We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
Storage Management – What is it and How to Implement
UPDATED: July 25, 2023
Increasing the storage capacity might be the easiest and most popular solution to the ever-expanding quantities of data. Just go out and buy more storage. Triple your storage every year by getting a couple of hundred terabytes (or petabytes!). But if you don’t know how to maximize your current resources, this approach is like buying a warehouse down the corner and leaving it half empty and disorganized.
This is where Storage Management comes into play!
Storage Management will attempt to maximize your current resources through various techniques, software, or hardware, or processes. In this article, we will dive deep into storage management, what it is, and how to implement it?
- What is Storage Management?
- Storage Management Advantages
- Software and Hardware: SRM and SAN
- Implementing Storage Management
- The Future of Storage Management Technology
What is Storage Management?
Storage Management refers to the processes that help make data storage easier through software or techniques. It tries to improve and maximize the efficiency of data storage resources. Storage management processes can deal with local or external storage such as NAS, SAN, USBs, SDDs, HDD, the Cloud, etc.,
Storage management techniques or software can be divided into the following four subsets:
- Performance,
- Availability,
- Recoverability, and
- Capacity.
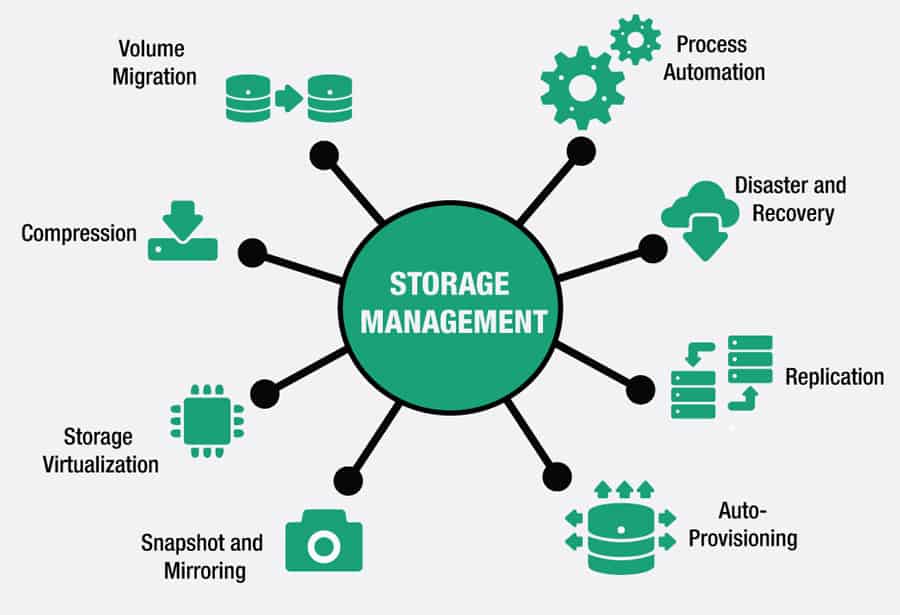
There are a variety of technologies or systems that fall into one or multiple of these subsets, these can be:
- Volume Migration
- Storage Virtualization
- Snapshot and Mirroring
- Auto-Provisioning
- Process Automation
- Disaster and Recovery
- And more…
As mentioned before, the goal of storage management is to improve the performance of resources, not to expand capacity.
These techniques and software will develop the ability to store data and secure it properly.
Storage Management Advantages
We already know what is storage management and what are its methodologies, but what are the characteristics that storage management can improve?
What advantages can it bring to the business to the IT department?
- Reduce Capital and Operational Expenses: The most significant expenses when it comes to storage is maintaining and operating the infrastructure.The CapEx can reduce because a business will not have to expand storage capacity that often. OpEx can also be reduced as ongoing operations on storage are decreased.
- Makes Management Easier: Storage management systems can help users save time through automated tasks, centralized consoles, or by logging remotely.It can also reduce the number of IT staff needed to run the storage infrastructure. Storage management can also make virtualized or cloud environments more comfortable to manage from a single location.
- Enhance Performance: One of the main goals of storage management is to improve the performance of the existing storage resources.For example, compressing data can dramatically reduce the amount of storage and improve file transfer speeds. Automatic storage provisioning can reduce the time it takes to provision storage resources.
- Speed and Flexibility: Storage management solutions should be able to work in real-time and adapt to sudden changes in the storage resources. For example, storage replication is a managed service that replicates stored data in real-time. Storage virtualization can also help improve flexibility and reduce wasted storage.Virtualization can create a pool of physical storage from multiple devices into a single logical storage device. Storage capacity can be easily relocated as the business changes needs.
- Higher Availability: This is probably one of the biggest benefits of storage management. For example, technologies such as Replication, Snapshot and Mirroring, Migration, and Disaster and Recovery (DR) can help you have higher availability and reliability on data.All these storage techniques can help backup and restore data fast, but some can also serve as primary storage.
Software and Hardware: SRM and SAN
There are many closely related concepts to store management, such as SRM or SAN. Such concepts also aim to manage the storage, either through software or hardware, but are not exactly considered “Management Processes.”
Storage Resource Management vs. Storage Management
SRM is a software solution that aims to optimize the speed and performance of the storage space that is used in the Storage Area Network (SAN).
It uses a variety of methodologies to identify underutilized storage, allocate storage capacity, transfer old data to alternative media, and can predict storage trends and requirements. SRM also helps to manage configurations, policies, storage media, and more.
Although it sounds the same, Storage Resource Management (SRM) is a different concept than storage management.
Some examples of SRMs are Symantec, DellEMC SRM, Northern Parklife, or DataCore Software.
On the other hand, storage management refers to the whole package as in, equipment, processes, and software.
So, that makes SRM a subset of storage management.
Networked Storage Management vs. Storage Management
Networked Storage Management solutions such as the Storage Area Networks (SAN) or the Network Area Storage (NAS) device are also similar concepts when it comes to managing storage.
A SAN particularly is a computer network used to improve the accessibility of storage resources.
The elements in the SAN could be disk arrays or tapes that are networked together but cannot be managed by a server, it is controlled by a SAN management software.
Most of the times, SAN and NAS used their proprietary software and hardware, so that makes them less flexible.
As mentioned above, SRM aims to improve the speed and efficiency of the storage used in SANs. So with an SRM, you could manage all SANs from a single server.
Implementing Storage Management.
Storage management is a broad concept, that includes techniques, software, processes that aim at improving the performance, availability, recoverability, and capacity of the storage resources.
The first step to implement storage management would be to train IT personnel and storage administrators on best storage management practices.
There are a couple of storage management standards and organizations to start getting information.
An example is the Storage Management Initiative Specification, (SMI-S), which is a data storage standard developed by the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA).
Aside from methodologies and processes, storage management can be implemented as software or included in the hardware. A couple of examples about the SRM software as mentioned before are, Symantec, DellEMC SRM, Northern Parklife, or DataCore Software, are good examples.
A NAS can be an excellent example of storage management in hardware.
Where can storage management be implemented?
Storage management processes and software can be implemented in any storage, whether it is primary, backup, or archives.
The Future of Storage Management Technology.
SRMs, NAS, SAN, and DAS (Direct Attached Storage) solutions present a fantastic set of methodologies to improve the performance, availability, or recoverability of your data.
But all of these have one common problem; you cannot manage all your storage resource from a single console. You need one admin console for each piece of storage.
The new concept of Software-Defined Storage (SDS) promises to revolutionize the way we store, manage, and collect data. SDS decouples data storage policy-based provisioning and management from its underlying hardware.
Software-Defined Storage virtualizes NAS, SANs, and DAS hardware as virtual disks. In other words, SDS introduces storage virtualization to separate the storage hardware resources from the management software.
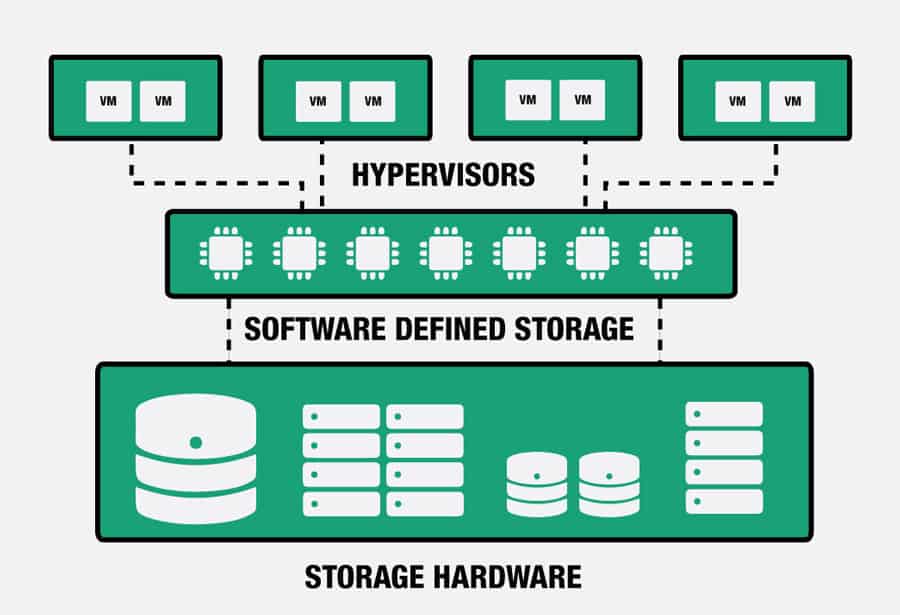
The best thing is that SDS can be implemented in a wide variety of appliances, from generic servers to traditional SANs, NAS, etc. Since the intelligence is decoupled from the hardware, it does not need any proprietary device to run.
The intelligence running on SDSs will provide all the methodologies shown above, such as thin provisioning, snapshot, mirroring, backup and DR, automation, etc.
The benefits of SDS on storage management?
- Manage and unify every storage resource as DAS and NAS in your data center.
- No dependence on proprietary hardware.
- 100% virtualized storage with the management interface that comes with countless features.
- Manage all storage from a single console, take snapshots, compress, create backups and DR copies, etc.
Summary
The goal of storage management is not precisely to expand capacity. If you want more storage capacity, go out and buy a couple of HDDs. Instead, storage management deals with the existing resources and finds ways to improve and maximize them.
This concept covers everything, from software, hardware, storage techniques, and processes. For example, compressing volumes to save space and increase data transfers, or create snapshots to decrease the size of backups.
Storage management software can address one or various of these techniques. Some tools may deal only with virtualization, while others might be focused on storage provisioning or security. The hardware such as NAS or SAN can have their proprietary management systems, which make them effective but less flexible.
But storage management is evolving.
One of the biggest reasons why enterprises are changing towards a Software-Defined Storage is because they can centralize and manage all resources under a single console.
Storage management FAQs
Why storage management is important?
Storage management has two main roles: to ensure availability and to enforce security. Storage servers can be provided on site or, increasingly, as rented space on cloud platforms. Whichever type of storage is deployed, it should be accessible at all times. The accessibility of storage can mean access to drives for user access to file storage or dissect access to storage space by applications, such as databases and Web applications. Access by applications can be catered for in non-traditional formats, such as block storage or object storage rather than file space. Security needs to be enforced both for access channels, for data transfer into and out of storage, and for the data at rest. This security is usually enforced through access rights management and data encryption.
What are the 3 types of storage?
There are three types of data storage formats:
- File storage – this is a well-understood drive format with a directory structure and identifiable field for access by users through editing software, such as word processors or spreadsheet systems.
- Block storage – Block-level storage is intended for access by applications. The data is referenced in memory blocks, which can be interpreted at a higher level as files, but is more efficient for applications that don’t need a file structure in order to manipulate data.
- Object storage – this is also known as unstructured data. It is a collection of objects, which can be images or videos, and requires an application to identify each object and facilitate access. This is also a type of storage used by “big data” systems.
What is system controlled storage management?
System-controlled storage management is also known as system-managed storage. This type of service manages the contents of a storage system according to a defined policy. These usually relate to the age of objects and will dictate whether contents should age out and be deleted, compressed, or archived after it has been stored in an immediately accessible space for a given period.
How does server storage management impact server performance?
Server storage management can impact server performance by affecting the speed at which data is stored and retrieved, and by reducing the amount of available storage space.
How do you choose a server storage solution?
Choosing a server storage solution requires considering factors such as the amount of data to be stored, the number of users that need access, and the required performance and security features.
What are the best practices for server storage management?
Best practices for server storage management include: using strong passwords and access control, regularly backing up data, and monitoring storage utilization to prevent overloading.