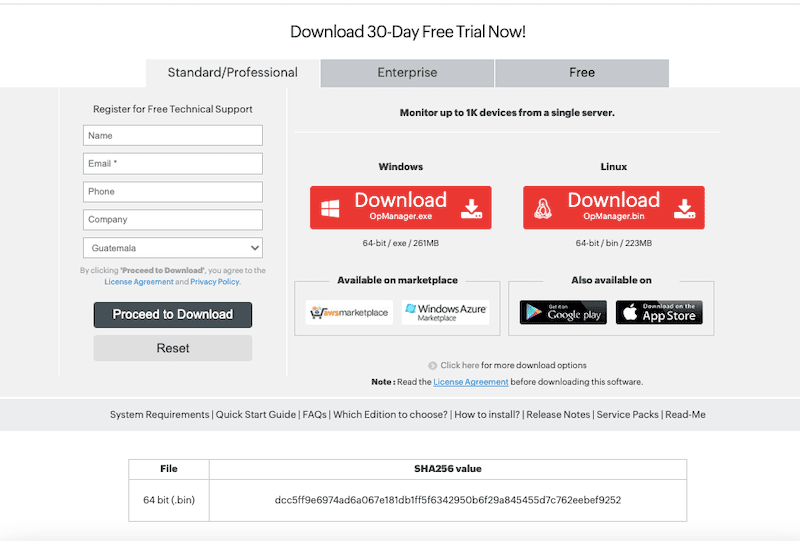
- Make sure you have admin rights and that you trust and authorize the application to download and install. The Free version (Windows 64-bit) is an .exe package of about 260 MBs.
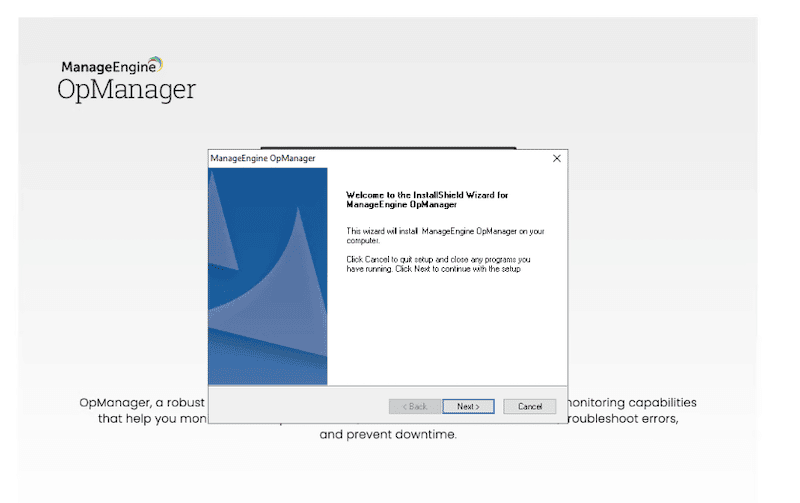
- The installation is a quite straightforward process. After looking at the installation wizard welcome page, click on “Next” and accept the license terms agreement.
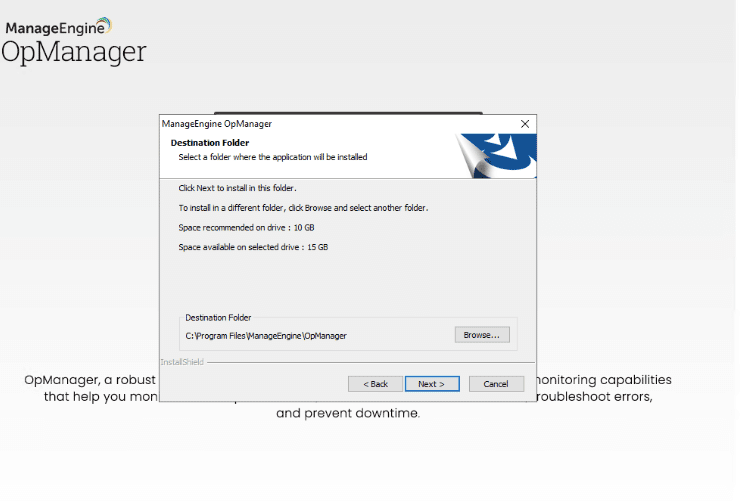
- Choose the destination folder. The ManageEngine OpManager installation wizard will suggest a recommended installation space. It will tell you if you have enough storage.
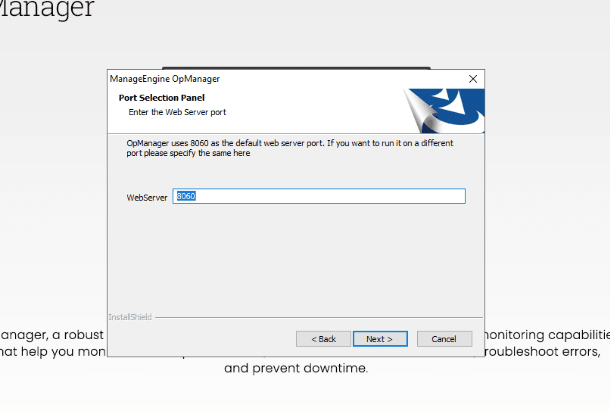
- The following window, “Port Selection Panel” will require you to enter the Web Server port, which, as suggested in the previous section, should be 8060 (default value).
- The following window will ask whether you would like to register with customer technical support. You may register or skip this section.
- If you choose to register, either select Classic or Premium technical support. If you are installing a free trial (or free edition), the support will only be available for the trial period. The Free support is free for everybody, Classic support is free with the subscription, and the Premium is a paid service.
- The ManageEngine OpManager installation wizard will be setting permissions, extracting files, unpacking jar files, and initializing the database.
- As mentioned in the previous section, the OpManager software is bundled with PostgreSQL — for the backend database. You can either continue with this default or select MSSQL for the installation.
- It is recommended to use the MSSQL database backend for production. This database provides higher failover and availability. If you have an MSSQL instance, you must ensure the communication between OpManager and MSSQL database server. Get the MSSQL credentials and IP address.
- Once you are through with the backend database configuration, the installation will restart services.
- You can close the installation, view the readme file, and start OpManager immediately. Click on “Finish.”
c. Opening OpManager
You can start the ManageEngine OpManager server in different ways.
- If you have installed OpManager as a Windows service, you’ll be asked to start the service immediately after the successful installation. You can check the OpManager service by going to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Services. Within the details page > right-click on ManageEngine OpManager > Click on Start.
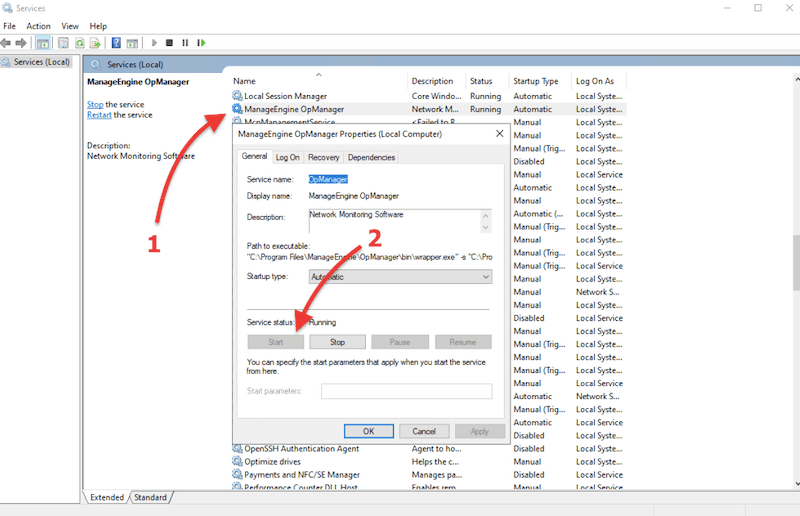
- Additionally, if you have installed OpManager on Windows, you’ll be able to find it on the Start Menu > Programs > ManageEngine OpManager.
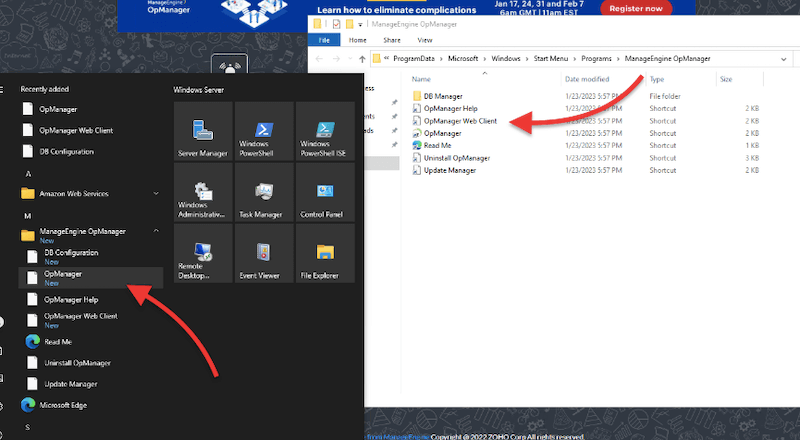
- The ManageEngine OpManager web client opens with the web browser. As suggested earlier, use an updated version of Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or IE11.
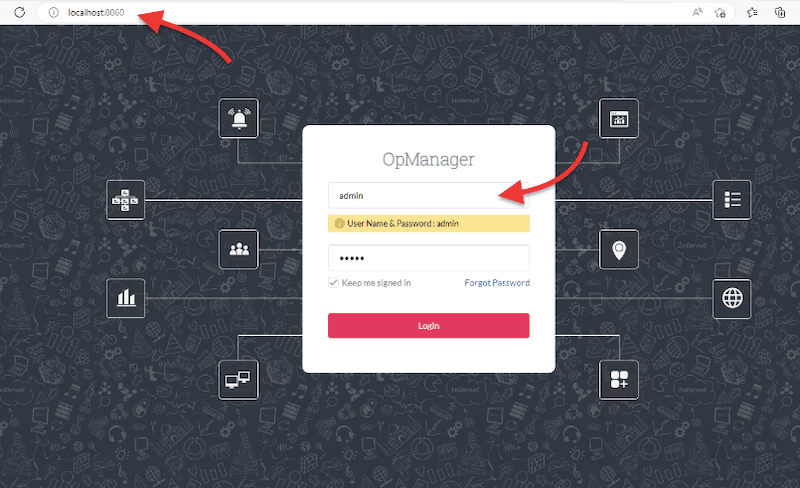
- Although OpManager opens automatically after double-clicking on the OpManager icon, you can also go to the web browser (including for other computers running on the same network) and type: https://IP_ADRESS:8060. Or, if you are logging in from the same machine (OpManager server and web browser), enter https://localhost:8060 or https:127.0.01:8060.
- Credentials. The first time you log in, the OpManager console will give you the default credentials, which are username: admin and password: admin. As soon as you log in, you’ll be able to change them.
d. Configuring OpManager
For demonstration purposes, we will perform a few vital basic configuration steps to start using OpManager. But, the complete configuration of ManageEngine OpManager is outside the scope of this Beginner’s Guide.
- Change the default password or add a new admin user
- For security reasons, you might want to change the default admin password. To do this, go to Settings > General Settings > User Management.
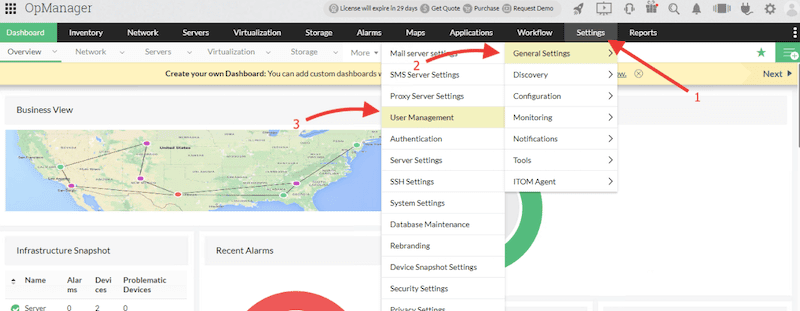
-
- User Management> Click on the user that you want to change the password (i.e., admin).
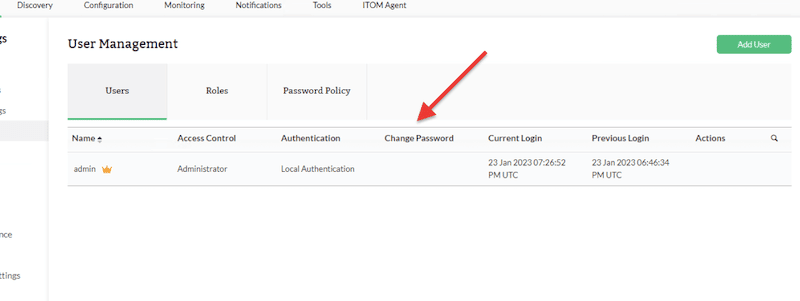
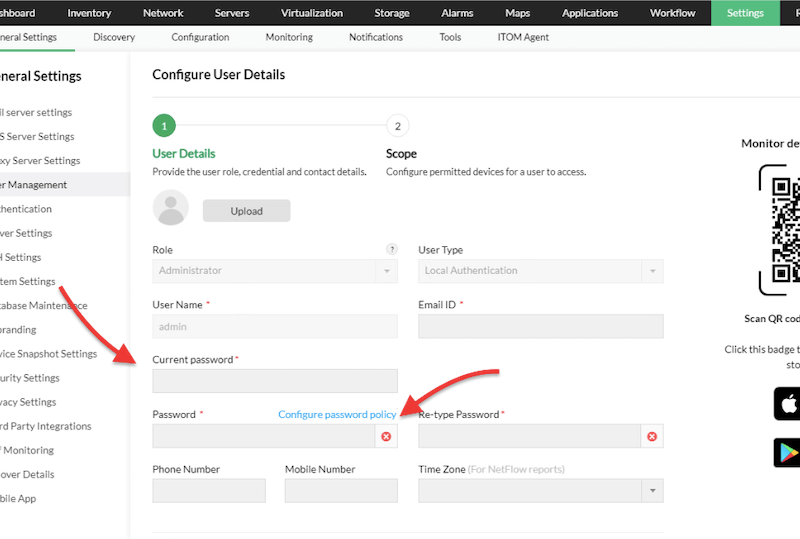
- Either change the current admin’s user password or disable the current default admin and create a new user.
- Registering OpManager. If you have bought an OpManager license but didn't register during the installation process, you can register it from the web client console. Ensure that you have the license file provided by ManageEngine.
-
- Go to your profile icon.
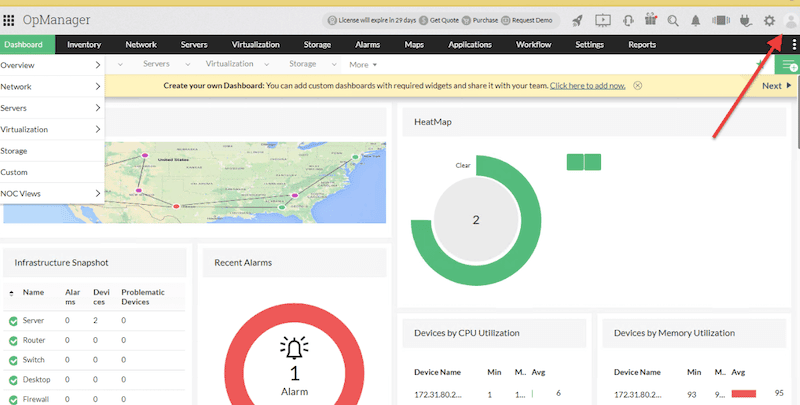
-
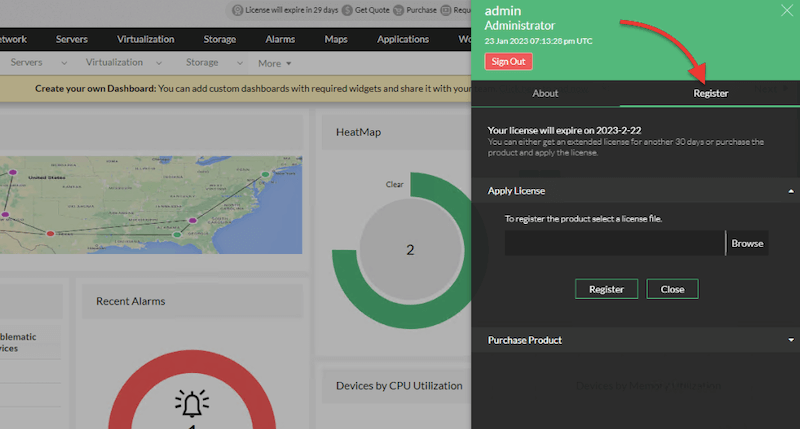
- Click on Register > Browse (find your file) > Register (to apply for the license).
- Changing general settings. One of the basic configurations when starting with OpManager is to update the system’s general settings, such as date and time format, client settings, logging, and mapping.
- To change these settings, go to Settings > General Setting > System Settings.
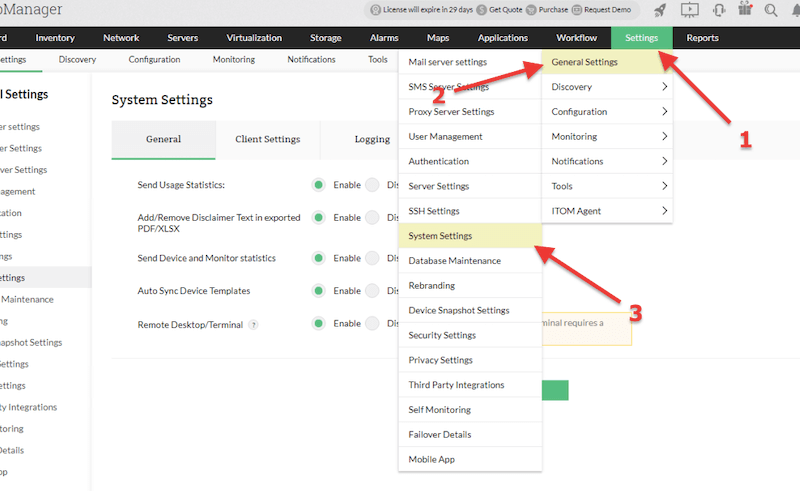
- Updating ports. If you want to change the OpManager’s UI port number, follow the next steps:
- Go to Settings > General settings > Server settings.
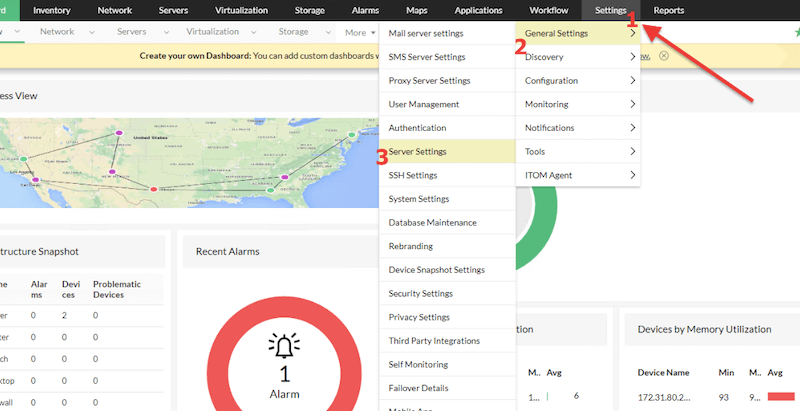
-
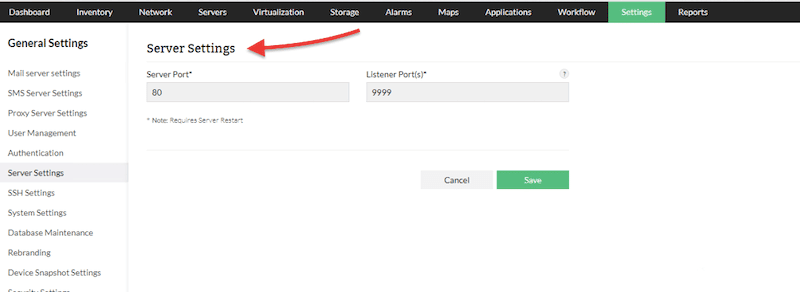
- Server Settings > Change the Server port and click Save
- Essential advanced software configurations. ManageEngine suggests five simple steps to get started with OpManager. These settings will help you get started with OpManager’s monitoring and management capabilities in no time.
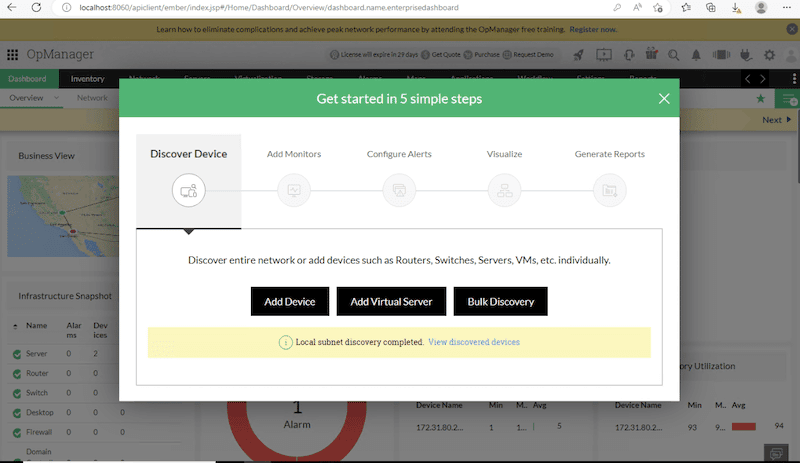
- Discover Devices. There are various ways to discover devices with OpManager; these include automatic discovery (SNMP, WMI, and ICMP), import from file, IP address range, or manually adding devices.
- Add Monitors. When a device is discovered, a set of default monitors will be automatically linked to these devices based on type. Monitors collect vital data from each device to calculate performance. To add a monitor, go to Inventory > Device > Monitors > Add Monitor.
- Configure alters. OpManager raises alarms to notify admins and managers of any network performance issue or abnormality. Whenever a device fails, an alarm is instantly generated. To access these alarms, go to the Alarms tab (on the upper menu bar) > List all alarms.
- Visualize. Once devices are discovered, they are organized and listed in the Inventory view. This view provides detailed information on the network devices, including DNS name, IP address, category, type, health status, and any custom field values. OpManager also offers more details to expand visualization with dashboards, maps, business views, and groups.
- Generate Reports. ManageEngine OpManager provides a variety of reports that allow you to monitor and analyze the performance and status of your network. To generate a report in OpManager > Go to the “Reports” tab > Select the report type. You can create Device Reports, Network Reports, Inventory Reports, and more here.
e. ManageEngine OpManager Integrations
ManageEngine OpManager’s integrations are designed to extend the software’s current capabilities and provide additional functionality. OpManager also comes with built-in settings on the console to integrate with other ManageEngine tools and third-party tools. Some other ways you can integrate ManageEngine OpManager with other tools include SNMP Traps, scripts, web services, agentless monitoring, email integrations, webhook, and OpManager’s REST APIs
- The proper steps to integrate OpManager will depend on the tools you are trying to integrate.
- To integrate ManageEngine OpManager with other tools, you must configure the appropriate settings in both the OpManager web console and the other tool.
- You can find pre-built integration configurations under, Settings > General Settings > Third-Party Integrations.
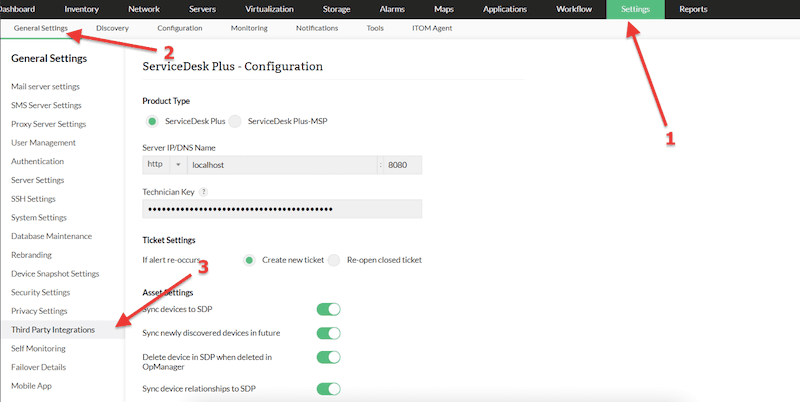
- For an example integration of OpManager with ServiceDesk Plus, we’ll only need to input certain details like IP/DNS name, technician key, ticket settings, and asset settings.
4. ManageEngine OpManager: Strengths and Limitations
This section will go through a few popular strengths and limitations of ManageEngine OpManager. Keep in mind that the following strengths (and limitations) may not benefit (or affect) every business in the same way. Always consider your network’s needs first and weigh the pros and cons before purchasing an OpManager license.
Some of its strengths include the following:
- Robust monitoring ManageEngine OpManager can monitor a wide range of network services, devices (hardware or virtual), and components, including servers, traffic, WAN connections, wireless, Cisco Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI)s, storage devices, cloud-based resources, and more.
- Fantastic notification system OpManager comes with a robust notification system that allows seamless and efficient communication of any issues that may occur within the network. This system can send alerts and notifications when certain conditions are met (i.e., a threshold), allowing you to respond to potential issues quickly.
- Easy to deploy and use ManageEngine OpManager can be quickly and easily deployed on a network (as you learned in the previous section). In addition, OpManager’s web-based interface was designed to be easy to use and navigate, making it accessible for users of all skill levels.
- Seamless integrations ManageEngine OpManager can be integrated with some essential third-party IT tools, including Service Desk, ServiceNow, and Slack, and seamless integration to other ManageEngine tools. Bear in mind that many other third-party tools or devices are not fully supported and require additional configuration to integrate with OpManager.
Some of its limitations include the following:
Although OpManager is one of the preferred network monitoring and management tools in the market, it may not be the best fit for everybody. It does come with a few limitations, including:
- Lack of customization in reports and dashboards ManageEngine could improve the reporting and dashboard features of OpManager for better performance. Although OpManager provides some capabilities to customize reports and dashboards, many users complain that they are only partially customizable. Also, it takes work to filter the information needed for specific cases.
- Resource-hungry One of the limitations of ManageEngine OpManager is that it can be resource-intensive, which could become an issue on low-end hardware or virtualized environments. As your network monitoring environment grows, you may require an increase of resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, to run effectively.
- Cost is only suitable for some types of organizations Another limitation of ManageEngine OpManager is that it can be expensive for small and medium-sized businesses or organizations with limited budgets. The cost of OpManager is based on the number of devices being monitored, which could get relatively high for unprepared small and medium-sized businesses. Additionally, the licensing and support pricing may not be affordable for such organizations.
5. Final Words
Throughout this guide, we have covered the fundamental concepts of OpManager and guided you through the process of setting up and configuring the software. We have also discussed the available integrations for OpManager and some strengths and limitations.
It is essential to remember that although ManageEngine OpManager is quite a popular monitoring software, it is not the only solution out there. So always evaluate software first against your specific needs. Fortunately, ManageEngine offers a fully-featured 30-day free trial. Download it, test it, and compare it to other options.