We may earn a commission if you make a purchase through the links on our website.
How to View & Manage Open Files on Windows Server 2012 and beyond
UPDATED: March 20, 2023
Microsoft introduced Windows Server 2012, a new version of the Windows Server operating system based on Windows Server 8. It is the sixth version with new features and upgrades in cloud computing and storage infrastructure. This latest version brings in a lot of new capabilities and enhancements in storage, deployment services, directory, networking, clustering, PowerShell, and file services.
Key Features of Windows server 2012
Check out a few new features and enhancements included in the Windows Server 2012:
- Graphical user interface (GUI) Windows Server 2012 is similar in look and feel to Windows 8 but is a more upgraded version. The new design focuses on easy management of multiple servers via GUI options. It exercises a Metro-based user interface similar to Windows 8 unless placed in a Server Core mode.
- Managing IP address To discover, monitor, audit, or manage the network's IP address space, Windows Server 2012 has a new feature. This new enhancement performs an IP address management (IPAM) role.
- Hyper-V This sixth version of the Windows Server operating system comprises Hyper-V 3.0 that offers a virtual extensible switch permitting virtual networks to extend their functionality in many ways.
- Active Directory Many changes have been made to the active directory in this version. These changes allow PowerShell-based Deployment Wizard to work remotely. Further on completion of the process, automation of other domain controllers permitting large-scale deployments.
- File System For file servers, a Resilient File System is introduced as an enhancement.
- Storage migration There is no additional requirement of a shared storage system for virtual machine (VM) migration under this version, especially with Hyper-V Replica. Windows Server 2012 permits live storage migration. Most small businesses lack virtualization. However, this feature enables both small and medium-sized businesses to take advantage of virtualization.
- Clustering The enhancement will enable Cluster-aware updating. In simple terms, this will permit the whole cluster to perform at the time of updating with minimum or no loss in availability. Also, under this version, the windows server can exercise nearly 63 nodes. However, earlier versions could manage clusters with only 16 nodes. Thus, the scalability of clusters has improved.
- NIC Teaming The only first version server with an in-built network interface card (NIC) teaming. This enhancement works for failover and bandwidth aggregation.
- An administrator can choose the Interface Earlier in the previous versions, or if you were working with server code, you could only use the command line as the interface. However, things are different with Windows Server 2012. Now, users have access to choose the interface of their choice. Microsoft analyzed and understood the importance of both the command line and Graphical User Interface (GUI) to perform various tasks. Thus, it enabled a design that allowed the exercise of both the interfaces.
- Server Manager This new feature enables easy deployments and multi-server capabilities. The new server manager works remotely for both virtual and physical servers. As a result, the chances of managing multiple servers simultaneously via a server group are high.
- 3.0 Version Server Message Block Many new features have been upgraded to the version including, SMB encryption, SMB Multichannel, SMB Scale out, and more. This redesigned model is best suitable for Hyper-V that allows VHD files and VM configuration files on SMB 3.0.
- Dynamic Access Control Microsoft has integrated in-built security systems to each part of the Windows Server operating system. Thus, it has shifted its approach to providing Dynamic Access Control rather than offering different security resources.
- PowerShell Management This feature is associated with a scripting language, task automation, and configuration management. Windows Server 2012 comprises PS command line and 2300+ cmdlets to manage Hyper V 3.0 and all Windows Server applications.
- Default Server Environment is formed via the server core The minimalist server core put to use performs like a default server environment. The user has access to use GUI to perform the initial server configuration and eliminate it once finished.
- Not Oriented Only Towards Single Server This design was brought into action keeping in mind the cloud concept. As a result, the design allows users to access multiple servers simultaneously. Thus, the server is no more oriented only towards single server management. Also, you have access to local servers via its dashboard.
- The SMB Enhancement It adds more resiliency without any requirement of additional specific configurations. Further, with the advancement of this feature in windows servers, the server application databases can now be stored on SMB 2.2. Let's say, for example, MS SQL Server.
- Removes any Duplicate Copy of Data The redesigned server supports another feature that is run in the background to detect and eliminate duplicate data copies automatically. These data copies are stored separately. The primary purpose of this feature is to enable data compression.
- Full Support for Live Migration The Live migration feature was initiated to support Hyper-V 2.0. In the older versions, only a single live migration could perform at a time. However, in this upgraded version, multiple migrations can be undertaken simultaneously.
- Live Migration Storage Options Even if the virtual machines are running, this feature enables you to move your CM storage. Also, shifting virtual hard disks from one location to the other is easy, in the case of this version. As a result, you do not require to stop running virtual machines or go offline to move files from one place to the other.
These advanced features and enhancements in windows server 2012 can make it easy for system administrators to manage and perform automation tasks and deployments at ease.
Step-by-step: How to view and manage Open Files on Windows Server 2012 and beyond
If you are new to Windows Server 2012 and unsure where is the share and storage management system, our guide will help you through it. Share and storage management keeps a record of past activities and other files. However, this feature no more exists in Server 2016. But if you are using Windows Server 2012, we have listed two different methods to view and manage open files or shared files/folders.
The Computer Management technique is one of the best ways to view open files or troubleshoot locked files. However, for checking the process or file details, method 2 is an appropriate choice.
How to View Open Files in Computer Management
Step 1: Go to the Start menu or press the Windows key and type Computer Management or compmgmt.msc in the search box. Now, select Computer Management and click open.
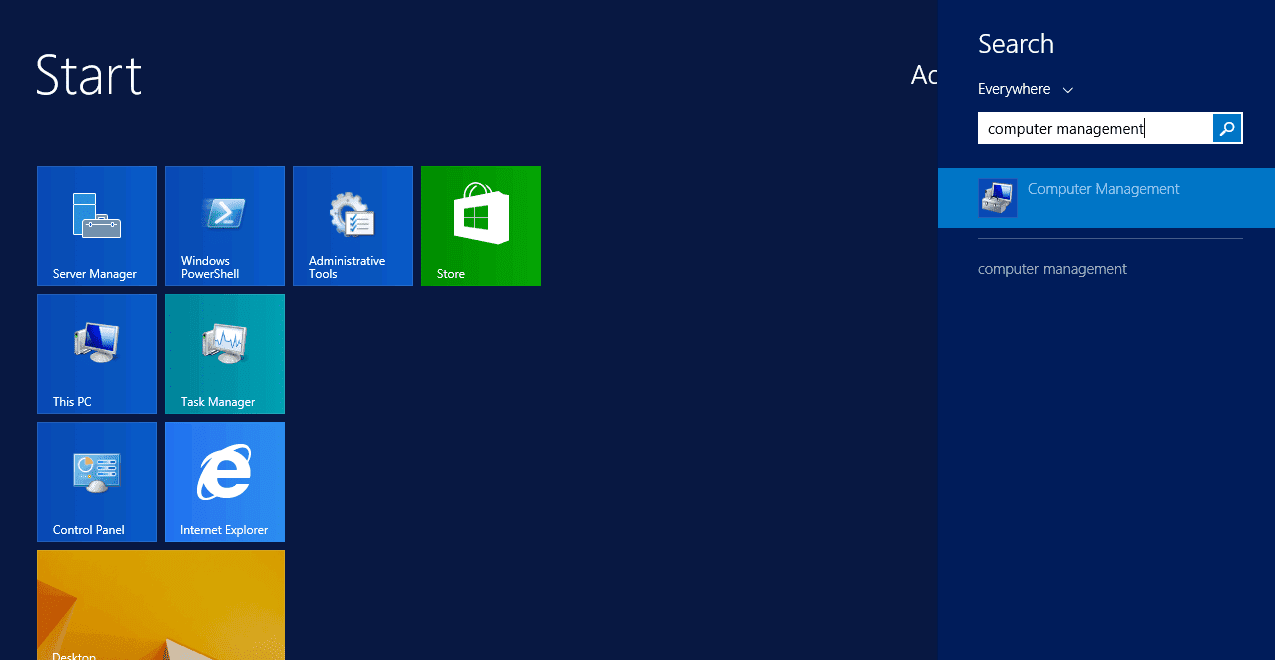
Make sure to open this application or console on the specific computer/server that comprises the shared folder. Then, to view the open files of the shared folder, I must open the computer management console from the server.
Step 2: Select the Shared Folders from the left panel and press on open files as the console opens.
A list of open directories will show up on your screen:
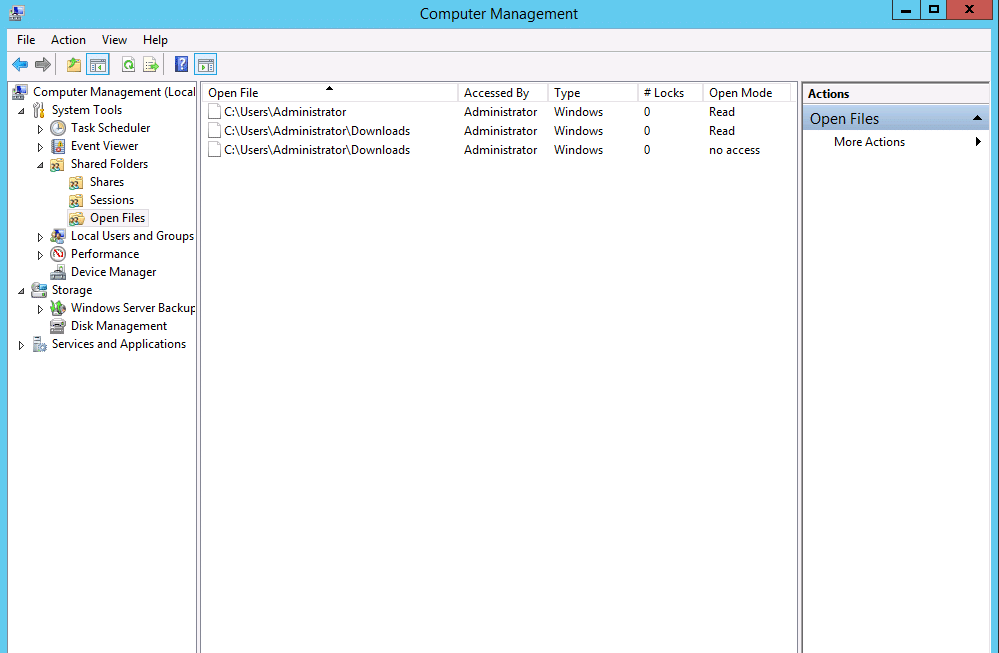
If you wish to close any of the listed files/folders, right-click the file and choose “Close Open File”. This will save your shared file/folder from being locked anymore.
How to View Open Files in Resource Monitor
You can also use the resource monitor to view files that are open on a system. Follow the below steps to open the resource monitor and manage the available files.
Step 1: Go to the Start menu, press the Windows key, and type Resource monitor in the search box. Now, select Resource monitor and click open. Another technique is to run task manager, select the performance tab and click Open Resource Monitor.
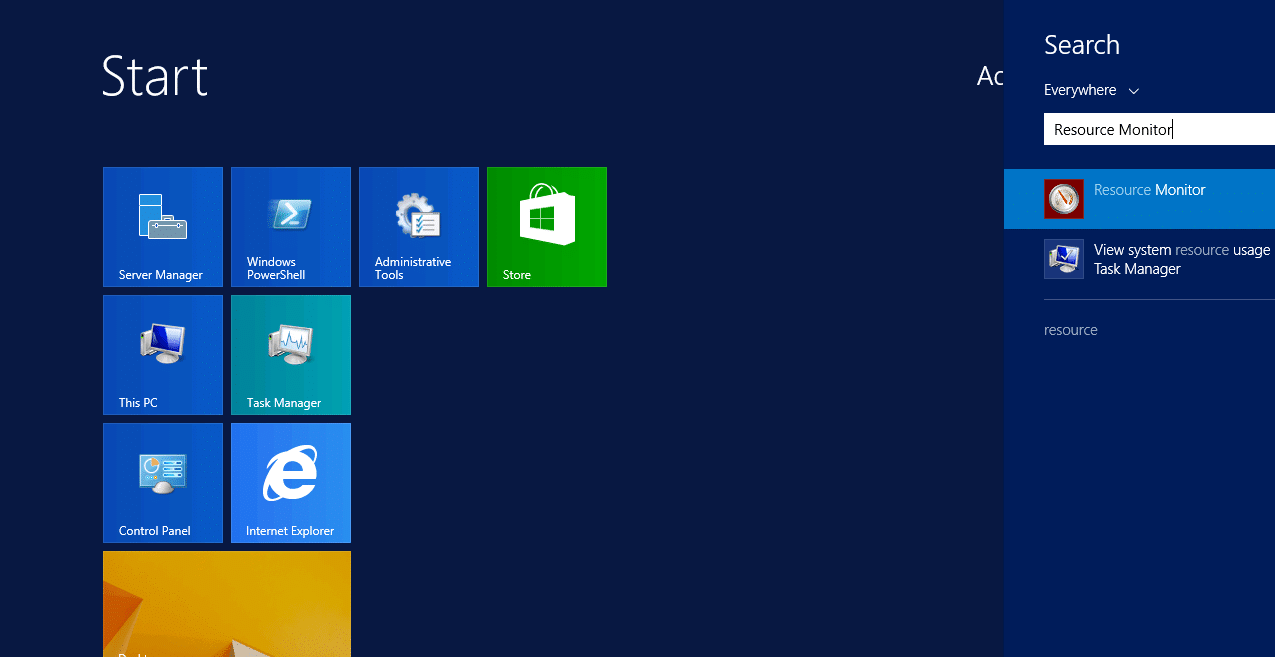
Step2: On the top of your screen, you will find many tabs. Choose the disk tab from the list. Now, you can view all the file details and disk activities, including PID, open files, read and write bytes per second, etc.
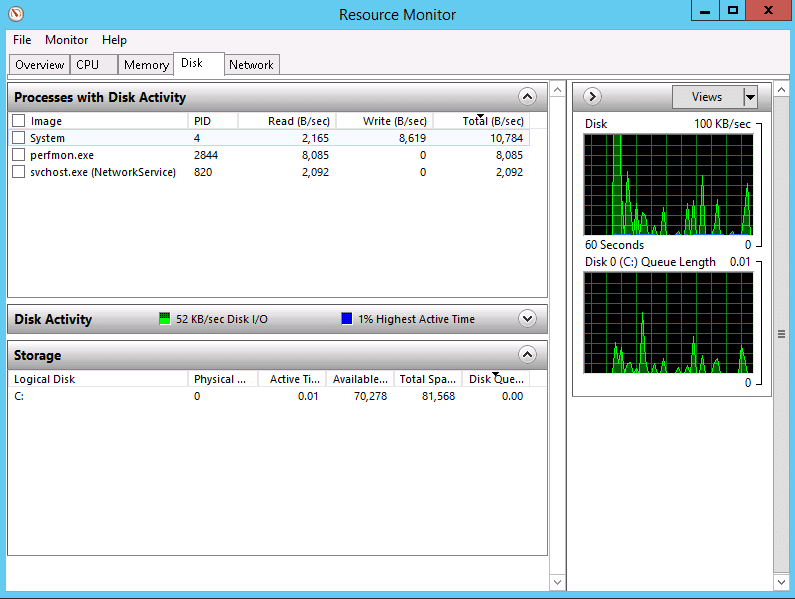
To view the full file path, scroll through the column section. If there are many disk activities visible on the screen, stop the live monitoring. Now, you can view only the open files.
Go to the Monitor menu and select stop monitoring to hold the live monitoring process.
Conclusion
Introduced by Microsoft, Windows Server 2012 is the sixth version with enhanced features. However, its successor Windows Server 2012 R2, was released the very next year. As a Windows Server 2012 no longer supports Itanium-based computers. Also, this upgraded version comprises features like Graphical User Interface (GUI), Dynamic Access Control, supports live migration storage, can access multiple servers simultaneously, Powershell Management, the SMB Enhancement, elimination of duplicate data copies, and more. Follow the above-listed pointers to get a clear idea of new features and enhancements of Windows Server 2012. Further, if you get stuck somewhere when running Windows Server 2012, check out the above-listed methods to view an open file from shared files/folders. We have listed each step to help the administrator easily view and manage available files under Windows Server 2012.
How to View & Manage Open Files on Windows Server 2012 FAQs
What are open files?
Open files are files that are currently being used by an application or a process on a Windows server.
Why is it important to view and manage open files?
Viewing and managing open files on Windows Server 2012 and later is important because it helps you understand which files are being used by which applications and processes, and helps you identify any potential conflicts or performance issues.
How can I view open files on Windows Server?
There are several ways to view open files on Windows Server 2012 and later, including using the Task Manager, using the built-in Computer Management tool, using the Sysinternals Process Explorer tool, and using third-party file-locking and process-monitoring tools.
How can I manage open files on Windows Server 2012?
You can manage open files on Windows Server 2012 and later by closing the application or process that has the file open, or by using the built-in Computer Management tool to forcibly close the file. You can also use third-party file-locking and process-monitoring tools to manage open files.
What is the Computer Management tool in Windows Server 2012?
The Computer Management tool in Windows Server 2012 and later is a built-in tool that provides a centralized view of the computer's management components, including the ability to view and manage open files.
What is the Sysinternals Process Explorer tool in Windows Server 2012?
The Sysinternals Process Explorer tool in Windows Server 2012 and later is a third-party tool that provides a detailed view of the processes running on a Windows server, including the ability to view and manage open files.
Can I use third-party tools to view and manage open files on Windows Server 2012 and beyond?
Yes, there are a variety of third-party tools available that provide advanced features for viewing and managing open files on Windows Server 2012 and later, including file-locking and process-monitoring tools.