We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Network Automation Tools – Here’s the Best Free & Paid Ones

UPDATED: July 9, 2024
“You’re either the one that creates the automation, or you’re getting automated,” said Tom Preston-Werner, the co-founder of GitHub.
Embracing automation is no longer an option; it is becoming almost a requirement in virtually any IT field.
There are hundreds of daily monotonous tasks that can be automated, from deployments, management, orchestration, securing, to monitoring. Still, many network engineers are indifferent to the impact that automation is having on the evolution of the networks (and their careers).
It is even evident in the popular network certifications that are being re-direct towards automation and Software-Defined Networks SDN. Automation is still green, but when it begins to mature, network admins and engineers will not even need to log into any router or firewall equipment.
Here is our list of the top network automation tools:
- ManageEngine Endpoint Central – EDITOR'S CHOICE Bridges the gap between endpoint management and security by offering asset discovery, patching, remote control in a single platform. Start a 30-day free trial.
- ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager – FREE TRIAL A security and management system that corrects configuration problems on network devices, backs them up, prevents tampering, and facilitates onboarding. Available for Windows Server and Linux. Download a 30-day free trial.
- Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL Offers a comprehensive and efficient solution for automated network monitoring and management. It excels in providing advanced monitoring for various network devices, AI-driven performance analysis, and customizable alert systems. This makes it highly valuable for organizations aiming to enhance network reliability and performance through automation, especially in complex network environments. Start a 30-day free trial.
- Ansible (Tower) An automation platform from the producers of RHEL. Available for Linux, macOS, Unix, and Windows.
- Netmiko A free library of network utilities that offers functions to integrate into Python programs.
- NAPALM A Python library for network device contacts. This is fully known as Network Automation and Programmability Abstraction Layer with Multivendor Support.
- Truesight Network Automation An AIOps suite that manages underlying networks and services whether on-premises, in the cloud, or both. Runs on Windows.
- VMware NSX – Network Automation Virtualizes a network to make services easier to adjust through software.
- Apstra OS This is a virtual overlay that standardizes the management of network hardware through a single interface. Runs on top of a hypervisor.
- NetBrain Automation An adaptive network automation platform that creates an operating system for your network. Requires one Linux server and one Windows Server host.
- AppViewX Automation + AppViewX is a low-code automation platform designed for NetOps and SecOps.
Of course, automation will not replace human intelligence (our jobs).
With the proper automation tool, we will be able to do thousands of tasks per day, something that probably took months before.
Automation will give us more time to think about network architecture, design, and plan for its capacity.

Network Automation: A Challenge and Opportunity
Today, network operation teams still perform hundreds of manual tasks every day.
Although they know about the benefits of automation, most of them don’t know how to start.
Embracing automating in the network is not so easy; it brings new challenges:
- Network engineers need to learn some coding/scripting
- There are still no new automation standards or regulations
- Traditional networking vendors have disparate configuration commands
- There is a lack of APIs and documentation
- The network has multiple points of configuration
Although 99% of network engineers are foreigners to software development and programming languages, they will inevitably start to see their importance, especially around tools like Python, Chef, and Ansible.
Automating the network also deviates from some regulatory standards and compliance.
Existing networking designs are not automation-friendly.
Any new automated configuration can fail existing regulatory compliance.
Without standards, all networking vendors can have different configuration commands, which makes it even more difficult.
Automation is a disruptive technology.
A software bug caused a major outage in Google in June 2019, which happened due to a runaway automation process.
Google, of course, is the king of disruptive innovation.
Google knows that there will always be bugs in any new technology.
And, still, humans are far more prone to error than automated machines, when putting the config into devices.
So why use Network Automation Tools
Automation is the process of removing the human factor from the equation of workflows or processes.
For the network, labor-intensive tasks can be automated— such as configuration, monitoring, backups, security, etc.
Using the right automation tool can save companies lots of money in the process.
A significant number of network operations can also be automated.
In fact there is a new term for NetOps (or NetOps 2.0), which refers to the new approach of networking that uses the same tools and techniques used by DevOps.
With advanced automation, network engineers will likely need to be working closely with software developers to create new networking solutions.
Some examples of how NetOps can benefit from automation tools:
- Configure equipment automatically – Workstations, distribution, access, and core equipment can be configured without human interaction.
- Test the state of the network – Automated validation and testing tasks can be deployed on the network. Testing connections, new protocols, stress tests, the software can all be performed by AI.
- Compliance checks – Automation software can perform daily checks on network configurations to fulfill a set of compliance and regulation standards.
- Other routine tasks – Network automation tools can also schedule automatic network config backups and scans.
Related Post: Best Router Monitoring Software
What should you look for in network automation tools?
We reviewed the market for free and paid network automation software and analyzed the options based on the following criteria:
- A package of tools that can take care of mundane tasks without human intervention
- Systems that perform repetitive tasks
- A method for automating administration tasks
- A service that logs all actions so that events can be reviewed after unattended processes have completed
- Systems that can be scheduled to run regularly out of office hours
- A free trial, a money-back guarantee, or a demo system that provides opportunities for risk-free assessments
- A package of services that pays for itself through improved productivity
With these selection criteria in mind, we have established a good list of tools that offer a range of network task automation solutions. We have made sure to include software for Windows and Linux and also cloud services.
The Best Network Automation Tools & Software
Below are ten of the best network automation tools, some are free, and others are paid.
Commercial automation software is usually not cheap, but they offer sophisticated high-end technology for automating workflows and tasks.
Open-source, free tools, on the other hand, have the fantastic benefit of being free and having a community supporting them, but they usually take advanced skills to master.
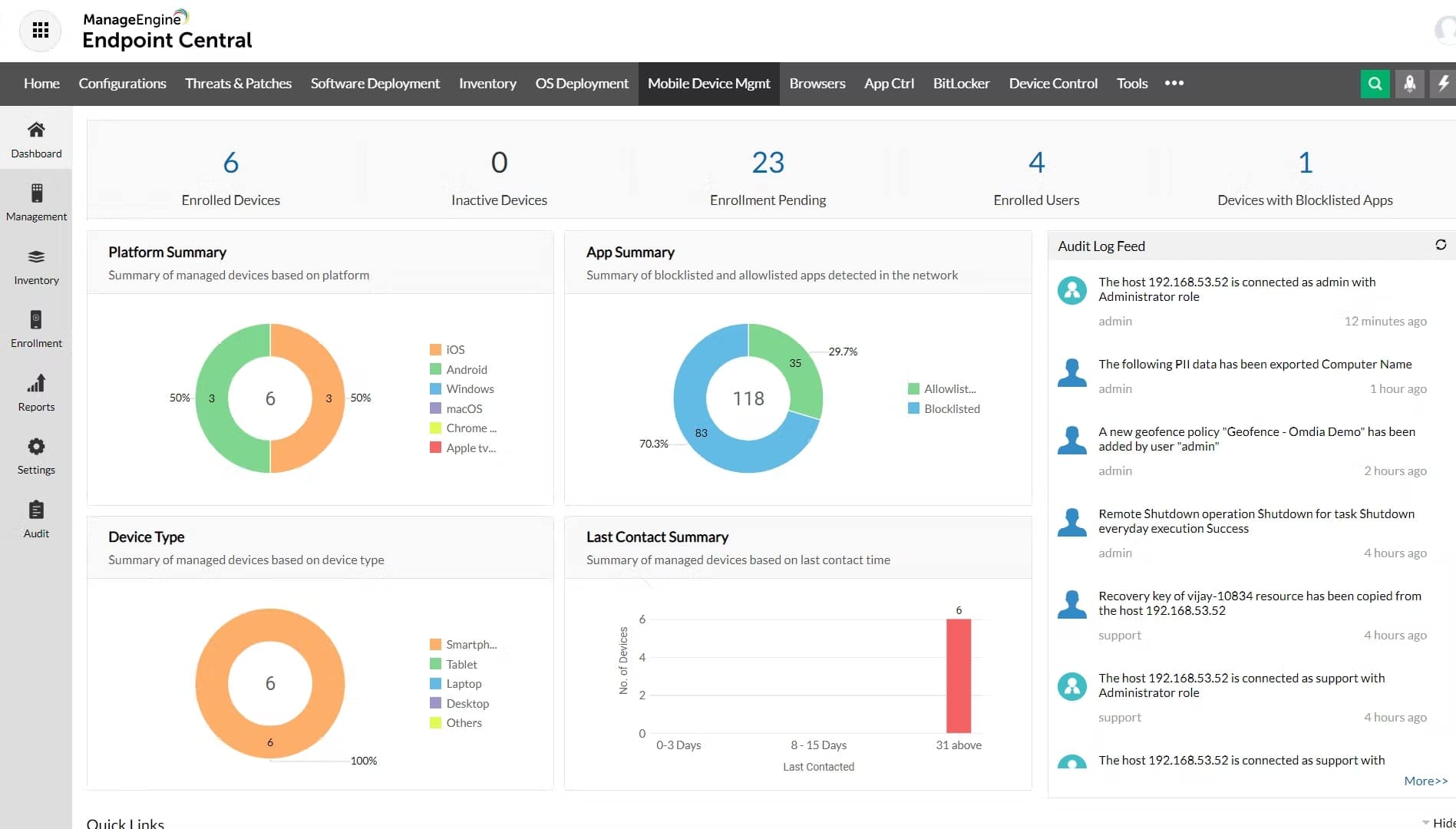
1. ManageEngine Endpoint Central – FREE TRIAL
ManageEngine Endpoint Central is a central management platform for ManageEngine Endpoint DLP (Data Loss Prevention) that allows IT professionals to monitor and manage multiple instances of Endpoint DLP from a single, centralized location. This can be useful for organizations with multiple locations, or for managed service providers who need to manage multiple clients.
Key Features:
- Over 25 pre-made configurations to deploy right away
- Remote asset control with team and collaboration tools
- In-depth endpoint monitoring and security
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Endpoint Central provides a high degree of automation for system documentation, performance monitoring, endpoint management, and security monitoring. This is a unified endpoint management package that covers mobile devices as well as workstations. The package has a very large number of functions, including onboarding and self-enrollment options.
With Endpoint Central, IT professionals can view and manage all of their Endpoint DLP instances from a single dashboard, making it easier to keep track of their network and devices.
Endpoint Central also provides additional features, such as consolidated reporting and advanced alerting, to help IT professionals manage their network more efficiently. Overall, Endpoint Central can help organizations to more effectively prevent the unauthorized transmission of sensitive data from their network.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is available in five editions, which gives the typical buyer a longer journey to pick the right package. The tool is offered as a cloud platform or as a software package for Windows Server. The system has a Free edition, which will manage up to 25 devices and includes mobile device management functions.
Pros:
- A good option for administrators who prefer on-premise solutions
- Can be installed on both Windows and Linux platforms, making it more flexible than some competing tools
- Offers in-depth reporting and inventory management – great for MSPs
- Includes vulnerability scanning as well as patch management
- Supports mobile device management
Cons:
- Better suited for medium to enterprise-size networks
Get a 30-day free trial of the ManageEngine Endpoint Central.
EDITOR'S CHOICE
ManageEngine Endpoint Central is our top pick for a network automation tool because it discovers your entire network and then documents your hardware and software. This package will manage networks by focusing on the performance of the endpoints connected to it. This system extends to mobile device management, including mobile application management and mobile content management functions. The service is designed for use by the IT support department for their management of in-house assets. ManageEngine produces a parallel package for managed service providers, called RMM Central.
Download: Download a 30-Day Free Trial
Official Site: https://www.manageengine.com/products/desktop-central/
OS: Windows Server or Cloud
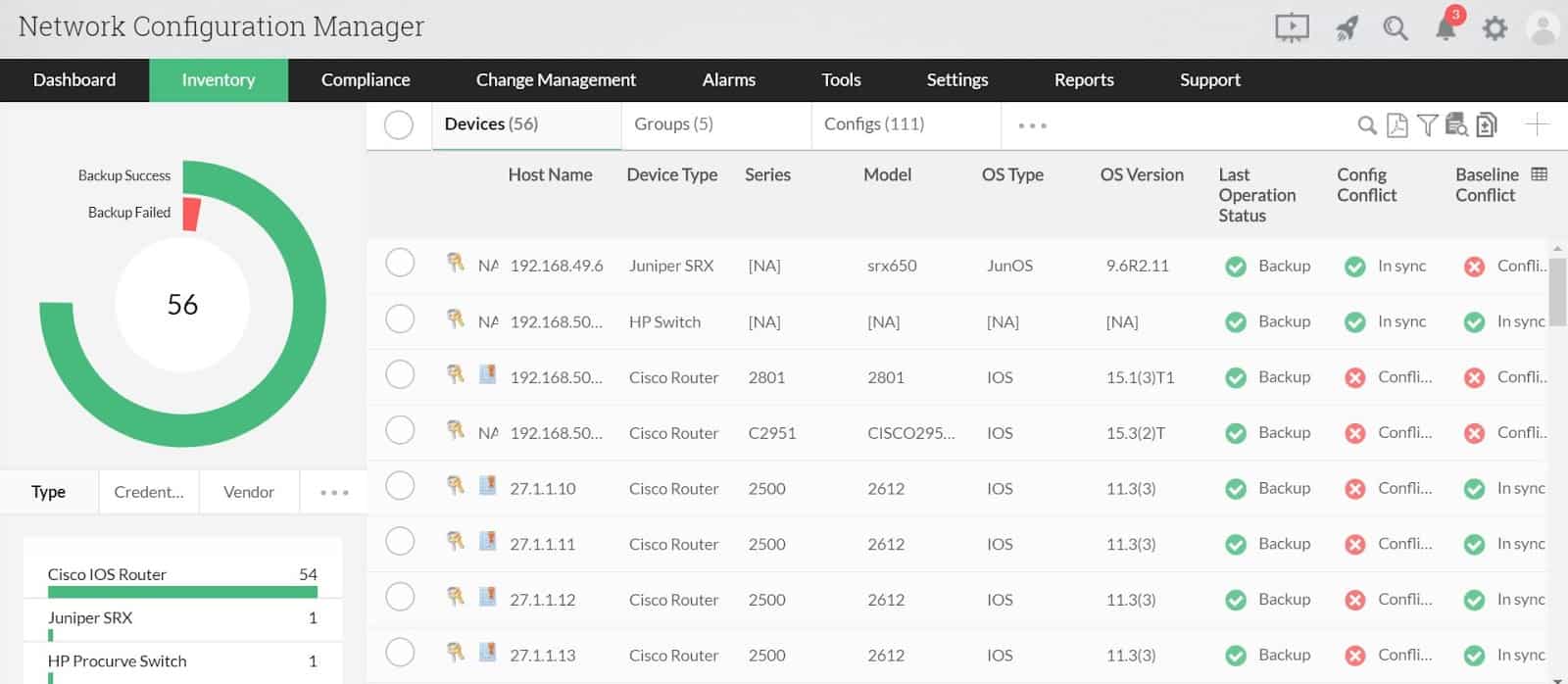
2. ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager – FREE TRIAL
Network Configuration Management (NCM) by ManageEngine is one of the most comprehensive software for network configuration, change, and compliance management. It supports multi-vendor networks with products from Cisco, NetGear, Fortinet, Juniper, HP, and more.
Key Features:
- Automate new or edit configuration in bulk
- Network automation using Configlets
- Configuration backups
- Configuration change notifications and rollback actions
Why do we recommend it?
ManageEngine Network Configuration Manager is an on-premises package that discovers and then analyzes each network device. You can use this system to improve configuration, tightening up security. You then take an image of the configuration and save it to an archive. The Network Configuration Manager then compares the archived image to current settings for each device and restores the backup if the configuration has changed.
NCM can help you automate the management of the entire lifecycle of network device configurations. You can automate daily monotonous configuration tasks in bulk. Instead of going one by one, which generally would take a long time, you can apply a new configuration or changes to multiple devices. You can also schedule automatic configuration backups that might be useful in case of rollbacks.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is an automated network security service. After you have perfected the configuration of each device with the support of the Network Configuration Manager, you lock those settings down. This prevents hackers from tampering with the security of network devices. Valid changes by an administrator are made through the NCM interface and are allowed.
Pros:
- Available for Windows, Mac, and Linux systems
- Continuously discovers assets with autodiscovery
- Can immediately alert when changes occur inventory or configuration changes are made
- Can neatly organize networks, devices, and infrastructure to support multi-site use
Cons:
- Is a full-service monitoring platform that can take time to fully explore all options available
The price for a perpetual NCM license starts at $595 (for up to ten devices). Try ManageEngine NCM free for 30 days and start automating the network configuration management.
3. Site24x7 – FREE TRIAL
In the evolving landscape of network management, where network automation tools play a crucial role, Site24x7 stands out as a comprehensive solution. It addresses the growing need for automated and efficient network monitoring and management. Site24x7 is particularly adept at providing insights and automation for complex network environments, making it a valuable tool for organizations looking to enhance their network performance and reliability through automation.
Key Features:
- Advanced network monitoring capabilities for a wide range of network devices and interfaces
- Automated network performance analysis and anomaly detection using AI algorithms
- Customizable alerting systems to automate responses to network issues
- Detailed reporting tools for network performance and health
- Integration with other IT infrastructure components for a holistic view of system health
Why do we recommend it?
Site24x7 is recommended for its advanced network monitoring and automation capabilities, coupled with AI-powered analytics. It's a robust tool for organizations seeking to streamline their network management through automation and proactive monitoring.
Who is it recommended for?
This tool is ideal for network administrators and IT professionals in medium to large enterprises that manage complex network infrastructures. Its comprehensive monitoring and automation features make it particularly suitable for environments where network performance is critical to business operations.
Pros:
- Comprehensive network monitoring for various devices and interfaces
- Advanced AI-driven analysis for network performance
- Customizable alerts and detailed reporting tools
Cons:
- Might be more complex and feature-rich for smaller network environments
4. Ansible (Tower)
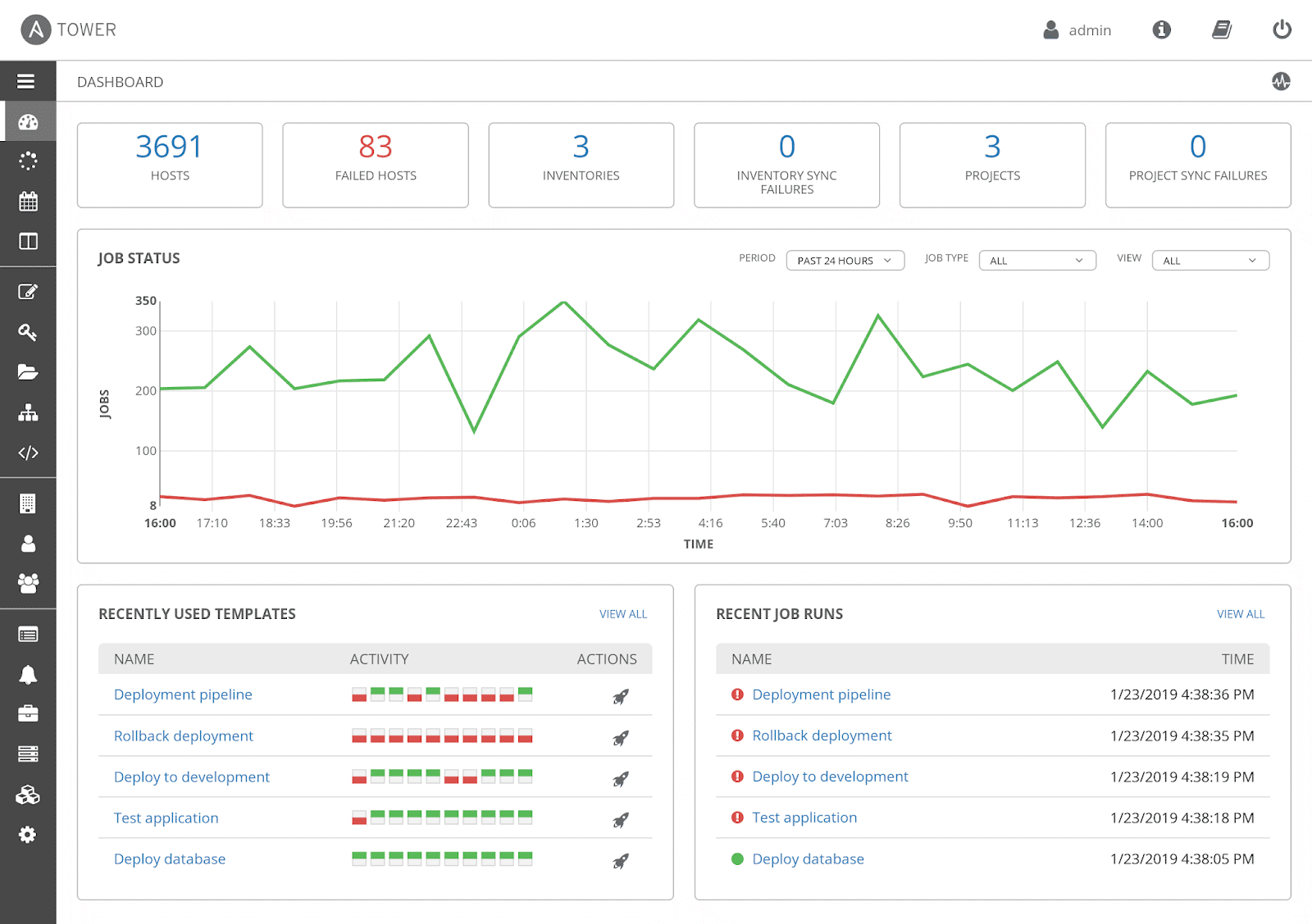
Ansible by RedHat, the simple automation framework, is definitely at the core of a lot of new networking DevOp solutions. It automates the configuration of servers and provides native support for legacy and open network infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Leverage the current network CLI commands to automate over 45 different networking vendors, between switches, routers, load balancers, and firewalls
- Provide automation for software-based controllers (SDN)
- Automate interconnection of hybrid and multi-clouds
Why do we recommend it?
Red Hat Ansible is a task automation platform that covers cloud platforms and edge services as well as systems on premises. The tool can generate scripts that run processes on multiple platforms. So, this system has many potential applications and the biggest problem any buyer is going to face is how exactly to use it.
Ansible is an open-source project built by the community, and is available for Linux/Unix-like OS and Windows. To automatically configure servers, Ansible uses playbooks, which are ordered units of scripts (written in YAML) that define how a server should work and behave through the Ansible automation tool.
Ansible Tower is the enterprise web-based GUI tool that makes Ansible easy to use. The software is designed to be the central platform for all automation tasks, and helps network teams manage complex deployments.
Who is it recommended for?
There are two versions of Ansible. The first is a free package, which is just called Ansible and the second is a paid tool, called Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform. The free version installs on RHEL, and the paid version can be found as a service on AWS Marketplace or Google Cloud Marketplace. RHEL provides a SaaS version, which is hosted on Azure.
Pros:
- Simple minimalistic interface – makes it easy to view key metrics
- Leverages playbooks to automate device configuration and deployments
- Supports numerous vendors, with plenty of community-built templates
- Completely open-source and free
Cons:
- Is a full-service monitoring platform that can take time to fully explore all option available
Ansible is a free, open-source IT automation system (GitHub Ansible Project). For the enterprise-based Ansible Tower, the pricing is based on the number of nodes that you manage. It comes in two editions:
- Standard
- Premium
For more information on pricing, request a quote. Get open-source Ansible through GitHub Ansible Project, or download a free trial of Ansible Tower for a limited time.
5. Netmiko
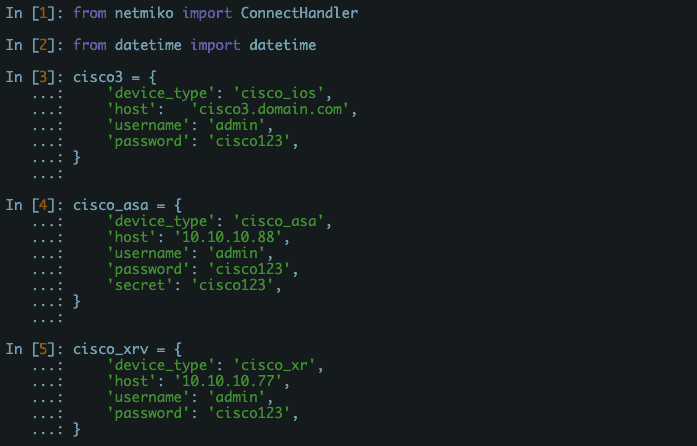
Netmiko is an open-source Python library based on the Paramiko SSH library. It allows easier management and connection of network devices through SSH.
Netmiko improves the library of Paramiko by including support to a wide range of networking vendors and platforms, such as Arista EOS, Cisco ASA, HP Comware7, Juniper Junos, Linux, and more. The tool simplifies and automates the logging to a network device through SSH and executes commands.
Key Features:
- Establish an SSH connection to network devices
- Execute “show” commands and retrieve the results
- Execute configuration commands
- Netmiko supports a wide range of vendors and platforms
Why do we recommend it?
Netmiko is a Python library, so you could integrate its functions into your own programs. This package isn’t an off-the-peg solution. It provides a method to set up and manage an SSH connection to a network device. The library also includes a way to remotely execute switch and router show commands.
Who is it recommended for?
This library is free to use and provides functions for communicating with network devices. So, the target audience for Netmiko includes network administrators who want to write their own network device query utility. If combined with a feed from a network discovery tool, the library could automatically check on the configuration of every device on the network.
Pros:
- Lightweight SHH-based tool
- Ideal for users who are looking for a CLI automation tool
- Features an extensive library of supported vendors
Cons:
- Not as beginner-friendly as other tools that offer both GUI and CLI options
Free and open-source. Get Netmiko from the Github library.
6. NAPALM

NAPALM (Network Automation and Programmability Abstraction Layer with Multivendor support) is a Python library that can interact with different network devices via a unified API.
Key Features:
- Connection to single or multiple devices
- Execute commands automatically. Replace, merge, and compare configurations
- Discards or rollbacks configuration
- Retrieve and audit information
Why do we recommend it?
NAPALM is a similar system to Netmiko because it is another Python library. This tool can interact with network devices from Cisco, Juniper Networks, and Arista. The library provides methods to query configurations and also to alter settings. As this is intended for integration into programs, you can write your own utilities to check on configurations, back them up, and restore approved settings.
The software is cross-platform and open-source. It uses different technologies to connect to the network devices, execute configurations, and retrieves the output data. It can support different networking operating systems such as Arista EOS, Cisco IOS, Cisco IOS-XR, Cisco NX-OS, and Juniper JunOS.
NAPALM collaborates with the most popular automation frameworks, such as Ansible, Salt, and Stackstorm.
Who is it recommended for?
As with Netmiko, this package will appeal to network administrators who like to write their own automation programs. However, the sort of utilities that this library will help you create are already available as pre-written device management tools from ManageEngine and Site24x7.
Pros:
- Open-source community-driven project
- Syntax is easy to learn, even for new users
- Supports cross-platform installations
Cons:
- No native visualization support for data
- CLI only – steepens the learning curve for beginners
Free and open-source. Get NAPALM free from the GitHub’s project library.
Related Post: Cisco Commands Cheat Sheet
7. TrueSight Network Automation
TrueSight, formerly known as BladeLogic, is now part of the BMC product portfolio, and is an APM with AIOps (Artificial Intelligence Operations) capabilities. It is designed to improve the performance and security of hybrid-cloud environments at a cost-efficient price.
Key Features:
- Service-aware analytics
- Auto-scans and auto-backups
- Automatic audits and security compliance checks
- Patch and image update automation
- Capacity Optimization
Why do we recommend it?
TrueSight offers performance monitoring and security tracking. The automation features of this package are part of the security monitoring section. The system takes a feed from your security tool, such as a vulnerability scanner, and implements remediation playbooks. You have to define those remediation steps but once it is set up, the orchestration system will run without human intervention.
TrueSight provides scalable and automated network configuration management capabilities. The software gives full control of the entire configuration across the network, from systems, routers, and firewalls. It can also be programmed to automatically keep track of changes in configuration and apply rollback in case of failure.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a suitable security system for any business but it will particularly appeal to large companies that have too many assets to track manually. This is an on-premises software package that runs on Windows Server or Linux. Vulnerability scanners and SIEMs are great but they just leave you a list of tasks to implement; TrueSight does that for you.
Pros:
- Comes with numerous preconfigured workflows to start using immediately
- Can set automated standards that help maintain compliance for standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, NIST, and SOX
- Can automatically recover devices to their last know “good” state
Cons:
- The interface is fairly barebones and tougher to navigate than competing products
Request a price quote. No free trial available.
8. VMware NSX – Network Automation
Network Automation with VMware NSX allows you to automate the provision and management of your network and security. The software was designed to improve the speed of the application’s lifecycle by leveraging automation.
Key Features:
- Automate native networking and security functions for containers and microservices
- Supports integration with PCF, PKS, Kubernetes, and Red Hat OpenShift
- Automatic compliance checks
Why do we recommend it?
VMware NSX is a network automation platform that can host other automation brands, such as Ansible, Terraform, and VMware Aria. This system installs on top of VMware ESXi and there is a cloud version for typical public cloud platforms, called NSX Cloud. The system is able to automate security remediation actions across servers, virtualizations, containers, and cloud platforms.
VMware uses virtualized networking functions (VNFs) to move your network from hardware to software. Now, all your routers, switches, firewalls and more, can be deployed within a single box that runs all VNFs. With Vmware NSX developers and network, admins can now run networking and security as code.
Running VMWare NSX’ VNFs together with a cloud platform like vRealize Cloud Automation can automate network and security deployments with the help of templates and blueprints. You can automate the network services that are provisioned and managed through VMs, containerized cloud-native applications, or microservices.
Who is it recommended for?
This is a complicated system with its own command language and the ability to integrate web scripting programs, such as Python, Perl, and Java. The command line system is called PowerCLI and it gives the administrator the ability to construct a second layer of automation to create a monitoring utility for VMware NSX operations.
Pros:
- A great option for those looking to automate microservices and cloud applications
- Can automated cloud-based deployment – great for keeping security policies consistent across products
- Supports continuous compliance checks
- Has a wide variety of integration into platforms like Kubernetes and OpenShift
Cons:
- Has a fairly steep learning curve – would like to see more tutorials
- Must contact sales for pricing
For information on pricing, contact VMware sales. Sign up for a free VMWare NSX here.
9. Apstra OS
Apstra OS (AOS) is referred to as a self-operating network, which automates the lifecycle of leaf-spine network switching. AOS supports multiple switches hardware vendors (Cisco, Juniper, Arista, and more) and operating systems (EOS, Junos, NX-OS, and more).
Key Features:
- Automated L3 design and deployment with intra-rack virtual networks
- Operational analytics. Intent-Based Analytics (IBA)
- Built-in Telemetry
- NSX-T and vSphere Integration
Why do we recommend it?
Juniper Apstra is an intent-based networking (IBN) system. This operating system standardizes access to switches and routers in a multi-vendor environment. The interface interprets commands issued in Apstra OS into the operating systems used by different device producers, such as Cisco, Juniper, and Arista.
Apstra comes with a single console to automate your network. It decouples the network (software) from the underlying physical and virtual infrastructure, and works at the management plan to control switches or other devices through their open APIs.
ApstraOS ensures that network elements such as protocols, design, cabling, etc. work continuously. With AOS, you can create, edit, or remove leaf-spine devices, instantly across different network vendors. AOS also comes with closed-loop real-time validation and advanced data analytics.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is suitable for network managers who are running a multi-vendor environment. The system has other benefits, such as security and activity scanning that predict problems before they occur and provides a method to head off disaster. As well as standardizing network device commands, the system creates an overlay network.
Pros:
- Simple interface with great modular visual elements
- Supports all popular vendors like Cisco, Juniper, and EOS
- Features automation design and deployment
Cons:
- No free trial
- Must request a quote
Apstra comes in three different editions, Enterprise Edition, Standard Edition, Advanced Telemetry Edition. For more information on pricing, request a quote. Request a Demo here.
10. NetBrain Automation
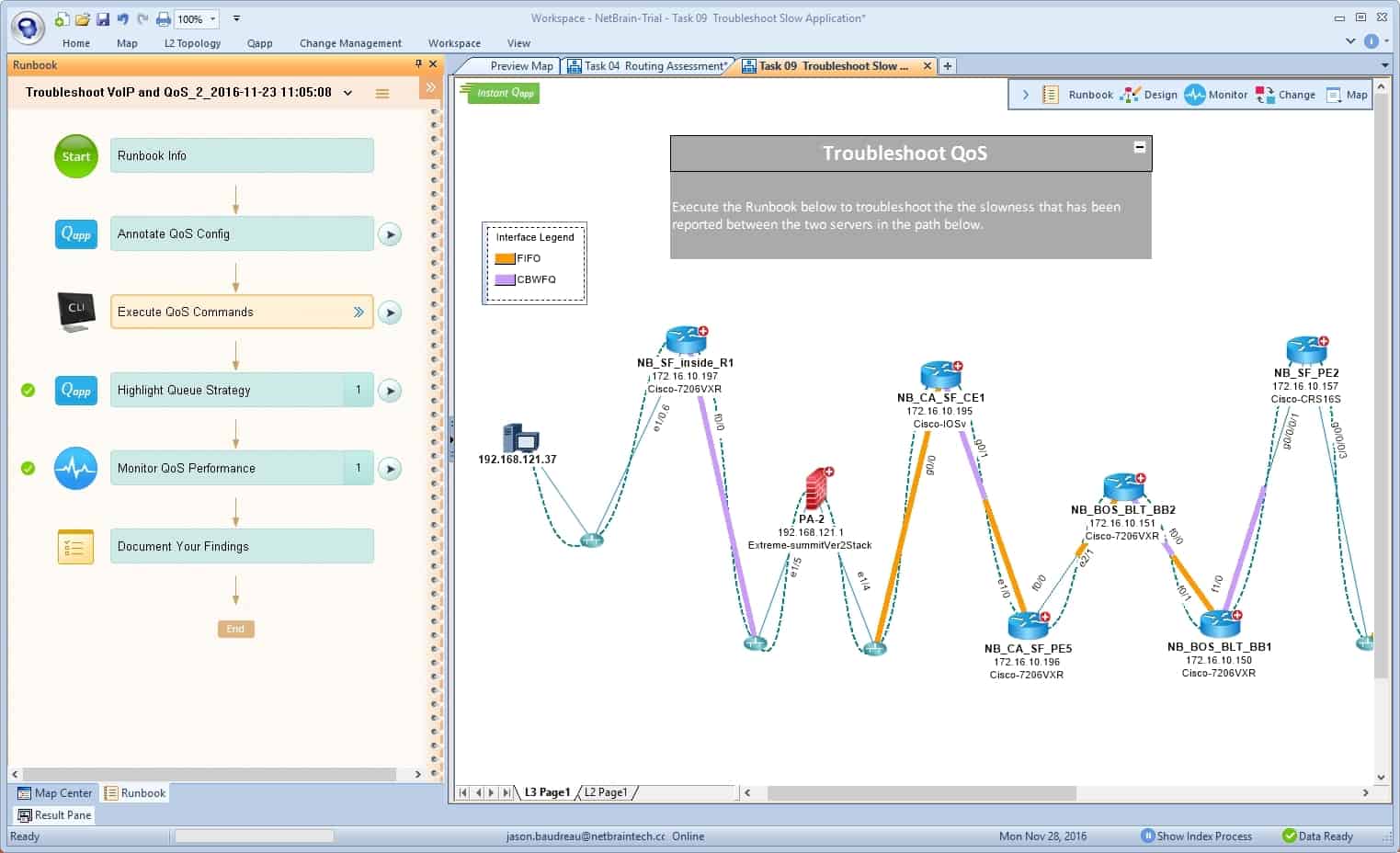
NetBrain is an adaptive network automation platform. It uses a single-pane-of-glass that shows all network data through mapping and visualization.
Key Features:
- Automatic network device inventorying
- Single-pane-of-glass and dynamic maps
- View device’s CLI at the map-level
- Automate workflows with Executable Runbooks
Why do we recommend it?
NetBrain Automation is more of a monitoring system than a system management tool. The package discovers all devices and creates a network map. Click on a device in the topology map to get details of the hardware and gain access to its operating system. The package includes configuration backup automation.
The software also comes with a powerful search engine that allows you to look through all your network elements. NetBrain performs an in-depth automatic network discovery to collect data from all network devices, and also decodes multi-vendor networks and builds a digital representation of the network.
NetBrain creates a dynamic map to be used as a UI to all devices and to configure automation tasks. The software improves the device map experience by adding CLI automation and data from third-party network vendors through API.
Who is it recommended for?
This package is a good network monitoring system because it lets you see how devices link together, which is an essential aid for tasks such as creating access control lists. The service doesn’t standardize device OSs, so you still need to remember the different command set for each device.
Pros:
- Simple graphics get the job done without cluttering the dashboard
- Autodiscovery can automatically identify Cisco ACI and other devices
- Provides insights through automatic diagnostic scans
- Great for mapping out complicated environments
Cons:
- Must contact sales for pricing
- Would like to see more out of the box features
- Could use better historical data analysis tools
Contact NetBrain to request a quote.
11. AppViewX Automation +
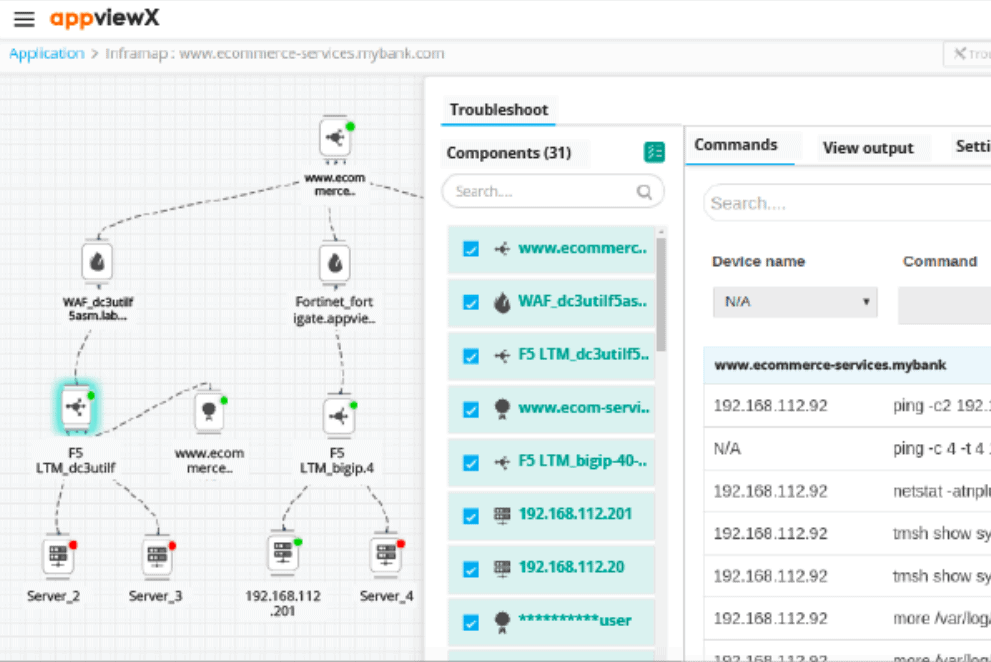
AppViewX is a low-code automation platform designed for NetOps and SecOps. It comes with a big library of workflows and tasks that can be instantly used for automation.
Key Features:
- Automate network and business workflows
- Manage roles for automation services
- Trigger automated workflows based on context awareness
- Run automated workflows in hybrid clouds, SDN, and hardware environments
Why do we recommend it?
AppViewX ADC+ is a load balancer that helps to speed up the delivery of traffic around the network. The tool can channel connections through different redundant paths on a heavily provisioned network, select between a cluster of gateways, and even queue non-urgent traffic to speed up the delivery of interactive protocols.
The software keeps track of the state of each automation, verifies the results, provides insights, and remediates failures automatically. The AppViewX Automation + allows application delivery and network security automation on the platform.
It helps network engineers with low scripting skills to automate and orchestrate the network infrastructure through easy visual workflows. With automation +, you can automate the entire lifecycle of your network devices and security services. The tool supports multiple networking and security vendors.
Who is it recommended for?
The AppViewX platform also includes units for key management and encryption, so it is an edge service that can be used as a logical endpoint for internet traffic enabling packet data to be decrypted, examined, and re-encrypted before being circulated over the network. The system can also selectively drop banned traffic.
Pros:
- Supports topology mapping – great for visualizing how automation impact your whole network
- Reports the success and failures of each automation through logs and alert notifications
- Doesn’t rely heavily on scripting – great for any skill level
Cons:
- Must contact sales for pricing
- Interface could be made easier to navigate
Get the AppViewX Automation + Enterprise free trial for 30 days and start automating and orchestrating your infrastructure.
Final Words & Conclusion
Networks are inevitably changing.
SDN, SD-WANs, virtualization, and automation are turning the networking landscape upside down.
Today, a network engineer or admin can no longer rely on their networking skills, but now needs to embrace coding and scripting.
Yes, SDN, virtualization, and automation at their core are based on code.
Usually, open-source automation tools like Ansible and Netmiko are amazing because they are free, open-source, and allow a lot of flexibility.
The challenge for the network admin when using these automation tools is that they require lots of coding skills.
Other commercial and enterprise-scale tools might be easier to use.
As they come with sophisticated AI and features that allow the network admin to configure automation with single-click or drag-and-drop.
Some of the tools here don’t have free trial, you can only see them by requesting a demo.
Others are more generous and offer a free trial.
Download any free trial and start automating your network, without going back to your scripting book.
Network automation FAQs
What is network automation framework?
Network automation requires interaction with network devices. The automation software is a central controller rather than the actual implementor of adjustments to improve performance. Therefore, the network automation system can best be described as a framework. It connects to all of the switches and routers on the network to extract performance data, which is then assessed, resulting in instructions sent back to the devices.
Which language is used for network automation?
These days, automation for any IT system is based on scripts, which are the updated equivalent of batch jobs. These are usually written in Python, Golang, Perl, or JavaScript.